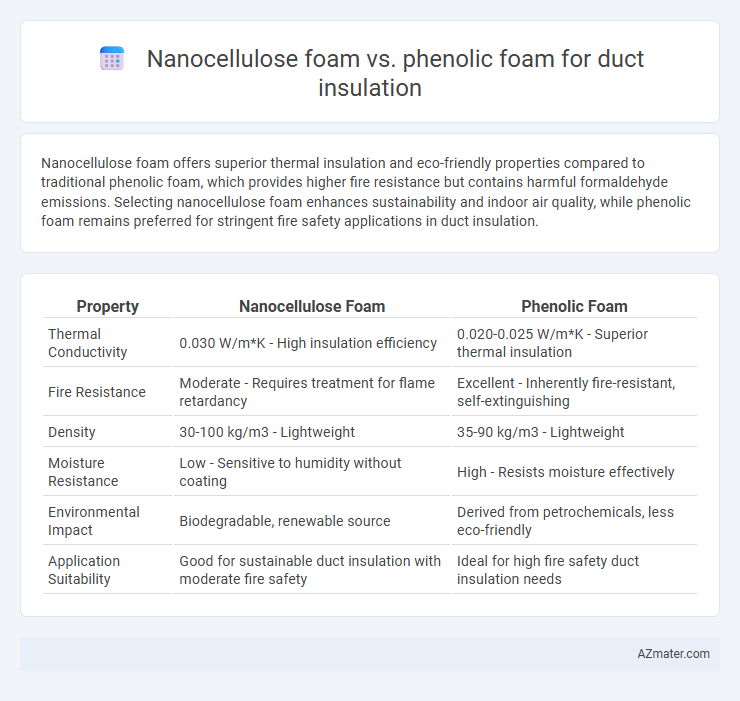
Nanocellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation and eco-friendly properties compared to traditional phenolic foam, which provides higher fire resistance but contains harmful formaldehyde emissions. Selecting nanocellulose foam enhances sustainability and indoor air quality, while phenolic foam remains preferred for stringent fire safety applications in duct insulation.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Nanocellulose Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.030 W/m*K - High insulation efficiency | 0.020-0.025 W/m*K - Superior thermal insulation |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate - Requires treatment for flame retardancy | Excellent - Inherently fire-resistant, self-extinguishing |
| Density | 30-100 kg/m3 - Lightweight | 35-90 kg/m3 - Lightweight |
| Moisture Resistance | Low - Sensitive to humidity without coating | High - Resists moisture effectively |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable, renewable source | Derived from petrochemicals, less eco-friendly |
| Application Suitability | Good for sustainable duct insulation with moderate fire safety | Ideal for high fire safety duct insulation needs |
Introduction to Duct Insulation Materials
Nanocellulose foam and phenolic foam are two advanced materials used for duct insulation, each offering distinct thermal and acoustic properties. Nanocellulose foam provides superior biodegradability, high thermal resistance, and excellent mechanical strength due to its nano-scale cellulose fibers, making it an eco-friendly alternative. Phenolic foam features low smoke emission, high fire resistance, and effective thermal insulation, widely applied in HVAC systems for safety and energy efficiency.
Overview of Nanocellulose Foam
Nanocellulose foam offers superior thermal insulation properties and excellent environmental sustainability compared to phenolic foam, being derived from renewable cellulose fibers. Its high porosity and low density contribute to enhanced sound absorption and fire resistance, making it ideal for duct insulation applications. Nanocellulose foam also exhibits greater flexibility and biodegradability, positioning it as a promising eco-friendly alternative in the construction industry.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a highly efficient insulation material commonly used in duct applications due to its excellent thermal resistance and low smoke emissions during combustion. It offers superior fire retardancy, dimensional stability, and low thermal conductivity, making it ideal for duct insulation where fire safety and energy efficiency are critical. Compared to nanocellulose foam, phenolic foam provides enhanced mechanical strength and long-term durability in harsh environments.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior thermal insulation performance compared to phenolic foam due to its lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.03 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency in duct systems. Phenolic foam generally has a thermal conductivity of 0.035-0.040 W/m*K, making it less effective in minimizing heat transfer in HVAC applications. The nanocellulose structure also provides better moisture resistance and mechanical stability, contributing to long-term insulation durability.
Fire Resistance and Safety Characteristics
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior fire resistance and safety characteristics compared to phenolic foam due to its higher thermal stability and low smoke emission during combustion. Phenolic foam, while offering good flame retardancy, often releases toxic gases such as formaldehyde and phenol under high temperatures, posing safety risks in duct insulation applications. Nanocellulose foam's eco-friendly composition and enhanced fire barrier properties make it an increasingly preferred material for safer duct insulation solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Nanocellulose foam for duct insulation offers superior environmental benefits due to its renewable biomass origin and biodegradability, significantly reducing landfill waste compared to phenolic foam, which relies on petrochemical sources and releases toxic compounds during production and disposal. Nanocellulose exhibits low embodied energy and carbon footprint, enhancing sustainability credentials versus phenolic foam's high greenhouse gas emissions and non-recyclable nature. The bio-based composition of nanocellulose foam supports circular economy principles, whereas phenolic foam's environmental persistence contributes to long-term ecological harm.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to phenolic foam, providing enhanced resistance to compression and impact in duct insulation applications. Its durable cellular structure maintains integrity under thermal cycling and mechanical stress, ensuring long-term performance without significant degradation. In contrast, phenolic foam, while fire-resistant, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking, which can compromise insulation efficiency and structural stability over time.
Installation and Handling Requirements
Nanocellulose foam offers superior flexibility and lightweight properties, making it easier to cut, shape, and install within complex duct geometries compared to phenolic foam, which is more rigid and brittle. The installation of nanocellulose foam requires minimal protective equipment due to its non-toxic and environmentally friendly composition, whereas phenolic foam installation demands stringent safety measures to manage its dust and potential formaldehyde emissions. Handling nanocellulose foam reduces the risk of material damage and worker fatigue, enhancing overall efficiency during duct insulation projects.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Nanocellulose foam offers a competitive edge in duct insulation with moderate production costs driven by abundant cellulose sources, but its market availability remains limited due to emerging technology status and scale-up challenges. Phenolic foam is widely available, benefiting from established manufacturing infrastructure and economies of scale that lower unit costs, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale duct insulation projects. While phenolic foam dominates market presence with extensive supplier networks, nanocellulose foam's biodegradability and insulation performance are driving niche market growth despite higher initial costs and constrained supply.
Future Trends in Duct Insulation Technologies
Nanocellulose foam exhibits superior sustainability and thermal insulation properties compared to traditional phenolic foam, positioning it as a key material in future duct insulation technologies. Innovations in nanocellulose production enable enhanced mechanical strength, biodegradability, and reduced environmental impact, meeting increasingly stringent building codes and green certification standards. Emerging trends emphasize integrating nanocellulose with smart sensors to optimize energy efficiency and indoor air quality in HVAC systems.
Infographic: Nanocellulose foam vs Phenolic foam for Duct insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com