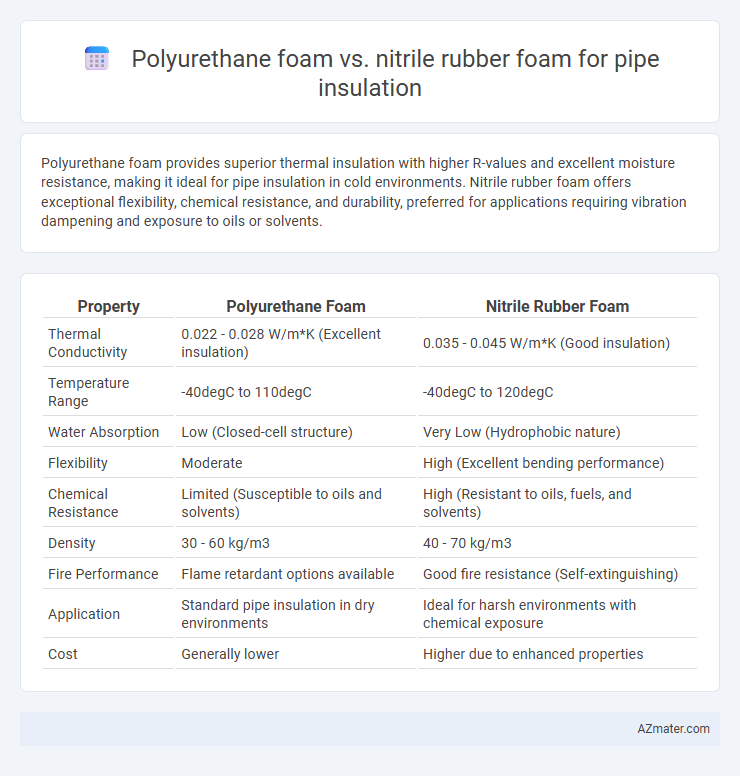
Polyurethane foam provides superior thermal insulation with higher R-values and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for pipe insulation in cold environments. Nitrile rubber foam offers exceptional flexibility, chemical resistance, and durability, preferred for applications requiring vibration dampening and exposure to oils or solvents.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polyurethane Foam | Nitrile Rubber Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.022 - 0.028 W/m*K (Excellent insulation) | 0.035 - 0.045 W/m*K (Good insulation) |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 110degC | -40degC to 120degC |
| Water Absorption | Low (Closed-cell structure) | Very Low (Hydrophobic nature) |
| Flexibility | Moderate | High (Excellent bending performance) |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited (Susceptible to oils and solvents) | High (Resistant to oils, fuels, and solvents) |
| Density | 30 - 60 kg/m3 | 40 - 70 kg/m3 |
| Fire Performance | Flame retardant options available | Good fire resistance (Self-extinguishing) |
| Application | Standard pipe insulation in dry environments | Ideal for harsh environments with chemical exposure |
| Cost | Generally lower | Higher due to enhanced properties |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Polyurethane foam and nitrile rubber foam are widely used materials for pipe insulation due to their thermal efficiency and durability. Polyurethane foam offers high R-values and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring strong thermal insulation and minimal water absorption. Nitrile rubber foam provides superior flexibility, resistance to oils and chemicals, and excellent compression set properties, making it suitable for environments exposed to mechanical stress and harsh substances.
Key Properties of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam offers excellent thermal insulation properties with a low thermal conductivity of around 0.022-0.028 W/m*K, making it highly efficient in reducing heat loss in pipe insulation. Its closed-cell structure provides superior moisture resistance, preventing water absorption and maintaining insulation performance over time. The material also exhibits good compressive strength and flexibility, allowing for durable pipe insulation that conforms well to various pipe shapes and sizes.
Essential Features of Nitrile Rubber Foam
Nitrile rubber foam excels in pipe insulation due to its superior resistance to oil, chemicals, and ozone, ensuring long-term durability in harsh environments. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance, preventing condensation and energy loss. Compared to polyurethane foam, nitrile rubber foam offers enhanced flexibility and compressibility, making it ideal for dynamic applications and vibration damping.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation performance for pipe insulation due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.022-0.028 W/m*K, which effectively minimizes heat loss. Nitrile rubber foam exhibits higher thermal conductivity values, generally ranging from 0.035 to 0.045 W/m*K, resulting in comparatively lower insulation efficiency. The closed-cell structure of polyurethane foam enhances its resistance to moisture and thermal bridging, making it more efficient for temperature retention in piping systems.
Moisture and Water Resistance Capabilities
Polyurethane foam demonstrates excellent moisture resistance with a closed-cell structure that inhibits water absorption, making it highly effective for pipe insulation in damp environments. Nitrile rubber foam offers superior water resistance due to its impermeability and flexibility, maintaining insulation integrity even under continuous exposure to moisture and condensation. Both materials provide durable solutions, but nitrile rubber foam excels in scenarios requiring enhanced resistance to water vapor and liquid ingress.
Fire Resistance and Safety Ratings
Polyurethane foam offers excellent thermal insulation but has a lower fire resistance rating, typically classified as Class 1 or Class 2, making it more susceptible to flame spread and smoke generation. Nitrile rubber foam provides superior fire safety with higher flame retardancy and lower smoke emission, often meeting stringent UL94 V-0 standards and ASTM E84 Class A fire ratings. For pipe insulation in environments requiring enhanced fire resistance and safety compliance, nitrile rubber foam is the preferred choice due to its better performance under high-temperature exposure and regulatory fire safety requirements.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Polyurethane foam offers excellent flexibility and compressibility, making it easy to conform around irregular pipe shapes and obstacles, which simplifies installation. Nitrile rubber foam is highly flexible with superior resilience and return to original shape after compression, providing durable insulation that adapts well to movement and vibration in piping systems. Both materials enable straightforward application, but nitrile rubber foam often requires less adhesive due to its self-sealing properties, enhancing installation efficiency.
Durability and Longevity Assessment
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior durability and longevity in pipe insulation applications due to its high resistance to moisture absorption, UV degradation, and chemical exposure, maintaining thermal efficiency over time. Nitrile rubber foam offers excellent flexibility and resilience but tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to ozone, heat, and solvents, which can reduce its lifespan in harsh environments. Considering long-term performance, polyurethane foam generally provides more reliable insulation durability, especially in industrial or outdoor settings.
Cost Analysis and Budget Considerations
Polyurethane foam insulation offers a lower initial cost and higher thermal efficiency, reducing long-term energy expenses for pipe insulation projects. Nitrile rubber foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior flexibility and durability, leading to fewer replacements and maintenance costs over time. Budget considerations should weigh the balance between immediate expenditure and lifecycle savings based on specific project demands and environmental conditions.
Best Applications for Each Insulation Type
Polyurethane foam excels in pipe insulation for chilled water and refrigeration systems due to its high thermal resistance (R-value around 6.0 per inch) and low water vapor permeability, making it ideal for preventing condensation and energy loss. Nitrile rubber foam offers superior flexibility, compression resistance, and excellent performance in environments exposed to oils, chemicals, and UV radiation, commonly used for HVAC ductwork and industrial piping with temperature ranges from -40degF to 230degF. Choosing polyurethane foam is optimal for chilled or cold applications requiring rigid insulation, while nitrile rubber foam suits dynamic systems needing durable, flexible, and moisture-resistant insulation.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Nitrile rubber foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com