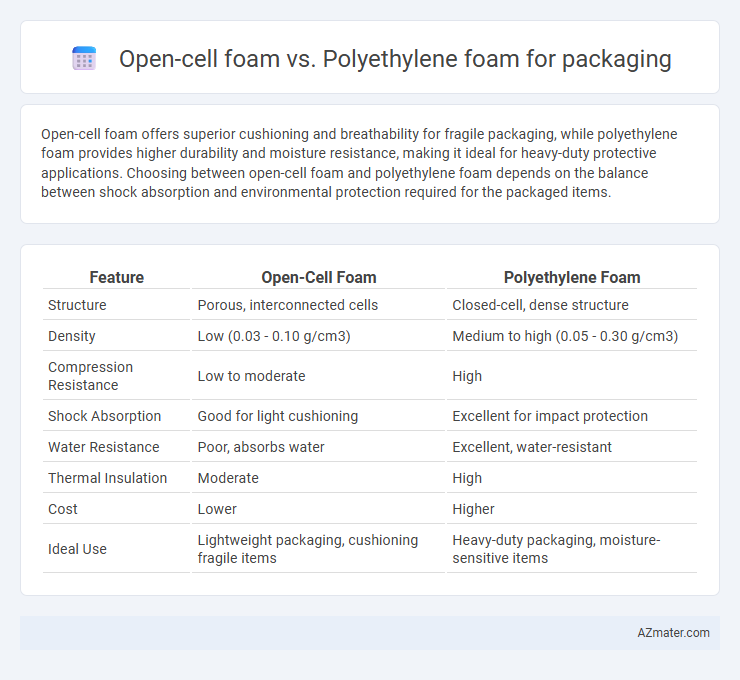
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning and breathability for fragile packaging, while polyethylene foam provides higher durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty protective applications. Choosing between open-cell foam and polyethylene foam depends on the balance between shock absorption and environmental protection required for the packaged items.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Open-Cell Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Porous, interconnected cells | Closed-cell, dense structure |
| Density | Low (0.03 - 0.10 g/cm3) | Medium to high (0.05 - 0.30 g/cm3) |
| Compression Resistance | Low to moderate | High |
| Shock Absorption | Good for light cushioning | Excellent for impact protection |
| Water Resistance | Poor, absorbs water | Excellent, water-resistant |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Ideal Use | Lightweight packaging, cushioning fragile items | Heavy-duty packaging, moisture-sensitive items |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Open-cell foam and polyethylene foam serve distinct roles in packaging, offering unique protective properties tailored to different needs. Open-cell foam, characterized by its porous structure, provides excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for fragile items requiring shock absorption while allowing moisture exchange. Polyethylene foam, known for its closed-cell design, delivers superior impact resistance, moisture barrier capabilities, and durability, often preferred for long-term storage and transport of heavy or delicate goods.
What is Open-Cell Foam?
Open-cell foam is a porous material characterized by interconnected air pockets, allowing air and moisture to pass through easily, making it highly compressible and lightweight. In packaging, open-cell foam provides cushioning and shock absorption for delicate items while offering breathability that prevents moisture buildup. Its structure contrasts with polyethylene foam, which is closed-cell and more rigid, providing greater resistance to water and impact.
Overview of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, lightweight material known for its excellent impact absorption, moisture resistance, and chemical stability, making it ideal for protective packaging. It provides superior cushioning and durability compared to open-cell foam, ensuring safe transportation of delicate items. Its resistance to water and chemicals also enhances its suitability for long-term storage and outdoor shipping conditions.
Key Differences in Material Structure
Open-cell foam features interconnected pores that allow air and moisture to pass through, providing excellent cushioning and shock absorption but less resistance to water. Polyethylene foam consists of closed-cell structures filled with gas pockets, offering superior compression resistance, moisture resistance, and durability for protective packaging. The choice depends on the packaging needs, where open-cell foam suits delicate, lightweight items and polyethylene foam excels in impact protection and water resistance.
Cushioning Performance Comparison
Open-cell foam offers superior cushioning performance due to its porous structure, which effectively absorbs shocks and vibrations by compressing air within the cells. Polyethylene foam provides excellent impact resistance and resilience, maintaining shape after heavy loads but with less energy absorption than open-cell foam. For packaging fragile items, open-cell foam excels in protecting against delicate impacts, while polyethylene foam is better suited for high-density cushioning and repeated use applications.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to open-cell foam due to its closed-cell structure that prevents water absorption, making it ideal for packaging sensitive products. Open-cell foam, while softer and more compressible, absorbs moisture easily, reducing its effectiveness in humid or wet environments. Polyethylene foam also provides enhanced durability and impact resistance, ensuring long-term protection during shipping and handling.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Open-cell foam offers significantly lower density, resulting in lighter packaging solutions that reduce shipping costs and carbon footprint. Polyethylene foam provides greater structural integrity with higher density, offering superior impact resistance but increasing overall package weight. Flexibility in open-cell foam allows for better cushioning and conformity to irregular shapes, whereas polyethylene foam maintains shape rigidity, ideal for protecting heavier or more sensitive products.
Cost Considerations for Packaging
Open-cell foam generally offers lower material costs compared to polyethylene foam, making it a budget-friendly option for packaging applications requiring cushioning and shock absorption. Polyethylene foam, while more expensive, provides superior durability and moisture resistance, which can reduce long-term costs by minimizing product damage during transit. Cost considerations should balance initial investment with performance requirements and potential reductions in product loss and returns.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Open-cell foam is typically made from polyurethane, which presents challenges in recycling and often ends up in landfills, negatively impacting the environment due to slow degradation and potential release of toxic substances. Polyethylene foam, being a closed-cell material, offers better recyclability through established polyethylene recycling streams and generally has a lower environmental footprint because it can be reprocessed into new foam products. The choice between these foams significantly affects sustainability efforts, with polyethylene foam preferred for eco-friendly packaging due to its improved recyclability and reduced ecological impact.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Open-cell foam offers excellent cushioning and breathability, making it ideal for packaging delicate or irregularly shaped products requiring shock absorption and airflow. Polyethylene foam provides superior density, moisture resistance, and durability, suited for heavy-duty packaging and long-term protection against impact and environmental factors. Selecting the right foam depends on product fragility, weight, exposure conditions, and budget considerations to ensure optimal protection and cost efficiency.
Infographic: Open-cell foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com