Polyethylene foam offers superior durability and moisture resistance for exercise mats, while rubber foam provides better cushioning and slip resistance. Selecting between them depends on prioritizing long-lasting support or enhanced comfort during workouts.
Table of Comparison
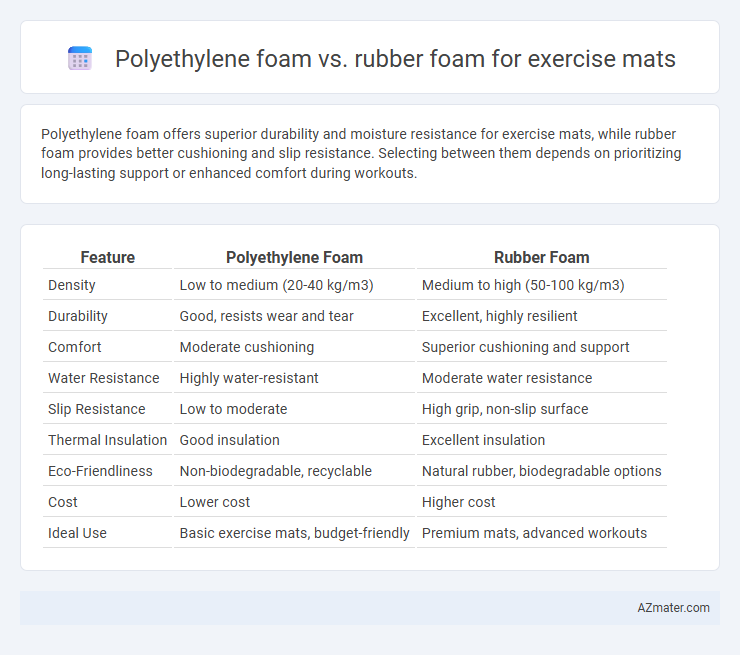
| Feature | Polyethylene Foam | Rubber Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (20-40 kg/m3) | Medium to high (50-100 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Good, resists wear and tear | Excellent, highly resilient |
| Comfort | Moderate cushioning | Superior cushioning and support |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant | Moderate water resistance |
| Slip Resistance | Low to moderate | High grip, non-slip surface |
| Thermal Insulation | Good insulation | Excellent insulation |
| Eco-Friendliness | Non-biodegradable, recyclable | Natural rubber, biodegradable options |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
| Ideal Use | Basic exercise mats, budget-friendly | Premium mats, advanced workouts |
Introduction to Exercise Mats: Polyethylene vs Rubber Foam
Exercise mats made from polyethylene foam offer lightweight durability and moisture resistance, making them ideal for indoor workouts and easy cleaning. Rubber foam mats provide superior cushioning and grip due to their dense, natural composition, enhancing comfort and stability during high-impact exercises. Choosing between polyethylene and rubber foam depends on factors like workout intensity, required traction, and budget.
Material Composition: Polyethylene Foam Explained
Polyethylene foam, composed of closed-cell polyethylene resin bubbles, offers superior water resistance and durability compared to rubber foam, which consists of natural or synthetic rubber polymers providing enhanced elasticity. The closed-cell structure of polyethylene foam ensures lightweight, high tensile strength, and excellent insulation properties, ideal for exercise mats requiring cushioning and moisture protection. Rubber foam, while providing better grip and flexibility, generally absorbs more moisture and can degrade faster under repeated stress and sweat exposure.
Material Composition: Rubber Foam Overview
Rubber foam for exercise mats is composed primarily of natural or synthetic rubber, offering superior elasticity and resilience compared to polyethylene foam. This material provides enhanced cushioning, shock absorption, and durability, making it ideal for high-impact workouts and prolonged use. Its closed-cell structure resists moisture and odor, maintaining hygiene and comfort during exercise sessions.
Cushioning and Comfort: Comparing Support Levels
Polyethylene foam offers firm cushioning with high density, providing excellent support and durability for exercise mats, making it ideal for high-impact activities. Rubber foam, characterized by its natural elasticity and softer texture, delivers superior comfort and shock absorption, reducing strain on joints during exercises. Comparing support levels, polyethylene foam ensures stable footing and long-term shape retention, while rubber foam excels in contouring to the body for enhanced comfort during prolonged workouts.
Durability and Longevity: Which Foam Lasts Longer?
Polyethylene foam offers superior durability and resistance to compression, making it an excellent choice for exercise mats subject to heavy and regular use. Rubber foam, while providing better elasticity and cushioning, tends to degrade faster over time due to its natural composition and exposure to sweat and UV light. For long-lasting performance and sustained shape retention, polyethylene foam generally outperforms rubber foam in exercise mat applications.
Weight and Portability: Ease of Transportation
Polyethylene foam exercise mats are significantly lighter, typically weighing around 1-2 pounds per mat, enhancing portability and making them ideal for on-the-go workouts. Rubber foam mats, often denser and heavier at 3-5 pounds, provide durability but can be cumbersome to transport. The lower weight and flexible structure of polyethylene foam improve ease of carrying, especially for activities like yoga or traveling.
Water and Moisture Resistance
Polyethylene foam offers superior water and moisture resistance compared to rubber foam, making it ideal for exercise mats used in humid or wet environments. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption, ensuring durability and quick drying times. Rubber foam, often open-cell, tends to absorb moisture, potentially leading to mold and odor issues over time.
Maintenance and Cleaning Requirements
Polyethylene foam exercise mats require minimal maintenance due to their closed-cell structure, which resists moisture, dirt, and odors, allowing for easy surface cleaning with mild soap and water. Rubber foam mats, with their open-cell design, tend to absorb sweat and dirt, necessitating more frequent deep cleaning using specialized rubber cleaners to prevent mold and odor buildup. Regular wiping and air drying are essential for both materials to maintain hygiene and prolong mat lifespan.
Cost Comparison: Polyethylene Foam vs Rubber Foam
Polyethylene foam exercise mats typically cost less than rubber foam mats due to lower raw material and manufacturing expenses. Rubber foam mats, especially those made from natural or high-density rubber, tend to be pricier because of their durability and superior cushioning properties. Budget-conscious buyers often prefer polyethylene foam for affordability, while those seeking long-term investment may opt for rubber foam despite the higher initial cost.
Best Applications: Choosing the Right Mat for Your Workout
Polyethylene foam exercise mats excel in durability and moisture resistance, making them ideal for high-intensity workouts and outdoor use where sweat and weather exposure are factors. Rubber foam mats offer superior cushioning and grip, perfect for yoga, pilates, or exercises requiring stability and joint protection. Selecting the right mat depends on your workout's intensity, environment, and need for comfort or traction.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Rubber foam for Exercise mat
 azmater.com
azmater.com