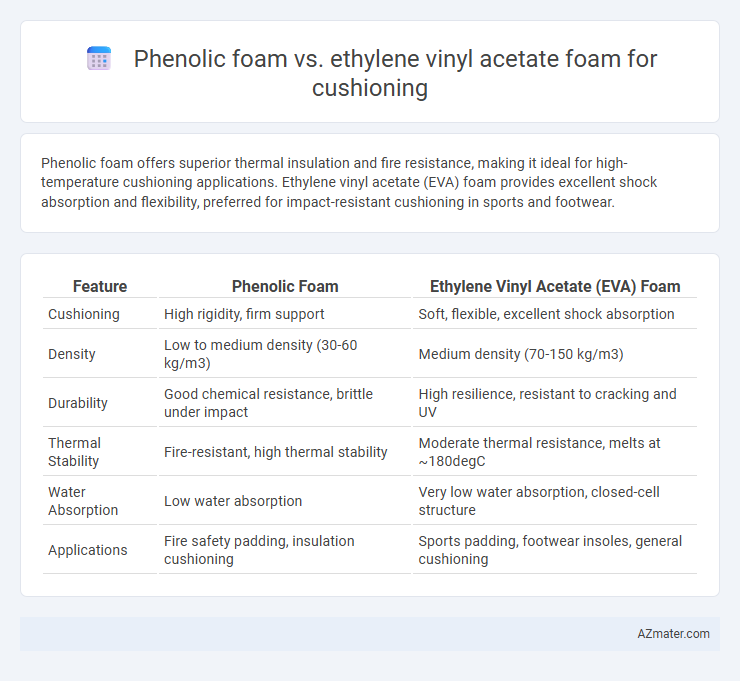
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature cushioning applications. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent shock absorption and flexibility, preferred for impact-resistant cushioning in sports and footwear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phenolic Foam | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Cushioning | High rigidity, firm support | Soft, flexible, excellent shock absorption |
| Density | Low to medium density (30-60 kg/m3) | Medium density (70-150 kg/m3) |
| Durability | Good chemical resistance, brittle under impact | High resilience, resistant to cracking and UV |
| Thermal Stability | Fire-resistant, high thermal stability | Moderate thermal resistance, melts at ~180degC |
| Water Absorption | Low water absorption | Very low water absorption, closed-cell structure |
| Applications | Fire safety padding, insulation cushioning | Sports padding, footwear insoles, general cushioning |
Introduction to Cushioning Materials
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation and high fire resistance, making it ideal for cushioning in applications requiring safety and durability. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent shock absorption, flexibility, and water resistance, commonly used in sports equipment and footwear cushioning. Both materials enhance comfort and protection by distributing impact forces and reducing pressure points, but the choice depends on specific performance needs like heat tolerance or elasticity.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, thermosetting material known for its excellent fire resistance, high thermal insulation, and dimensional stability, making it ideal for cushioning applications where safety and durability are critical. It exhibits low smoke emissions and strong chemical resistance, distinguishing it from Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam, which is softer, more flexible, and predominantly used for impact absorption in sports and footwear. The unique closed-cell structure of phenolic foam enhances its cushioning properties by providing resilience against compression while maintaining its shape under prolonged stress.
Overview of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is a highly flexible, durable, and lightweight cushioning material known for its excellent shock absorption and resilience, making it ideal for footwear, sports equipment, and packaging applications. Unlike phenolic foam, which is rigid and primarily used for thermal insulation and fire resistance, EVA foam offers superior elasticity and water resistance, enhancing comfort and impact protection. Its closed-cell structure prevents moisture ingress, contributing to enhanced durability and support in cushioning products.
Physical Properties Comparison
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance, low thermal conductivity, and high compressive strength compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which offers greater elasticity, resilience, and impact absorption. EVA foam's lower density and excellent flexibility make it ideal for cushioning applications requiring comfort and shock absorption, whereas phenolic foam's rigid structure provides enhanced dimensional stability and insulation. Moisture resistance in EVA foam surpasses that of phenolic foam, influencing application environments and durability in cushioning products.
Cushioning Performance: Impact Absorption
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation but has lower impact absorption compared to Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam, which provides excellent cushioning and high energy return under compressive forces. EVA foam's open-cell structure enhances shock absorption and resilience, making it ideal for protective padding and footwear insoles. Phenolic foam's rigidity results in less effective impact damping, limiting its use in applications requiring superior cushioning performance.
Durability and Longevity
Phenolic foam offers superior durability and resistance to compression, maintaining cushioning properties over extended periods even under heavy loads, making it ideal for long-term protective applications. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent flexibility and shock absorption but tends to degrade faster under UV exposure and repeated mechanical stress. For longevity and sustained structural integrity in cushioning, phenolic foam generally outperforms EVA foam in demanding environments.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, characterized by its inherent low flammability, self-extinguishing properties, and low smoke production, making it ideal for applications demanding high safety standards. EVA foam, while flexible and commonly used in cushioning, has higher flammability and tends to emit more smoke and toxic gases when ignited, posing greater risks in fire scenarios. For cushioning in environments where fire resistance and safety are critical, phenolic foam provides enhanced protection and compliance with stringent fire safety regulations.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam is valued for its exceptional fire resistance and low smoke emission but has a higher environmental impact due to its formaldehyde-based chemicals and limited biodegradability. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility and cushioning with better recyclability and lower toxicity, enhancing its sustainability profile. Manufacturers increasingly prefer EVA foam for eco-friendly cushioning solutions, supported by initiatives to improve its biodegradability and reduce carbon footprint.
Cost-Effectiveness and Availability
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal insulation but is generally more expensive and less readily available compared to ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam provides excellent cushioning properties at a lower cost, making it a cost-effective option for mass-market applications due to widespread availability. Manufacturers selecting foam for cushioning prioritize EVA foam when budget constraints and material accessibility are critical factors.
Application Suitability: Phenolic vs EVA Foam
Phenolic foam offers excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance, making it suitable for cushioning applications in high-temperature or fire-sensitive environments. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior flexibility, impact absorption, and durability, ideal for sports equipment, footwear, and general cushioning uses. Choosing between Phenolic and EVA foam depends on application requirements for thermal stability versus comfort and resilience.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Ethylene vinyl acetate foam for Cushioning
 azmater.com
azmater.com