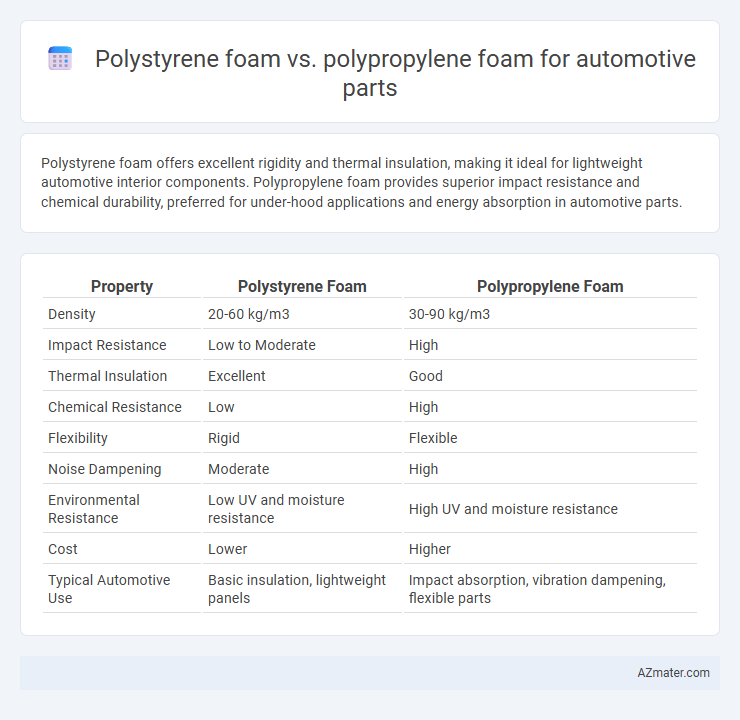
Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity and thermal insulation, making it ideal for lightweight automotive interior components. Polypropylene foam provides superior impact resistance and chemical durability, preferred for under-hood applications and energy absorption in automotive parts.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene Foam | Polypropylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 20-60 kg/m3 | 30-90 kg/m3 |
| Impact Resistance | Low to Moderate | High |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent | Good |
| Chemical Resistance | Low | High |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Flexible |
| Noise Dampening | Moderate | High |
| Environmental Resistance | Low UV and moisture resistance | High UV and moisture resistance |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Automotive Use | Basic insulation, lightweight panels | Impact absorption, vibration dampening, flexible parts |
Introduction to Polystyrene Foam and Polypropylene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a rigid, lightweight material known for its excellent thermal insulation and impact resistance, making it suitable for automotive parts requiring cushioning and energy absorption. Polypropylene foam features a flexible, durable structure with superior chemical resistance and fatigue durability, ideal for automotive components subjected to vibration and repeated stress. Both foams offer distinct advantages in weight reduction and cost efficiency, influencing material selection based on specific automotive application demands.
Material Properties Comparison
Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity and dimensional stability, making it suitable for lightweight interior automotive components that require precise molding. Polypropylene foam provides superior impact resistance, higher fatigue strength, and better chemical resistance, ideal for exterior automotive parts exposed to harsh conditions. Thermal insulation and moisture resistance in polypropylene foam outperform polystyrene foam, enhancing durability and comfort in automotive applications.
Weight Differences in Automotive Applications
Polystyrene foam weighs significantly less than polypropylene foam, making it more attractive for automotive applications focused on reducing vehicle weight and improving fuel efficiency. Polypropylene foam, while slightly heavier, offers enhanced durability and impact resistance, which can justify its use in structural or safety components. Weight differences typically range from 10% to 30%, influencing design choices based on the balance between lightweight performance and mechanical properties in automotive parts.
Impact Resistance and Durability
Polystyrene foam offers excellent impact absorption but is brittle, making it less durable under repeated stress in automotive parts. Polypropylene foam exhibits superior impact resistance with better energy absorption and higher resilience, maintaining structural integrity over prolonged use. Its enhanced durability and flexibility make polypropylene foam a preferred choice for automotive applications demanding long-lasting performance.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Polystyrene foam exhibits lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.03-0.04 W/m*K, providing superior thermal insulation for automotive parts compared to polypropylene foam, which generally ranges between 0.04-0.05 W/m*K. The closed-cell structure of polystyrene foam enhances its effectiveness in minimizing heat transfer, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive automotive components. Polypropylene foam offers moderate insulation but excels in impact resistance and flexibility, which may influence material choice depending on specific automotive part requirements.
Chemical and Water Resistance
Polystyrene foam exhibits moderate chemical resistance but tends to degrade when exposed to solvents and oils, limiting its durability in harsh automotive environments. Polypropylene foam offers superior chemical resistance against fuels, oils, and many solvents, making it more suitable for automotive parts requiring prolonged contact with chemicals. Both foams provide good water resistance, but polypropylene foam's closed-cell structure enhances its moisture barrier properties, ensuring better performance in wet conditions.
Manufacturing Processes and Cost Efficiency
Polystyrene foam manufacturing involves a steam-chest molding process that enables rapid expansion and shaping, making it cost-effective for high-volume automotive parts with complex geometries. Polypropylene foam uses a bead foam molding process, which offers superior impact resistance and chemical stability but requires higher energy input and longer cycle times, increasing production costs. Cost efficiency favors polystyrene foam for large-scale lower-cost applications, while polypropylene foam suits specialized parts demanding enhanced durability and lightweight properties.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polystyrene foam, commonly used for automotive insulation and cushioning, poses significant environmental challenges due to its non-biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, often ending up in landfills or as microplastic pollutants. Polypropylene foam offers improved environmental benefits with better recyclability and a lower carbon footprint, as it can be remelted and reused multiple times without significant degradation. The automotive industry is increasingly favoring polypropylene foam to reduce ecological impact and enhance circular economy practices in vehicle manufacturing.
Safety Considerations in Vehicle Components
Polystyrene foam exhibits high stiffness but limited energy absorption, making it less effective in crash impact scenarios compared to polypropylene foam, which offers superior cushioning and deformation resilience. Polypropylene foam's enhanced crack resistance and thermal stability contribute to improved durability and occupant protection in automotive parts. Selecting polypropylene foam supports regulatory compliance for vehicle safety standards due to its ability to absorb and dissipate collision forces more efficiently than polystyrene alternatives.
Application Suitability: Choosing the Right Foam for Automotive Parts
Polystyrene foam offers excellent impact absorption and thermal insulation, making it ideal for automotive interior components like door panels and dashboards where lightweight durability is crucial. Polypropylene foam provides superior chemical resistance and flexibility, suitable for under-the-hood parts and exterior trims exposed to harsher environments. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific automotive application requirements, balancing factors such as mechanical strength, temperature resistance, and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Polypropylene foam for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com