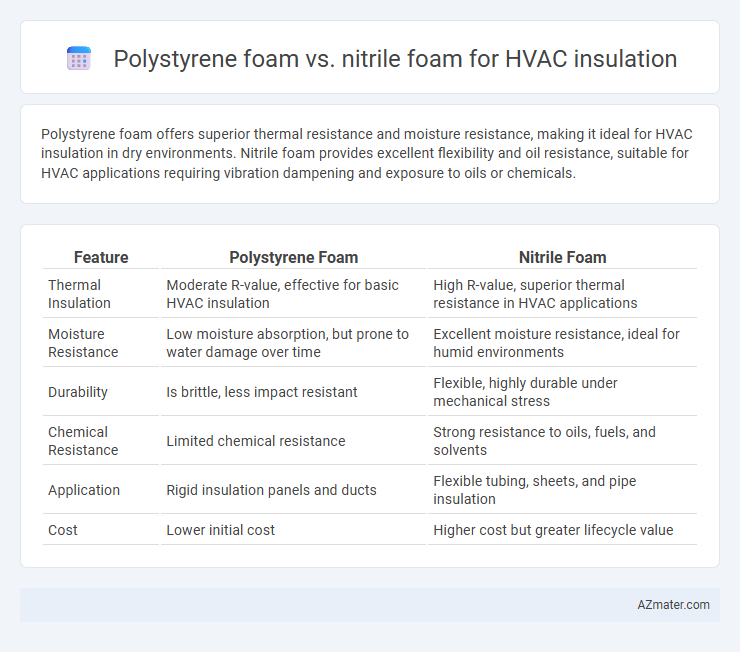
Polystyrene foam offers superior thermal resistance and moisture resistance, making it ideal for HVAC insulation in dry environments. Nitrile foam provides excellent flexibility and oil resistance, suitable for HVAC applications requiring vibration dampening and exposure to oils or chemicals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polystyrene Foam | Nitrile Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate R-value, effective for basic HVAC insulation | High R-value, superior thermal resistance in HVAC applications |
| Moisture Resistance | Low moisture absorption, but prone to water damage over time | Excellent moisture resistance, ideal for humid environments |
| Durability | Is brittle, less impact resistant | Flexible, highly durable under mechanical stress |
| Chemical Resistance | Limited chemical resistance | Strong resistance to oils, fuels, and solvents |
| Application | Rigid insulation panels and ducts | Flexible tubing, sheets, and pipe insulation |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher cost but greater lifecycle value |
Introduction to HVAC Insulation Materials
Polystyrene foam and nitrile foam are widely used HVAC insulation materials with distinct properties tailored for thermal efficiency and durability. Polystyrene foam offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture barrier capabilities, making it ideal for airborne temperature control and energy conservation. Nitrile foam provides superior flexibility, chemical resistance, and sound absorption, enhancing HVAC system performance in environments prone to vibration and exposure to oils or solvents.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid insulation material known for its high thermal resistance and moisture resistance, making it suitable for HVAC applications. It offers excellent compressive strength and durability, contributing to long-term energy efficiency and protection against heat transfer. Commonly used in both expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, polystyrene foam provides effective insulation performance in various HVAC systems.
Overview of Nitrile Foam
Nitrile foam is a synthetic rubber material known for its excellent thermal insulation, durability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it ideal for HVAC applications. Its closed-cell structure provides superior sound absorption and energy efficiency compared to polystyrene foam, which is more rigid and less resistant to environmental factors. Nitrile foam's flexibility and long lifespan contribute to improved system performance and reduced maintenance in HVAC insulation systems.
Thermal Insulation Properties: Polystyrene vs Nitrile
Polystyrene foam provides excellent thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity ranging from 0.03 to 0.04 W/m*K, making it effective for reducing heat transfer in HVAC systems. Nitrile foam, while slightly higher in thermal conductivity at around 0.04 to 0.05 W/m*K, offers superior flexibility and moisture resistance, enhancing its durability in varying HVAC conditions. The choice between polystyrene and nitrile foam depends on balancing insulation efficiency and environmental factors such as humidity and mechanical stress.
Moisture Resistance Comparison
Polystyrene foam offers moderate moisture resistance, making it suitable for HVAC insulation where minimal water exposure occurs, but it may absorb some water over time, potentially reducing its insulating efficiency. Nitrile foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure and inherent chemical properties, preventing water absorption and maintaining thermal performance in high-humidity environments. Choosing nitrile foam for HVAC insulation ensures enhanced durability and consistent insulation value in moist or condensation-prone areas.
Fire Safety and Flame Retardance
Polystyrene foam offers moderate flame retardance but tends to produce toxic smoke and can melt when exposed to high heat, posing significant fire safety risks in HVAC insulation applications. Nitrile foam exhibits superior fire resistance with inherent flame-retardant properties and lower smoke toxicity, enhancing safety in ventilation systems. Selecting nitrile foam improves compliance with fire codes and minimizes hazards compared to polystyrene foam in insulation environments.
Durability and Longevity
Polystyrene foam offers moderate durability with resistance to moisture and compression but tends to degrade under prolonged UV exposure and fluctuating temperatures in HVAC systems. Nitrile foam exhibits superior longevity due to its excellent resistance to ozone, chemicals, and mechanical wear, maintaining flexibility and insulation properties over extended periods. For HVAC insulation applications requiring long-term performance in harsh environments, nitrile foam is generally more durable and reliable than polystyrene foam.
Installation Ease and Flexibility
Polystyrene foam offers rigid structure but limited flexibility, making installation in complex HVAC configurations more challenging, often requiring precise cutting and fitting. Nitrile foam provides superior elasticity and compressibility, allowing easier wrapping around ducts and irregular shapes, which enhances installation speed and reduces gaps. The flexibility of nitrile foam improves sealing effectiveness, leading to better thermal insulation performance and reduced labor costs.
Cost Analysis: Which is More Economical?
Polystyrene foam offers lower upfront costs compared to nitrile foam, making it an economical choice for HVAC insulation in budget-sensitive projects. Nitrile foam, although more expensive initially, provides superior resistance to oils, chemicals, and extreme temperatures, potentially reducing long-term maintenance and replacement costs. Evaluating total lifecycle expenses, including installation, durability, and energy efficiency, nitrile foam can be more cost-effective for environments with harsh conditions despite its higher initial price.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene foam, commonly used for HVAC insulation, has a significant environmental impact due to its non-biodegradable nature and reliance on petroleum-based resources, contributing to long-term waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Nitrile foam offers improved sustainability by being more resistant to microbial growth and moisture, thereby enhancing HVAC system efficiency and reducing energy consumption, although it is still derived from synthetic rubber with limited biodegradability. Choosing nitrile foam can support better environmental outcomes compared to polystyrene foam, but incorporating recycled content and proper disposal methods is essential for maximizing sustainability in HVAC insulation materials.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Nitrile foam for HVAC insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com