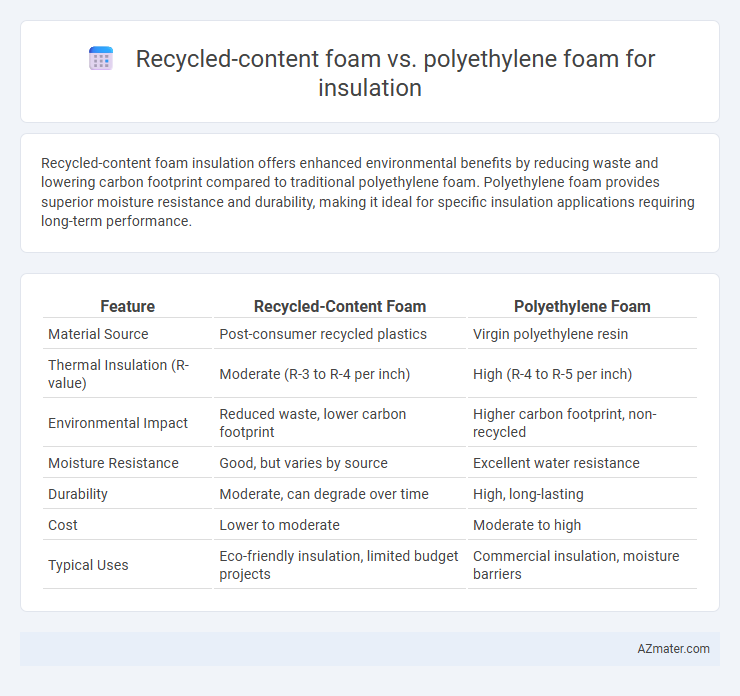
Recycled-content foam insulation offers enhanced environmental benefits by reducing waste and lowering carbon footprint compared to traditional polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam provides superior moisture resistance and durability, making it ideal for specific insulation applications requiring long-term performance.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Recycled-Content Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Source | Post-consumer recycled plastics | Virgin polyethylene resin |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Moderate (R-3 to R-4 per inch) | High (R-4 to R-5 per inch) |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced waste, lower carbon footprint | Higher carbon footprint, non-recycled |
| Moisture Resistance | Good, but varies by source | Excellent water resistance |
| Durability | Moderate, can degrade over time | High, long-lasting |
| Cost | Lower to moderate | Moderate to high |
| Typical Uses | Eco-friendly insulation, limited budget projects | Commercial insulation, moisture barriers |
Introduction to Foam Insulation Materials
Foam insulation materials, including recycled-content foam and polyethylene foam, are widely used for thermal and acoustic insulation in residential and commercial construction. Recycled-content foam offers environmentally friendly advantages by utilizing post-consumer or post-industrial waste, reducing landfill impact while maintaining comparable insulating properties measured by R-value. Polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance, durability, and cushioning, making it suitable for applications requiring water vapor barriers and impact protection alongside insulation.
What is Recycled-Content Foam?
Recycled-content foam is an environmentally friendly insulation material made from repurposed plastic waste, including post-consumer and industrial sources, reducing landfill use and resource consumption. It offers thermal insulation properties comparable to polyethylene foam, with the added benefit of supporting circular economy goals by minimizing virgin material extraction. This type of foam is often used in sustainable building projects seeking LEED certification or other green building standards.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam Insulation
Polyethylene foam insulation is a closed-cell material known for its excellent thermal resistance, moisture barrier properties, and durability in various environmental conditions. It typically features a lightweight structure with high compressive strength, making it ideal for applications requiring shock absorption and consistent insulation performance. Compared to recycled-content foam, polyethylene foam often offers superior resistance to mold, mildew, and chemical exposure, enhancing its longevity in building and industrial insulation.
Environmental Impact: Recycled-Content vs Polyethylene Foam
Recycled-content foam significantly reduces environmental impact by utilizing post-consumer and post-industrial waste, lowering landfill contributions and conserving natural resources. Polyethylene foam, while effective for insulation, is typically derived from non-renewable petroleum-based materials, resulting in higher carbon emissions during production. Choosing recycled-content foam supports sustainability goals by promoting circular economy principles and reducing overall ecological footprint in insulation applications.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Recycled-content foam insulation often demonstrates thermal resistance (R-value) comparable to or slightly lower than that of polyethylene foam, with R-values typically ranging from 3.5 to 4.5 per inch, while polyethylene foam offers R-values around 3.6 to 4.0 per inch. The closed-cell structure of polyethylene foam provides superior moisture resistance and consistent thermal performance over time, enhancing its insulation efficiency in variable conditions. Both materials contribute to energy efficiency, but recycled-content foam's environmental benefits complement its effective thermal insulation properties in sustainable building applications.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Recycled-content foam insulation offers a cost-effective alternative with an average price reduction of 15-25% compared to traditional polyethylene foam, making it attractive for budget-conscious projects. Polyethylene foam, widely available in commercial markets, benefits from established supply chains and consistent quality, whereas recycled-content foam's availability can vary regionally due to reliance on recycled raw materials. Cost analysis highlights that recycled-content foam not only reduces material expenses but also supports sustainability goals, though project planners must consider potential supply limitations and longer lead times in some markets.
Durability and Lifespan
Recycled-content foam insulation offers comparable durability to polyethylene foam but often features enhanced environmental benefits through material reuse. Polyethylene foam is known for its excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and physical damage, providing a lifespan ranging from 20 to 50 years depending on environmental conditions. Choosing recycled-content foam can balance sustainability goals with reliable long-term insulation performance.
Installation Procedures and Ease of Use
Recycled-content foam insulation offers straightforward installation with flexible cutting and shaping properties, making it ideal for conforming to irregular spaces without specialized tools. Polyethylene foam, while also easy to handle, provides excellent compressive strength but may require additional adhesives or fasteners for secure placement in insulation projects. Both materials ensure efficient thermal performance, but recycled-content foam typically allows quicker installation due to its lightweight and pliable nature.
Suitability for Different Applications
Recycled-content foam offers excellent environmental benefits and sufficient thermal insulation, making it suitable for applications focused on sustainability and moderate temperature control, such as packaging and eco-friendly building projects. Polyethylene foam provides superior moisture resistance and durability, ideal for high-impact protection, soundproofing, and industrial insulation where consistent thermal performance and structural integrity are critical. Choosing between these foams depends on specific requirements including environmental impact, moisture exposure, and mechanical stress tolerance in the intended application.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Insulation Needs
Recycled-content foam offers an eco-friendly insulation option with comparable thermal performance to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for environmentally conscious projects. Polyethylene foam provides superior moisture resistance and durability, suitable for areas exposed to damp conditions or heavy wear. Assessing insulation requirements, such as R-value, moisture exposure, and environmental impact, guides the optimal selection between recycled-content foam and polyethylene foam for effective thermal protection.
Infographic: Recycled-content foam vs Polyethylene foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com