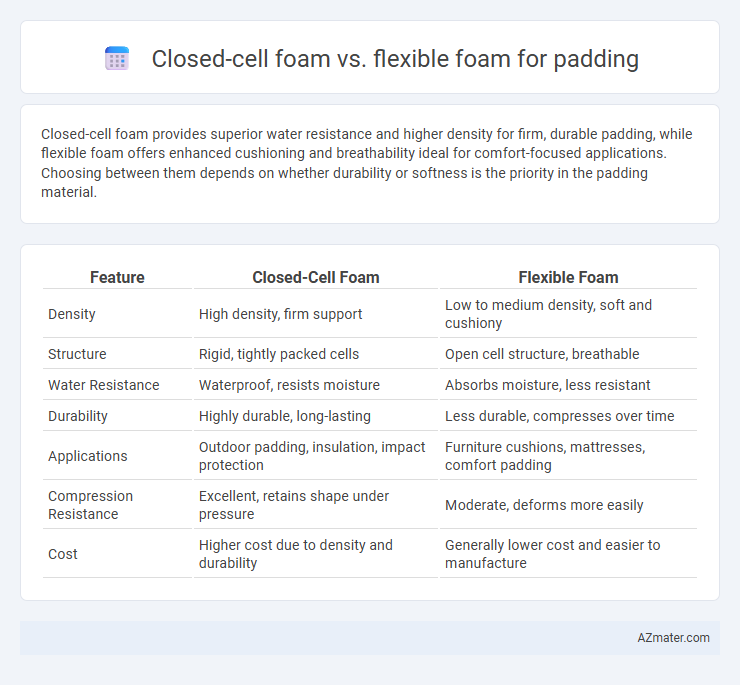
Closed-cell foam provides superior water resistance and higher density for firm, durable padding, while flexible foam offers enhanced cushioning and breathability ideal for comfort-focused applications. Choosing between them depends on whether durability or softness is the priority in the padding material.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Flexible Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | High density, firm support | Low to medium density, soft and cushiony |
| Structure | Rigid, tightly packed cells | Open cell structure, breathable |
| Water Resistance | Waterproof, resists moisture | Absorbs moisture, less resistant |
| Durability | Highly durable, long-lasting | Less durable, compresses over time |
| Applications | Outdoor padding, insulation, impact protection | Furniture cushions, mattresses, comfort padding |
| Compression Resistance | Excellent, retains shape under pressure | Moderate, deforms more easily |
| Cost | Higher cost due to density and durability | Generally lower cost and easier to manufacture |
Introduction to Foam Padding Materials
Closed-cell foam provides superior compression resistance and moisture resistance, making it ideal for high-impact and water-exposed padding applications. Flexible foam offers enhanced cushioning and breathability, suited for comfort-focused uses like upholstery and bedding. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing durability requirements with flexibility and comfort needs.
What is Closed-cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam consists of tiny, compressed cells sealed tightly to prevent air or water infiltration, resulting in a dense, rigid material with high durability and moisture resistance. Its structure provides superior insulation, impact absorption, and structural support compared to flexible foam, making it ideal for high-performance padding applications such as sports equipment and protective gear. The closed-cell construction also offers excellent chemical and environmental resistance, extending the lifespan of the padding in harsh conditions.
What is Flexible Foam?
Flexible foam is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by its open-cell structure, allowing for greater airflow and cushioning. It provides excellent shock absorption and comfort, making it ideal for applications such as upholstery, mattresses, and seating padding. In contrast to closed-cell foam, flexible foam is softer, more breathable, and compressible, offering enhanced flexibility and resilience in padding solutions.
Key Differences Between Closed-cell and Flexible Foam
Closed-cell foam features a dense structure with tightly packed cells that provide superior water resistance, higher durability, and excellent insulation, making it ideal for outdoor and high-impact padding. Flexible foam, characterized by its open-cell composition, offers greater cushioning, breathability, and compression recovery, which is preferred for comfort-oriented applications like upholstery and bedding. The choice between the two depends on balancing requirements for firmness, moisture resistance, and flexibility in padding solutions.
Durability and Longevity of Each Foam Type
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longevity due to its dense, rigid structure that resists moisture, compression, and wear over time, making it ideal for heavy-duty padding applications. Flexible foam, while providing excellent comfort and cushioning, tends to degrade faster under frequent use because its open-cell structure absorbs moisture and compresses more easily, reducing its lifespan. Choosing between closed-cell and flexible foam for padding depends largely on the required balance between long-lasting resilience and softness.
Comfort and Support: Comparing Foam Options
Closed-cell foam offers firm support and excellent durability, making it ideal for applications requiring consistent cushioning and resistance to compression. Flexible foam excels in providing superior comfort with its softer, more conforming texture that adapts to body contours for pressure relief. For padding applications, combining closed-cell foam's structural support with flexible foam's comfort enhances overall ergonomic performance.
Moisture Resistance and Absorption
Closed-cell foam features a dense, impermeable structure that provides superior moisture resistance, preventing water absorption and mold growth. Flexible foam, with its open-cell composition, absorbs moisture more readily, leading to potential degradation and reduced durability in damp environments. For applications requiring enhanced moisture resistance, closed-cell foam is the preferred choice due to its ability to maintain structural integrity and hygiene.
Applications: Best Uses for Each Foam
Closed-cell foam provides excellent moisture resistance and high durability, making it ideal for marine cushions, outdoor seating, and protective packaging where water exposure is common. Flexible foam offers superior cushioning and breathability, making it perfect for upholstery, mattresses, and gym mats that require softness and comfort. Choosing between these foams depends on the need for either structural support and water resistance or comfort and flexibility in padding applications.
Cost Considerations and Value
Closed-cell foam typically costs more per cubic foot than flexible foam due to its denser structure and enhanced durability, making it a worthwhile investment for long-lasting padding applications. Flexible foam offers greater affordability and comfort, often chosen for budget-friendly projects where cushioning and flexibility are priorities. Evaluating long-term value involves balancing initial expense against performance, with closed-cell foam delivering superior moisture resistance and longevity, while flexible foam excels in shock absorption and ease of installation.
Choosing the Right Foam Padding for Your Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance, high-density durability, and excellent insulation, making it ideal for outdoor or heavy-duty padding applications. Flexible foam provides better cushioning, breathability, and adaptability, which suits ergonomic seating, mattresses, and custom comfort solutions. Select closed-cell foam for moisture-prone environments and rigid support, while flexible foam is preferred for softness, flexibility, and shock absorption in everyday use.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Flexible foam for Padding
 azmater.com
azmater.com