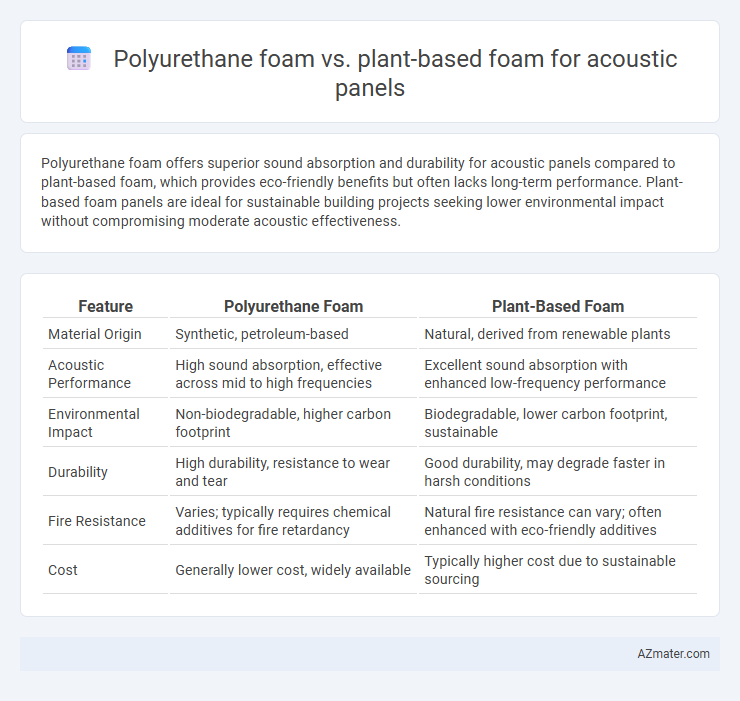
Polyurethane foam offers superior sound absorption and durability for acoustic panels compared to plant-based foam, which provides eco-friendly benefits but often lacks long-term performance. Plant-based foam panels are ideal for sustainable building projects seeking lower environmental impact without compromising moderate acoustic effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Plant-Based Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Origin | Synthetic, petroleum-based | Natural, derived from renewable plants |
| Acoustic Performance | High sound absorption, effective across mid to high frequencies | Excellent sound absorption with enhanced low-frequency performance |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, higher carbon footprint | Biodegradable, lower carbon footprint, sustainable |
| Durability | High durability, resistance to wear and tear | Good durability, may degrade faster in harsh conditions |
| Fire Resistance | Varies; typically requires chemical additives for fire retardancy | Natural fire resistance can vary; often enhanced with eco-friendly additives |
| Cost | Generally lower cost, widely available | Typically higher cost due to sustainable sourcing |
Introduction to Acoustic Panel Materials
Acoustic panels commonly use polyurethane foam and plant-based foam as core materials, each offering different properties for sound absorption and environmental impact. Polyurethane foam is widely favored for its high noise reduction coefficient (NRC) ranging from 0.6 to 0.9, ensuring effective sound dampening in diverse settings. Plant-based foams, derived from renewable resources like soy or castor oil, provide lower VOC emissions and greater sustainability while maintaining comparable acoustic performance.
Overview of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is a versatile, synthetic material widely used in acoustic panels due to its excellent sound absorption properties and durability. Its open-cell structure effectively traps sound waves, reducing noise and echo in various environments such as studios, offices, and theaters. Industrial-grade polyurethane foam offers customizable density and thickness, making it a cost-efficient choice for high-performance acoustic treatment compared to plant-based alternatives.
Overview of Plant-Based Foam
Plant-based foam for acoustic panels offers a sustainable alternative to traditional polyurethane foam by utilizing renewable materials such as soy, castor oil, or other bio-based polymers. This foam type delivers effective sound absorption through open-cell structures, while reducing environmental impact and VOC emissions. Advances in bio-polymer technology have enhanced its durability and performance, making plant-based foam a viable, eco-friendly option in acoustic insulation solutions.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Polyurethane foam demonstrates superior sound absorption coefficients across mid to high frequencies, making it highly effective in reducing noise reflections and reverberations in various environments. Plant-based foam, often derived from soy or other natural materials, offers competitive acoustic insulation but generally exhibits lower density and sound absorption rates compared to traditional polyurethane foam. For applications demanding optimal acoustic performance, polyurethane foam remains the preferred choice due to its enhanced porosity and controlled cell structure.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam, derived from petrochemicals, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and is non-biodegradable, posing long-term environmental challenges. Plant-based foam, often made from renewable resources like soy or algae, offers a lower carbon footprint and improved biodegradability, aligning better with sustainable building practices. Choosing plant-based foam for acoustic panels supports reduced reliance on fossil fuels and enhances eco-friendly construction efforts.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyurethane foam used in acoustic panels often contains volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and can release hazardous chemicals during installation and degradation, posing respiratory risks and requiring proper ventilation and protective equipment. Plant-based foam alternatives, derived from natural materials like soy, typically emit lower VOC levels and are biodegradable, making them a safer choice for indoor air quality and reducing environmental impact. Selecting plant-based foam enhances health safety by minimizing exposure to toxic substances while providing effective sound absorption in acoustic applications.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and longevity for acoustic panels due to its high resistance to compression, moisture, and microbial growth, maintaining acoustic performance over time. Plant-based foam, while environmentally friendly, tends to degrade faster under humidity and physical stress, leading to reduced lifespan and acoustic effectiveness. Selecting polyurethane foam ensures extended durability and sustained sound absorption in demanding environments.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Polyurethane foam generally offers a lower initial cost compared to plant-based foam, making it a more affordable option for budget-conscious acoustic panel projects. Plant-based foam, while often more expensive upfront due to sustainable materials and production processes, may provide long-term savings through enhanced durability and environmental incentives. Evaluating the total cost of ownership, including installation, maintenance, and lifecycle impact, is essential for an accurate affordability comparison between these two acoustic panel materials.
Installation and Maintenance
Polyurethane foam offers straightforward installation due to its lightweight nature and flexible form, allowing easy cutting and fitting on various surfaces with minimal tools. Maintenance is generally low, requiring only occasional dusting and avoiding exposure to moisture, which can degrade its properties over time. Plant-based foam panels, while eco-friendly and biodegradable, may require more careful handling during installation to prevent damage and often need protection from humidity to maintain acoustic performance and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Foam for Acoustic Panels
Polyurethane foam offers excellent sound absorption with high NRC ratings, durability, and fire resistance, making it a reliable choice for acoustic panels in commercial and residential settings. Plant-based foam provides an eco-friendly alternative with natural noise dampening properties and lower VOC emissions, appealing to sustainable building projects. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing acoustic performance requirements, environmental impact, and budget constraints.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Plant-based foam for Acoustic panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com