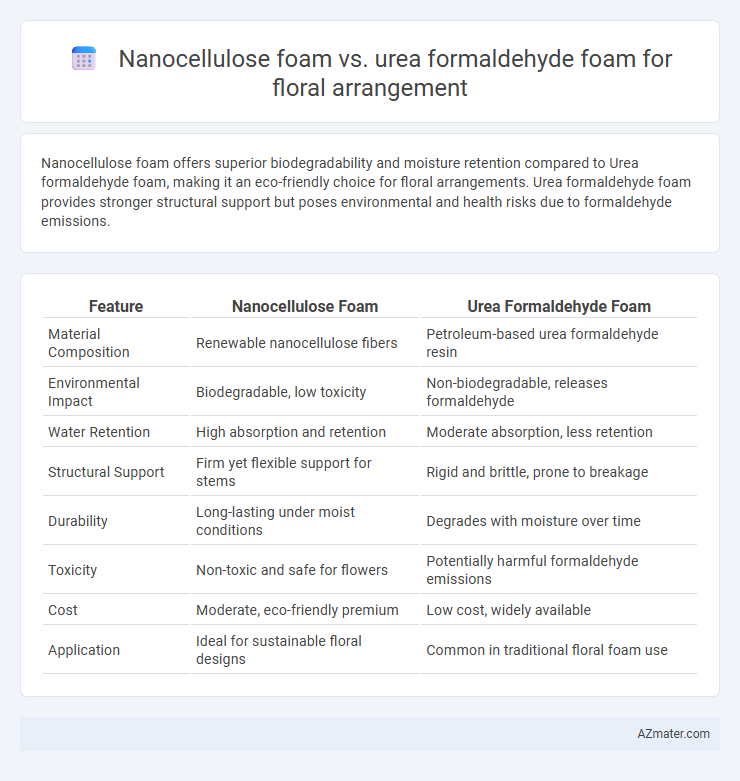
Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability and moisture retention compared to Urea formaldehyde foam, making it an eco-friendly choice for floral arrangements. Urea formaldehyde foam provides stronger structural support but poses environmental and health risks due to formaldehyde emissions.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nanocellulose Foam | Urea Formaldehyde Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Renewable nanocellulose fibers | Petroleum-based urea formaldehyde resin |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, low toxicity | Non-biodegradable, releases formaldehyde |
| Water Retention | High absorption and retention | Moderate absorption, less retention |
| Structural Support | Firm yet flexible support for stems | Rigid and brittle, prone to breakage |
| Durability | Long-lasting under moist conditions | Degrades with moisture over time |
| Toxicity | Non-toxic and safe for flowers | Potentially harmful formaldehyde emissions |
| Cost | Moderate, eco-friendly premium | Low cost, widely available |
| Application | Ideal for sustainable floral designs | Common in traditional floral foam use |
Introduction to Floral Arrangement Foams
Nanocellulose foam and urea formaldehyde foam serve as essential floral arrangement foams with distinct environmental and functional properties. Nanocellulose foam offers superior biodegradability and water retention, promoting prolonged freshness in floral displays compared to urea formaldehyde foam, which is more rigid but less eco-friendly due to its chemical composition and potential toxicity. Selecting the appropriate foam impacts floral hydration, structural support, and sustainability in floral design.
Overview of Nanocellulose Foam
Nanocellulose foam, derived from cellulose nanofibers, offers a lightweight, biodegradable, and highly absorbent medium ideal for floral arrangements, promoting sustainability compared to traditional foams. Its porous structure provides excellent water retention and oxygen flow, enhancing flower longevity without the toxic emissions associated with Urea formaldehyde foam. As a renewable material, nanocellulose foam supports environmentally friendly floral design by reducing chemical exposure and waste.
Overview of Urea Formaldehyde Foam
Urea formaldehyde foam is a rigid, synthetic polymer commonly used as a floral foam for its excellent water retention and structural support properties, making it ideal for arranging and securing flowers. Although cost-effective and readily available, it poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential release of formaldehyde emissions. Its dense composition contrasts with nanocellulose foam, which offers a biodegradable, eco-friendly alternative with comparable water-holding capacity.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Nanocellulose foam, derived from renewable cellulose fibers, offers superior biodegradability and lower toxicity compared to synthetically produced urea formaldehyde foam, which releases harmful formaldehyde gases contributing to indoor air pollution. The production of nanocellulose foam involves fewer carbon emissions and generates less hazardous waste, enhancing its environmental sustainability in floral arrangement applications. In contrast, urea formaldehyde foam's persistence in the environment and potential to release carcinogenic compounds pose significant ecological and health risks.
Water Retention and Absorption Properties
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior water retention and absorption properties compared to urea formaldehyde foam, making it highly effective for floral arrangements by maintaining optimal moisture levels. The high porosity and hydrophilic nature of nanocellulose enhance capillary water uptake and gradual release, supporting prolonged flower freshness. Urea formaldehyde foam, with its lower water absorbency and potential formaldehyde emissions, is less favorable for sustained hydration in delicate floral displays.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
Nanocellulose foam offers superior safety and low toxicity for floral arrangements due to its biodegradable nature and absence of harmful chemicals, reducing risks to human health and the environment. Urea formaldehyde foam emits formaldehyde gas, a known carcinogen, posing significant health hazards including respiratory irritation and long-term toxicity concerns. Selecting nanocellulose foam enhances eco-friendly floral displays while minimizing exposure to volatile organic compounds found in urea formaldehyde products.
Structural Support and Durability
Nanocellulose foam provides superior structural support in floral arrangements due to its high tensile strength and lightweight properties, enhancing stem stability and reducing the risk of deformation over time. Urea formaldehyde foam, while offering rigidity, tends to be more brittle and susceptible to cracking, compromising long-term durability under moisture exposure. Nanocellulose's moisture-resistant characteristics and biodegradability make it a more sustainable and durable option for maintaining floral arrangement integrity.
Cost and Availability Evaluation
Nanocellulose foam offers a sustainable and biodegradable option for floral arrangements, but it typically comes at a higher cost and limited availability compared to urea formaldehyde foam. Urea formaldehyde foam is more widely available and cost-effective, making it a common choice for florists despite environmental and health concerns related to formaldehyde emissions. Evaluating these materials highlights a trade-off between budget-friendly access and eco-friendly innovation in floral foam selection.
Sustainability and Biodegradability
Nanocellulose foam offers superior sustainability and biodegradability compared to urea formaldehyde foam, as it is derived from renewable plant fibers and decomposes naturally without releasing toxic chemicals. Urea formaldehyde foam, a synthetic polymer produced from petrochemicals and formaldehyde, poses environmental hazards due to its non-biodegradable nature and potential formaldehyde emissions. Choosing nanocellulose foam enhances eco-friendly floral arrangements by minimizing environmental impact and supporting circular bioeconomy principles.
Future Trends in Floral Arrangement Foams
Nanocellulose foam offers a biodegradable and sustainable alternative to urea formaldehyde foam, aligning with the growing demand for eco-friendly floral arrangement materials. Future trends indicate increased adoption of nanocellulose foams due to their superior water retention, structural support, and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional formaldehyde-based options. Advances in nanocellulose production techniques are expected to lower costs and enhance foam customization, driving widespread use in innovative and sustainable floral design practices.
Infographic: Nanocellulose foam vs Urea formaldehyde foam for Floral arrangement
 azmater.com
azmater.com