Plant-oil based foam offers sustainable, biodegradable packaging with lower carbon emissions compared to petroleum-based foam, which relies on non-renewable fossil fuels and generates higher environmental pollutants. Switching to plant-oil based foam reduces reliance on petroleum, enhancing eco-friendly packaging solutions.
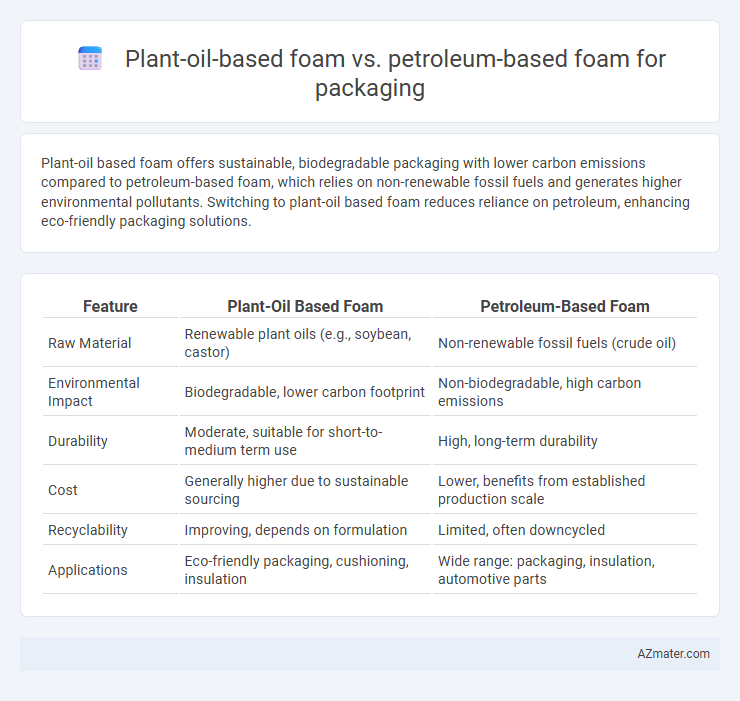
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plant-Oil Based Foam | Petroleum-Based Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material | Renewable plant oils (e.g., soybean, castor) | Non-renewable fossil fuels (crude oil) |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint | Non-biodegradable, high carbon emissions |
| Durability | Moderate, suitable for short-to-medium term use | High, long-term durability |
| Cost | Generally higher due to sustainable sourcing | Lower, benefits from established production scale |
| Recyclability | Improving, depends on formulation | Limited, often downcycled |
| Applications | Eco-friendly packaging, cushioning, insulation | Wide range: packaging, insulation, automotive parts |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Materials
Plant-oil based foam packaging materials use renewable resources such as soybean or castor oil, offering biodegradable and environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional petroleum-based foams. Petroleum-based foams, derived from fossil fuels, provide excellent cushioning and durability but contribute significantly to environmental pollution and non-renewable resource depletion. Advances in plant-oil based foam formulations have improved performance characteristics, making them increasingly viable for sustainable packaging solutions.
What Are Plant-Oil Based Foams?
Plant-oil based foams are sustainable packaging materials derived from renewable plant oils such as soybean, castor, or palm oil, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional petroleum-based foams. These bio-based foams exhibit biodegradability and lower carbon footprints due to their origin from natural resources. Their chemical structure allows for comparable cushioning and protective properties, making them viable for reducing environmental impact in packaging applications.
Overview of Petroleum-Based Foams
Petroleum-based foams are widely used in packaging due to their lightweight, cushioning properties, and cost-effectiveness. These foams, typically made from polyurethane or polystyrene, offer excellent shock absorption and insulation but are derived from non-renewable fossil fuels, contributing to environmental concerns. Despite their durability and versatility, petroleum-based foams have limited biodegradability, leading to long-term pollution and challenges in waste management.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Plant-oil based foam for packaging significantly reduces carbon footprint due to its renewable bio-based sources, unlike petroleum-based foams which rely on finite fossil fuels contributing to greenhouse gas emissions. Biodegradability and compostability of plant-oil foams enhance waste management and decrease landfill pollution, whereas petroleum-based foams persist for centuries, causing environmental contamination. Lifecycle assessments consistently show plant-oil foams have lower energy consumption and carbon emissions across production, use, and disposal phases compared to traditional petroleum-derived foams.
Biodegradability and Sustainability
Plant-oil based foam for packaging offers superior biodegradability compared to petroleum-based foam, breaking down naturally within months in composting environments without leaving harmful residues. Derived from renewable resources such as soybean, castor, and palm oils, these foams significantly reduce carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels. Their sustainable production and end-of-life compostability contribute to minimizing landfill waste and promoting circular economy principles in packaging industries.
Performance and Protective Qualities
Plant-oil based foam offers comparable cushioning and impact resistance to petroleum-based foam, with superior biodegradability and reduced environmental impact. Both foams provide effective shock absorption and thermal insulation, but plant-oil foam excels in reducing carbon footprint due to renewable raw materials. Performance metrics such as compression strength and resilience indicate plant-oil foam meets industry standards for protective packaging while enhancing sustainability.
Cost Analysis: Plant vs Petroleum Foams
Plant-oil based foams often present higher initial production costs compared to petroleum-based foams due to raw material sourcing and processing complexities. However, plant-based foams can lead to long-term savings through lower carbon taxes, potential subsidies, and increased consumer demand for sustainable packaging. Petroleum-based foams benefit from established manufacturing infrastructure and lower raw material prices but face rising costs associated with environmental regulations and supply volatility.
Health and Safety Considerations
Plant-oil based foam for packaging significantly reduces exposure to toxic chemicals and carcinogens commonly found in petroleum-based foam, promoting a safer environment for both manufacturers and consumers. These bio-based foams often exhibit lower VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions, decreasing risks of respiratory irritation and long-term health problems. Furthermore, plant-oil foams are biodegradable and less likely to release harmful microplastics, enhancing environmental safety and reducing pollution-related health hazards.
Industrial Adoption and Market Trends
Plant-oil based foam is gaining industrial adoption due to its sustainability, biodegradability, and reduced carbon footprint compared to petroleum-based foam, which remains widely used but faces regulatory pressures and environmental concerns. Market trends reveal increasing demand for bio-based packaging materials, driven by consumer preferences and corporate commitments to eco-friendly alternatives. Innovations in plant-oil foam formulations are improving performance and cost competitiveness, accelerating its integration in sectors such as electronics, food packaging, and consumer goods.
Future Prospects in Sustainable Packaging
Plant-oil based foam offers a renewable and biodegradable alternative to petroleum-based foam, aligning with global sustainability goals and reducing reliance on fossil fuels. Innovations in biopolymer chemistry and increased scalability are driving down costs, making plant-oil foams more competitive in the packaging industry. Enhanced environmental regulations and consumer demand for eco-friendly materials are expected to accelerate adoption, positioning plant-oil based foam as a key player in the future of sustainable packaging.
Infographic: Plant-oil based foam vs Petroleum-based foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com