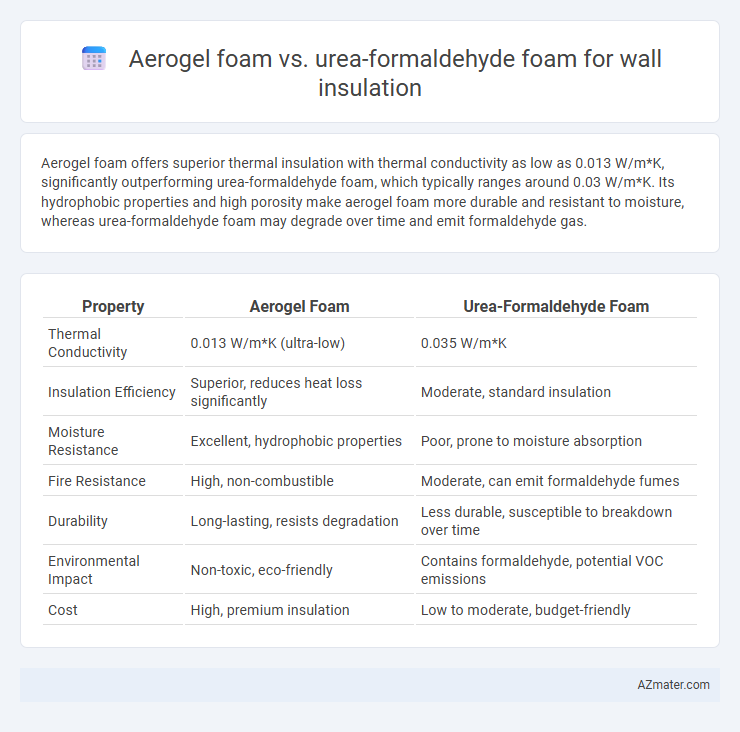
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with thermal conductivity as low as 0.013 W/m*K, significantly outperforming urea-formaldehyde foam, which typically ranges around 0.03 W/m*K. Its hydrophobic properties and high porosity make aerogel foam more durable and resistant to moisture, whereas urea-formaldehyde foam may degrade over time and emit formaldehyde gas.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aerogel Foam | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.013 W/m*K (ultra-low) | 0.035 W/m*K |
| Insulation Efficiency | Superior, reduces heat loss significantly | Moderate, standard insulation |
| Moisture Resistance | Excellent, hydrophobic properties | Poor, prone to moisture absorption |
| Fire Resistance | High, non-combustible | Moderate, can emit formaldehyde fumes |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resists degradation | Less durable, susceptible to breakdown over time |
| Environmental Impact | Non-toxic, eco-friendly | Contains formaldehyde, potential VOC emissions |
| Cost | High, premium insulation | Low to moderate, budget-friendly |
Introduction to Wall Insulation Materials
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with a thermal conductivity as low as 0.013 W/m*K, outperforming traditional urea-formaldehyde foam, which typically ranges around 0.022 W/m*K. Aerogel's lightweight, hydrophobic properties enhance moisture resistance and air-tightness in wall assemblies, while urea-formaldehyde foam provides cost-effective insulation but may off-gas formaldehyde and degrade over time. Selecting between these materials depends on balancing high-performance insulation and environmental safety with budget considerations in building design.
What is Aerogel Foam?
Aerogel foam is an ultra-lightweight, highly porous material composed primarily of silica, known for its exceptional thermal insulation properties due to its minimal thermal conductivity, which is often lower than traditional insulating materials. Its nanoscale structure traps air efficiently, reducing heat transfer and making it ideal for wall insulation where space-saving and energy efficiency are crucial. Compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, aerogel foam offers superior moisture resistance and durability, enhancing long-term insulation performance in building applications.
What is Urea-Formaldehyde Foam?
