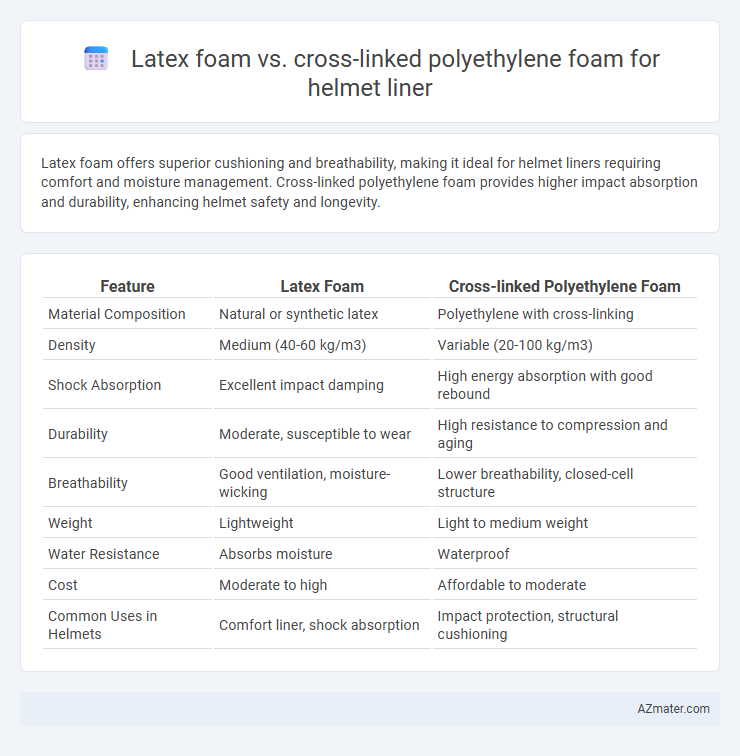
Latex foam offers superior cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for helmet liners requiring comfort and moisture management. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides higher impact absorption and durability, enhancing helmet safety and longevity.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Latex Foam | Cross-linked Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic latex | Polyethylene with cross-linking |
| Density | Medium (40-60 kg/m3) | Variable (20-100 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent impact damping | High energy absorption with good rebound |
| Durability | Moderate, susceptible to wear | High resistance to compression and aging |
| Breathability | Good ventilation, moisture-wicking | Lower breathability, closed-cell structure |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to medium weight |
| Water Resistance | Absorbs moisture | Waterproof |
| Cost | Moderate to high | Affordable to moderate |
| Common Uses in Helmets | Comfort liner, shock absorption | Impact protection, structural cushioning |
Introduction to Helmet Liner Materials
Latex foam offers high elasticity and excellent cushioning, making it ideal for helmet liners requiring comfort and impact absorption. Cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam provides superior durability, moisture resistance, and consistent shock attenuation, enhancing helmet safety and longevity. Choosing between latex foam and XLPE foam depends on the desired balance of flexibility, breathability, and protective performance in helmet liner applications.
Overview of Latex Foam and Cross-Linked Polyethylene Foam
Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic rubber, offers excellent flexibility, durability, and shock absorption, making it a popular choice for helmet liners due to its cushioning and moisture-wicking properties. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, a closed-cell synthetic material, provides superior impact resistance, lightweight structure, and high resilience, ensuring effective energy dispersion during impacts. Both materials enhance helmet safety, but latex foam excels in comfort and breathability while cross-linked polyethylene foam is favored for its robust protective performance and long-term stability.
Physical Properties Comparison
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and resilience with excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for comfort in helmet liners. Cross-linked polyethylene foam provides higher impact absorption, greater compression resistance, and lower water absorption, enhancing durability and protection under extreme conditions. The choice depends on balancing comfort and safety, where latex excels in flexibility and ventilation, while cross-linked polyethylene delivers superior shock absorption and longevity.
Impact Absorption Capabilities
Latex foam offers excellent shock absorption with its natural elasticity and resilient cell structure, effectively dissipating impact forces in helmet liners. Cross-linked polyethylene foam (XLPE) provides superior impact energy absorption due to its closed-cell structure and enhanced compression set resistance, ensuring consistent performance over repeated impacts. The choice between latex foam and XLPE foam depends on balancing lightweight flexibility with lasting impact protection for optimal helmet safety.
Durability and Longevity
Latex foam offers excellent resilience and maintains its cushioning properties over extended use, but it is more susceptible to degradation from moisture and UV exposure compared to cross-linked polyethylene (XLPE) foam. Cross-linked polyethylene foam demonstrates superior durability with high resistance to compression set, chemical exposure, and environmental factors, making it ideal for long-term helmet liner applications. The inherent structural stability of XLPE foam ensures prolonged longevity, retaining shape and protective qualities better than latex foam under harsh conditions.
Comfort and Fit for Helmet Users
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and conformability, adapting closely to the head's contours, which enhances comfort and provides a personalized fit for helmet users. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, known for its closed-cell structure and firmness, delivers consistent cushioning and impact absorption but may lack the same level of flexibility found in latex foam. The choice between latex and cross-linked polyethylene foams significantly impacts helmet comfort by balancing softness, breathability, and form retention for optimal fit during extended wear.
Moisture Resistance and Breathability
Latex foam offers excellent breathability due to its open-cell structure, allowing efficient moisture vapor transmission and reducing sweat buildup in helmet liners. Cross-linked polyethylene foam, with its closed-cell composition, provides superior moisture resistance by preventing water absorption and maintaining cushioning performance under humid conditions. For helmet liners requiring a balance of moisture resistance and airflow, cross-linked polyethylene foam excels in preventing moisture ingress while latex foam enhances ventilation and comfort.
Allergy and Skin Sensitivity Considerations
Latex foam may cause allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to natural rubber proteins, potentially leading to skin irritation or contact dermatitis when used in helmet liners. Cross-linked polyethylene foam offers a hypoallergenic alternative, as it is chemically inert and less likely to provoke allergic responses or skin sensitivity issues. Choosing cross-linked polyethylene foam reduces the risk of adverse skin reactions, making it a safer option for users with sensitive skin or latex allergies.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Latex foam generally offers lower material costs and greater availability due to widespread natural rubber sources, making it economically favorable for helmet liners. Cross-linked polyethylene foam involves higher manufacturing expenses related to chemical cross-linking processes, resulting in increased price points and more limited supplier options. Cost efficiency and accessibility often drive helmet manufacturers toward latex foam when prioritizing budget constraints and production scale.
Conclusion: Choosing the Best Foam for Helmet Liners
Latex foam offers excellent elasticity and breathability, making it ideal for comfort in helmet liners, while cross-linked polyethylene foam provides superior impact absorption and durability, essential for safety in high-impact scenarios. Helmet manufacturers should prioritize cross-linked polyethylene foam when maximum protection is critical, especially in sports like motocross or mountain biking. For applications valuing comfort and moisture management, latex foam remains a preferred choice, but integrating both materials can optimize both protection and comfort in advanced helmet designs.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Cross-linked polyethylene foam for Helmet liner
 azmater.com
azmater.com