Polyurethane foam offers superior insulation with higher R-values and greater flexibility, making it ideal for energy-efficient building panels. Phenolic foam provides excellent fire resistance and low smoke emission, ensuring enhanced safety in construction applications.
Table of Comparison
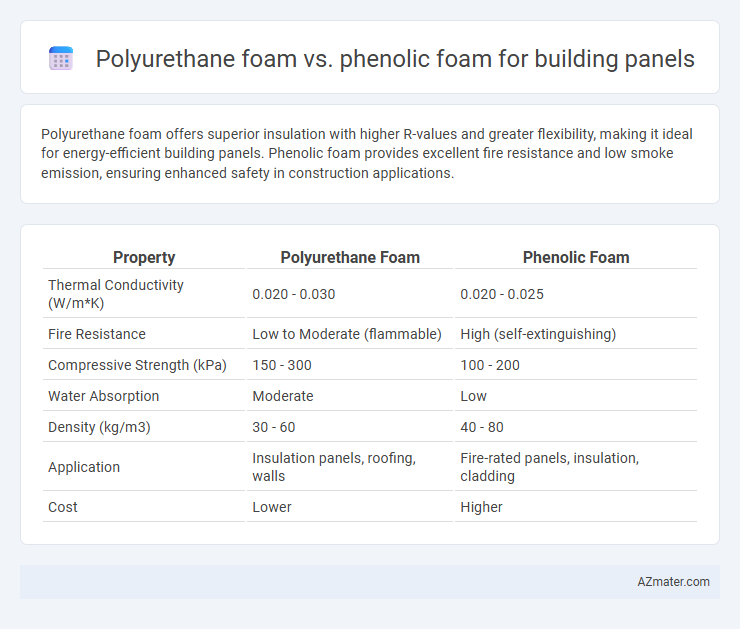
| Property | Polyurethane Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m*K) | 0.020 - 0.030 | 0.020 - 0.025 |
| Fire Resistance | Low to Moderate (flammable) | High (self-extinguishing) |
| Compressive Strength (kPa) | 150 - 300 | 100 - 200 |
| Water Absorption | Moderate | Low |
| Density (kg/m3) | 30 - 60 | 40 - 80 |
| Application | Insulation panels, roofing, walls | Fire-rated panels, insulation, cladding |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Phenolic Foam
Polyurethane foam, known for its excellent thermal insulation and high compressive strength, is widely used in building panels to enhance energy efficiency and structural durability. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke emissions, making it ideal for applications with stringent fire safety requirements. Comparing the two, polyurethane foam provides better moisture resistance, while phenolic foam excels in chemical stability and thermal performance under high temperatures.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Polyurethane foam consists of polyols and isocyanates reacting through a controlled chemical process forming a cellular structure with excellent thermal insulation properties. Phenolic foam is produced by the interaction of phenol and formaldehyde resins in a condensation polymerization reaction, resulting in rigid foam with high fire resistance and low smoke emission. Manufacturing polyurethane foam involves mixing liquid components and curing under precise temperature and pressure, while phenolic foam production requires acid catalysis and controlled foaming with subsequent thermal curing to achieve structural stability.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation with a low thermal conductivity typically around 0.022-0.025 W/m*K, making it highly efficient for reducing heat transfer in building panels. Phenolic foam also provides excellent thermal resistance, with thermal conductivity values approximately 0.020-0.026 W/m*K, alongside enhanced fire retardant properties that increase panel safety. Both foams are effective insulators, but phenolic foam generally performs better in high-temperature scenarios while polyurethane foam excels in moisture resistance and structural flexibility.
Fire Resistance and Safety Performance
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polyurethane foam, with a low flame spread index and minimal smoke production, making it highly suitable for building panel safety standards. Polyurethane foam, while providing effective thermal insulation, tends to exhibit higher flammability and releases more toxic fumes during combustion. Building panels incorporating phenolic foam enhance fire safety performance by reducing fire propagation risks and improving occupant protection.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior mechanical strength, providing excellent compressive and tensile resistance ideal for load-bearing building panels. Phenolic foam offers exceptional fire resistance and dimensional stability, maintaining durability under extreme thermal conditions. Both materials deliver valuable performance, but polyurethane foam generally ensures enhanced long-term structural integrity in building applications.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane foam exhibits excellent moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, making it highly effective in preventing water absorption and mold growth in building panels. Phenolic foam provides superior chemical resistance, especially against acids, bases, and solvents, ensuring long-term durability in harsh industrial environments. Both foams offer valuable properties, but polyurethane foam is preferred for moisture control, while phenolic foam excels in chemical stability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam and phenolic foam both serve as insulation materials in building panels, with distinct environmental impacts and sustainability profiles. Polyurethane foam typically has higher global warming potential (GWP) due to its reliance on hydrofluorocarbon (HFC) blowing agents, whereas phenolic foam often uses low-GWP blowing agents and exhibits superior fire resistance and smoke emission characteristics. Phenolic foam's inherent biodegradability and lower toxicity during production and disposal further enhance its sustainability credentials compared to conventional polyurethane foam.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polyurethane foam generally offers lower initial costs compared to phenolic foam, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious building projects. Phenolic foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior fire resistance and thermal performance, which can lead to long-term savings through reduced energy consumption and insurance premiums. Economic considerations often balance immediate expenditure against lifecycle benefits, where phenolic foam's durability and efficiency may justify higher costs in large-scale or high-risk construction.
Building Codes and Certification Compliance
Polyurethane foam and phenolic foam differ significantly in building codes and certification compliance for building panels, with phenolic foam offering superior fire resistance classified under ASTM E84 Class A standards, often required by stringent fire safety regulations. Polyurethane foam panels typically meet industry standards such as ASTM E84 Class B but may require additional fire retardants to comply with local building codes focused on flame spread and smoke development criteria. Both materials commonly hold certifications like ISO 9001 and UL listings, though phenolic foam's enhanced thermal stability and lower smoke emissions make it preferable in regions enforcing higher safety certifications like NFPA 285 or Euroclass B-s1,d0.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type in Building Panels
Polyurethane foam excels in building panels requiring superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance, making it ideal for walls, roofs, and cold storage facilities. Phenolic foam offers exceptional fire resistance and low smoke emission, making it the preferred choice for commercial buildings and passive fire protection systems. Selecting the appropriate foam type depends on the balance between thermal performance and fire safety requirements for the specific building application.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Phenolic foam for Building Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com