Urea-formaldehyde foam is a closed-cell insulation material created by mixing urea and formaldehyde resins with a foaming agent, resulting in a lightweight and rigid foam ideal for wall insulation. This foam offers excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 3.7 to 4.2 per inch, helping to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency. Compared to aerogel foam, urea-formaldehyde foam is more cost-effective but has higher moisture susceptibility and lower insulating performance under humid conditions.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with a thermal conductivity as low as 0.013 W/m*K compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, which typically ranges around 0.024-0.035 W/m*K, resulting in better energy efficiency and reduced heat transfer in walls. The low density and high porosity of aerogel foam contribute to its exceptional insulating properties, making it ideal for applications requiring minimal thickness and maximum thermal resistance. Urea-formaldehyde foam, while cost-effective, provides lower thermal performance and is more susceptible to moisture absorption, which can degrade its insulating effectiveness over time.
Energy Efficiency: Aerogel vs Urea-Formaldehyde
Aerogel foam offers superior energy efficiency for wall insulation due to its extremely low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.013 W/m*K, compared to urea-formaldehyde foam's thermal conductivity of approximately 0.03 W/m*K. This significant difference enables aerogel insulation to provide better heat retention and reduced energy consumption in buildings. Additionally, aerogel foam's hydrophobic properties enhance durability and maintain insulation performance over time, unlike urea-formaldehyde, which can degrade with moisture exposure.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Aerogel foam exhibits superior moisture resistance and significantly lower water absorption compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, making it highly effective in preventing mold growth and structural damage in wall insulation. Its nanoscale porous structure repels water while maintaining breathability, whereas urea-formaldehyde foam tends to absorb moisture, leading to reduced insulation performance and potential material degradation. Choosing aerogel foam enhances long-term durability and energy efficiency in moisture-prone environments.
Fire Safety and Toxicity
Aerogel foam offers superior fire resistance with a high ignition point and low flame spread, making it safer for wall insulation compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, which can release toxic formaldehyde gas during combustion. The non-combustible nature of aerogel minimizes toxic fumes and smoke, reducing health hazards in fire incidents. Urea-formaldehyde foam poses greater risks due to potential off-gassing of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carcinogenic formaldehyde, impacting indoor air quality and occupant safety.
Installation Process and Practical Concerns
Aerogel foam insulation offers a lightweight and flexible installation process, requiring minimal curing time and allowing for easy application in tight spaces due to its high compressibility and hydrophobic properties. Urea-formaldehyde foam involves a more complex installation with the need for specialized equipment to mix and inject the chemical components on-site, and it requires careful handling to avoid formaldehyde emissions and ensure proper curing to prevent shrinkage or brittleness. Practical concerns favor aerogel foam for durability and moisture resistance, while urea-formaldehyde foam is more cost-effective but poses potential health risks and may degrade over time if exposed to moisture.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Aerogel foam offers superior thermal insulation with low embodied energy and is non-toxic, enhancing sustainability by reducing energy consumption and emissions over its lifecycle. Urea-formaldehyde foam, while cost-effective and widely used, releases formaldehyde, a hazardous volatile organic compound, raising health and environmental concerns during installation and disposal. Aerogel's longer lifespan and recyclability further contribute to a reduced environmental footprint compared to the shorter durability and chemical off-gassing associated with urea-formaldehyde insulations.
Cost Analysis and Value for Money
Aerogel foam insulation, though significantly more expensive upfront, offers superior thermal performance with R-values up to 10 per inch, providing long-term energy savings and durability compared to urea-formaldehyde foam, which costs less but typically delivers lower R-values around 3.5 to 4. Urea-formaldehyde foam is cost-effective for initial installation but may require replacement or supplementation over time due to moisture sensitivity and degradation, impacting overall value. Aerogel's higher price is offset by enhanced energy efficiency and lifespan, making it a better investment for sustainable insulation despite the higher initial cost.
Infographic: Aerogel foam vs Urea-formaldehyde foam for Wall insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com