Polyethylene foam offers superior durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for crafts requiring structural integrity and water protection. Ethylene vinyl acetate foam provides greater flexibility and cushioning, perfect for detailed, soft-touch craft projects.
Table of Comparison
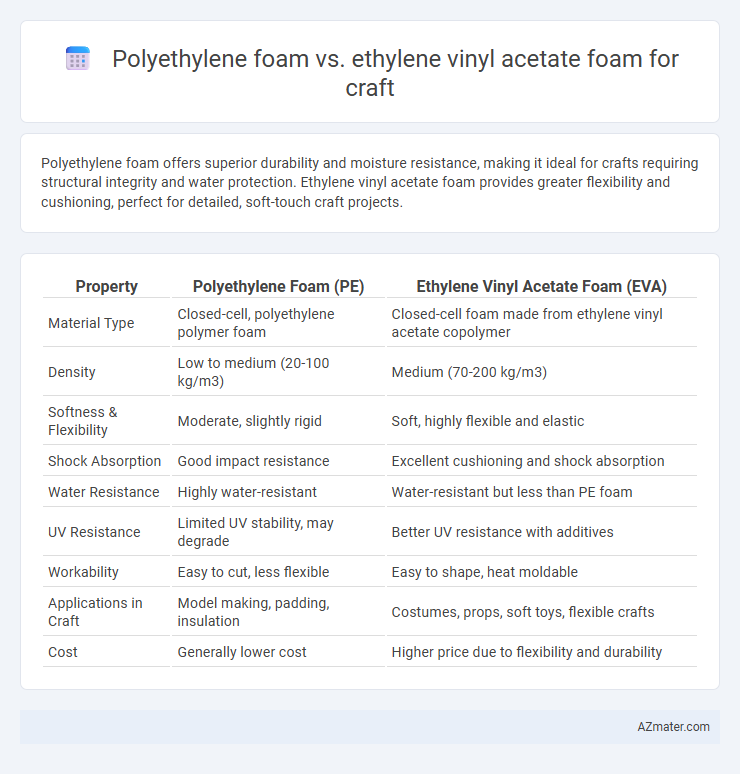
| Property | Polyethylene Foam (PE) | Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Foam (EVA) |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Closed-cell, polyethylene polymer foam | Closed-cell foam made from ethylene vinyl acetate copolymer |
| Density | Low to medium (20-100 kg/m3) | Medium (70-200 kg/m3) |
| Softness & Flexibility | Moderate, slightly rigid | Soft, highly flexible and elastic |
| Shock Absorption | Good impact resistance | Excellent cushioning and shock absorption |
| Water Resistance | Highly water-resistant | Water-resistant but less than PE foam |
| UV Resistance | Limited UV stability, may degrade | Better UV resistance with additives |
| Workability | Easy to cut, less flexible | Easy to shape, heat moldable |
| Applications in Craft | Model making, padding, insulation | Costumes, props, soft toys, flexible crafts |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher price due to flexibility and durability |
Introduction to Polyethylene Foam and EVA Foam in Crafting
Polyethylene foam offers excellent cushioning, durability, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protective craft projects and structural components. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior flexibility, softness, and ease of cutting, favored for detailed, wearable, or decorative crafts. Both materials deliver unique benefits, with polyethylene foam emphasizing strength and EVA foam highlighting comfort and versatility in crafting applications.
Material Composition: Polyethylene vs EVA Foam
Polyethylene foam consists of a closed-cell structure made from polyethylene polymer, offering excellent rigidity, impact resistance, and moisture barrier properties ideal for precise craft applications. In contrast, Ethylene Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam combines ethylene and vinyl acetate monomers, resulting in a softer, more flexible material with superior shock absorption and cushioning characteristics. The distinct polymer compositions influence durability and texture: polyethylene foam provides firm support and density, while EVA foam delivers pliability and a smoother surface, catering to different crafting needs.
Physical Properties Comparison
Polyethylene foam offers higher density and greater resistance to compression, making it ideal for impact absorption and structural support in crafts. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior flexibility, elasticity, and resilience, which enhances comfort and moldability for intricate designs. Both materials demonstrate excellent water resistance, but EVA foam exhibits better UV stability and durability for outdoor craft applications.
Flexibility and Malleability in Craft Projects
Polyethylene foam offers moderate flexibility with a firm structure, making it suitable for projects requiring lightweight cushioning and shape retention. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam excels in malleability and elasticity, allowing intricate bending and shaping, ideal for detailed craft designs and wearable art. The superior elasticity of EVA foam provides enhanced comfort and adaptability compared to the stiffer polyethylene foam in craft applications.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Polyethylene foam offers superior durability with excellent resistance to impact, moisture, and chemical exposure, making it ideal for long-lasting craft projects. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides moderate durability while maintaining flexibility and cushioning, but it may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and heavy mechanical stress. For crafts requiring extended lifespan and robust wear resistance, polyethylene foam is generally the preferred material.
Ease of Cutting and Shaping
Polyethylene foam offers excellent ease of cutting and shaping due to its firm yet flexible structure, making it ideal for precise craft projects that require clean edges and detailed contours. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is softer and more pliable, allowing effortless sculpting and manipulation with basic tools, which suits crafts needing more intricate or rounded shapes. Both materials respond well to hot wire cutters, knives, and scissors, but EVA foam generally requires less force, resulting in smoother finishes and reduced tool wear.
Adhesion and Paintability Performance
Polyethylene foam offers moderate adhesion but poses challenges for paintability due to its low surface energy, often requiring surface treatment or primers for effective bonding. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior adhesion properties and better paint receptivity, thanks to its polar vinyl acetate groups enhancing surface compatibility with adhesives and coatings. For craft applications demanding strong adhesion and high-quality paint finishes, EVA foam presents a more versatile and reliable material choice.
Cost Effectiveness for Crafters
Polyethylene foam offers a more cost-effective option for crafters due to its lower price point and durable, lightweight properties, making it ideal for bulk projects and general cushioning. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, while slightly more expensive, provides greater flexibility, resilience, and ease of cutting, which can reduce material waste and increase efficiency in precision craft applications. For budget-conscious crafters, polyethylene foam maximizes value with its affordability and versatility, whereas EVA foam justifies its higher cost by enhancing project quality and longevity in specialized crafts.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Polyethylene foam offers excellent chemical resistance and is non-toxic, making it a safe option for crafting projects involving direct skin contact, while Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is also hypoallergenic but can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during heating processes. Both materials are widely recyclable, though EVA foam generally has a lower environmental impact due to its biodegradable components and lower energy requirements for production. In terms of sustainability, polyethylene foam typically involves petroleum-based sources, whereas EVA foam provides an eco-friendlier alternative with better biodegradability and reduced toxicity.
Best Craft Applications: Polyethylene Foam vs EVA Foam
Polyethylene foam excels in craft applications requiring robust cushioning, impact absorption, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for protective packaging, padding, and insulation projects. Ethylene vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior flexibility, softness, and ease of cutting, perfect for crafts like custom stamps, cosplay accessories, and footwear inserts. Comparing both, polyethylene foam is favored for durability and water resistance, while EVA foam is preferred for comfort, versatility, and detailed craft designs.
Infographic: Polyethylene foam vs Ethylene vinyl acetate foam for Craft
 azmater.com
azmater.com