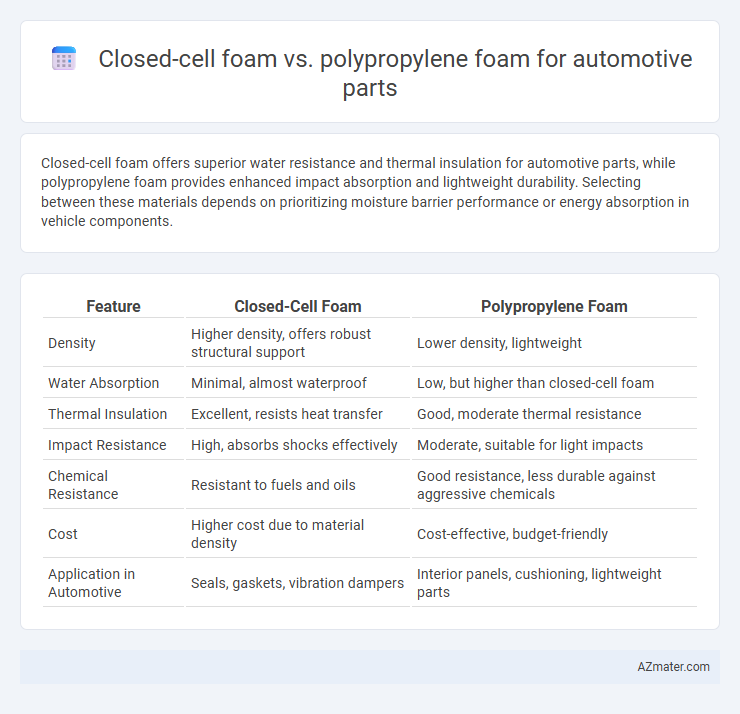
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and thermal insulation for automotive parts, while polypropylene foam provides enhanced impact absorption and lightweight durability. Selecting between these materials depends on prioritizing moisture barrier performance or energy absorption in vehicle components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Polypropylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Higher density, offers robust structural support | Lower density, lightweight |
| Water Absorption | Minimal, almost waterproof | Low, but higher than closed-cell foam |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, resists heat transfer | Good, moderate thermal resistance |
| Impact Resistance | High, absorbs shocks effectively | Moderate, suitable for light impacts |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to fuels and oils | Good resistance, less durable against aggressive chemicals |
| Cost | Higher cost due to material density | Cost-effective, budget-friendly |
| Application in Automotive | Seals, gaskets, vibration dampers | Interior panels, cushioning, lightweight parts |
Introduction to Automotive Foam Materials
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance, structural rigidity, and thermal insulation, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to moisture and temperature fluctuations. Polypropylene foam provides excellent impact absorption, lightweight durability, and chemical resistance, enhancing vehicle safety and performance. Both materials contribute significantly to noise reduction, vibration dampening, and overall energy efficiency in automotive applications.
Overview of Closed-Cell Foam
Closed-cell foam is a highly durable material known for its excellent water resistance, thermal insulation, and superior compression strength, making it ideal for automotive parts that require moisture barriers and impact absorption. Its dense structure prevents fluid absorption, enhancing longevity in harsh environments, while providing consistent cushioning and vibration dampening. Compared to polypropylene foam, closed-cell foam offers better sealing properties, making it suitable for gaskets, seals, and noise reduction in vehicle assemblies.
Overview of Polypropylene Foam
Polypropylene foam offers excellent chemical resistance, low density, and high impact absorption, making it ideal for automotive components requiring lightweight durability. Its closed-cell structure provides superior moisture resistance and thermal insulation compared to other foams, enhancing vehicle performance and comfort. Due to its recyclability and cost-effectiveness, polypropylene foam is increasingly favored for door panels, instrument panels, and under-hood applications in the automotive industry.
Key Material Properties Comparison
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance, higher compressive strength, and better thermal insulation compared to polypropylene foam, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to harsh environmental conditions. Polypropylene foam excels in impact absorption, lightweight characteristics, and chemical resistance, providing enhanced durability and fuel efficiency benefits. Both materials exhibit excellent fatigue resistance, but closed-cell foam's reduced water absorption makes it preferable for long-term automotive applications requiring structural integrity.
Durability and Longevity in Automotive Applications
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior durability and longevity in automotive applications due to its high resistance to moisture, compression, and chemical degradation, making it ideal for sealing and cushioning components that endure harsh environments. Polypropylene foam offers excellent impact absorption and chemical resistance but tends to have lower compression set resistance and may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and mechanical stress. Selecting closed-cell foam enhances the lifespan of automotive parts by maintaining structural integrity and preventing material breakdown over extended use.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior thermal insulation properties with higher temperature tolerance, making it ideal for automotive parts exposed to heat fluctuation and engine proximity. Polypropylene foam offers excellent chemical resistance against oils, solvents, and fuels, ensuring durability in harsh automotive environments. Choosing between closed-cell and polypropylene foam depends on prioritizing thermal stability versus chemical exposure in automotive applications.
Weight and Density Considerations
Closed-cell foam offers higher density and superior structural rigidity, making it ideal for automotive parts requiring enhanced impact resistance, though it can increase overall weight. Polypropylene foam is significantly lighter due to its low density, providing effective cushioning and vibration absorption while contributing to vehicle weight reduction and improved fuel efficiency. Selecting between the two depends on balancing the need for structural strength against the critical goal of minimizing component mass in automotive design.
Cost Implications and Economic Benefits
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and moisture resistance, reducing maintenance costs for automotive parts, but typically has a higher initial price compared to polypropylene foam. Polypropylene foam provides a cost-effective lightweight solution with good impact absorption, leading to fuel efficiency and lower production expenses. Selecting polypropylene foam can enhance economic benefits through material savings and improved vehicle performance, while closed-cell foam adds value by extending part lifespan and reducing replacement frequency.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Closed-cell foam offers superior insulation and durability for automotive parts but poses challenges in recyclability due to its cross-linked polymer structure, often requiring specialized processing methods. Polypropylene foam, widely used for its lightweight and impact absorption properties, boasts higher environmental benefits through easier recyclability and lower environmental footprint during production. Choosing polypropylene foam supports sustainable automotive manufacturing by facilitating circular economy practices and reducing landfill waste.
Choosing the Right Foam for Automotive Parts
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and higher structural rigidity, making it ideal for door panels and engine covers in automotive applications. Polypropylene foam provides excellent impact absorption and lightweight properties, commonly used for bumper cores and interior cushioning. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing durability, weight, and thermal insulation requirements specific to each automotive part's function.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polypropylene foam for Automotive part
 azmater.com
azmater.com