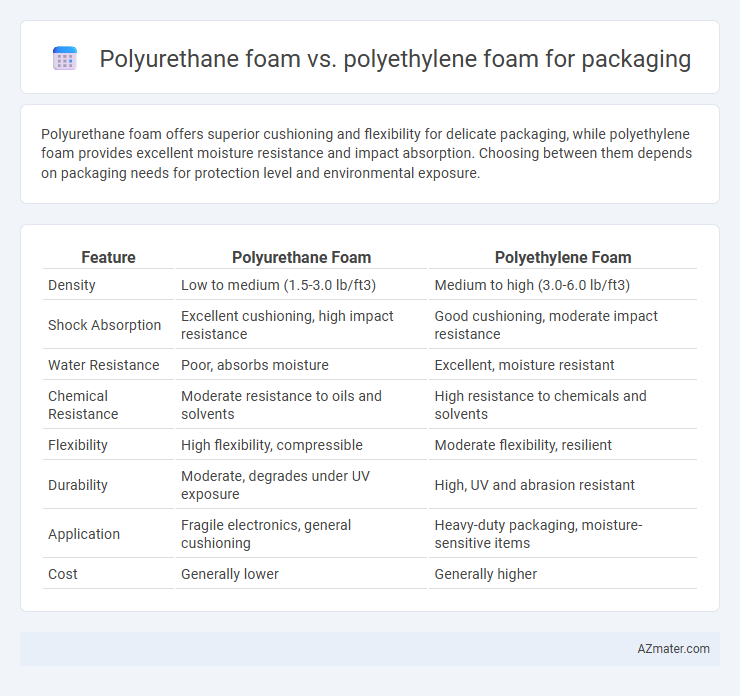
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and flexibility for delicate packaging, while polyethylene foam provides excellent moisture resistance and impact absorption. Choosing between them depends on packaging needs for protection level and environmental exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Low to medium (1.5-3.0 lb/ft3) | Medium to high (3.0-6.0 lb/ft3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning, high impact resistance | Good cushioning, moderate impact resistance |
| Water Resistance | Poor, absorbs moisture | Excellent, moisture resistant |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate resistance to oils and solvents | High resistance to chemicals and solvents |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, compressible | Moderate flexibility, resilient |
| Durability | Moderate, degrades under UV exposure | High, UV and abrasion resistant |
| Application | Fragile electronics, general cushioning | Heavy-duty packaging, moisture-sensitive items |
| Cost | Generally lower | Generally higher |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Materials
Polyurethane foam and polyethylene foam are widely used in packaging due to their distinct properties and protective capabilities. Polyurethane foam offers excellent cushioning, resilience, and versatility for fragile items, while polyethylene foam provides superior moisture resistance, lightweight durability, and impact absorption. Selecting the appropriate foam depends on the specific packaging requirements, such as product fragility, environmental exposure, and transportation conditions.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile polymer material widely used in packaging for its excellent cushioning and impact absorption properties. It consists of a network of flexible, open or closed cells that provide superior protection for delicate items during shipping and storage. Its high resilience and ability to conform to different shapes make polyurethane foam ideal for safeguarding electronics, fragile components, and heavy-duty products.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a lightweight, closed-cell foam commonly used in packaging for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties. It provides moisture resistance, chemical resistance, and durability, making it ideal for protecting sensitive electronics, medical devices, and fragile items during shipping. Unlike polyurethane foam, polyethylene foam offers better water resistance and is less prone to tearing, ensuring enhanced protection against environmental factors.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and elasticity with a density range of 1.8 to 2.5 lb/ft3, making it ideal for shock absorption in delicate packaging applications. Polyethylene foam, with densities from 1.5 to 3 lb/ft3, excels in chemical resistance and moisture barrier properties, providing enhanced protection against environmental factors. The compressive strength of polyurethane foam typically measures around 1-3 psi, whereas polyethylene foam exhibits higher resilience with compressive strength values up to 5 psi, benefiting heavy-duty packaging needs.
Cushioning Performance and Shock Absorption
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning performance and excellent shock absorption due to its open-cell structure, making it ideal for protecting delicate and heavy items during transit. Polyethylene foam features a closed-cell structure that provides moderate cushioning with high resilience and water resistance, suitable for packaging lighter, moisture-sensitive products. When comparing shock absorption, polyurethane foam can dissipate impact energy more effectively, whereas polyethylene foam excels in durability and resistance to compression set over repeated impacts.
Durability and Longevity in Packaging
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and excellent resistance to compression, making it ideal for protecting heavy or delicate items over long-term shipping and storage. Polyethylene foam provides high impact resistance and excellent moisture resistance, extending the longevity of packaging in environments prone to humidity and physical stress. For extended shelf life and repeated handling, polyethylene foam typically outlasts polyurethane foam due to its closed-cell structure and chemical stability.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Polyurethane foam offers moderate moisture resistance but can absorb water over time, making it less ideal for high-humidity environments compared to polyethylene foam, which is highly resistant to moisture due to its closed-cell structure. Chemically, polyurethane foam is more vulnerable to degradation from solvents and oils, whereas polyethylene foam exhibits superior chemical resistance, providing better protection against a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents used in packaging applications. Choosing polyethylene foam enhances durability and reliability in packaging scenarios requiring strong moisture and chemical resistance.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Polyurethane foam exhibits limited recyclability and produces toxic byproducts during degradation, posing significant environmental concerns compared to polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam, often made from recyclable high-density polyethylene (HDPE), offers better environmental profiles through easier recycling processes and reduced chemical emissions. The lower ecological footprint of polyethylene foam positions it as a more sustainable packaging material in terms of end-of-life management and resource recovery.
Cost Analysis of Polyurethane vs Polyethylene Foam
Polyurethane foam generally costs more than polyethylene foam due to its complex manufacturing process and superior cushioning properties. Polyethylene foam offers a cost-effective solution with lower production and material expenses, making it ideal for large-scale packaging applications requiring basic protection. Analyzing lifecycle costs, polyurethane foam may provide better value for delicate or high-value items, despite its higher upfront price.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and excellent resistance to impact, making it ideal for packaging fragile or high-value items. Polyethylene foam provides lightweight, flexible protection with excellent moisture and chemical resistance, suitable for shipping electronics or packaging with exposure to damp conditions. Selecting the right foam depends on considering factors such as product fragility, environmental exposure, and shipping logistics to ensure optimal protection and cost-effectiveness.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com