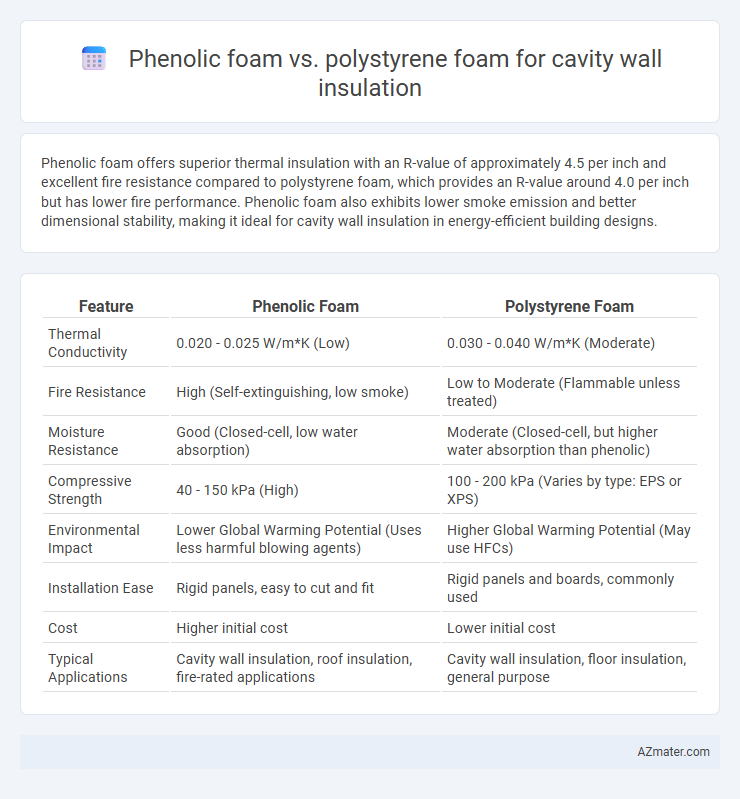
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value of approximately 4.5 per inch and excellent fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam, which provides an R-value around 4.0 per inch but has lower fire performance. Phenolic foam also exhibits lower smoke emission and better dimensional stability, making it ideal for cavity wall insulation in energy-efficient building designs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Phenolic Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.020 - 0.025 W/m*K (Low) | 0.030 - 0.040 W/m*K (Moderate) |
| Fire Resistance | High (Self-extinguishing, low smoke) | Low to Moderate (Flammable unless treated) |
| Moisture Resistance | Good (Closed-cell, low water absorption) | Moderate (Closed-cell, but higher water absorption than phenolic) |
| Compressive Strength | 40 - 150 kPa (High) | 100 - 200 kPa (Varies by type: EPS or XPS) |
| Environmental Impact | Lower Global Warming Potential (Uses less harmful blowing agents) | Higher Global Warming Potential (May use HFCs) |
| Installation Ease | Rigid panels, easy to cut and fit | Rigid panels and boards, commonly used |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Typical Applications | Cavity wall insulation, roof insulation, fire-rated applications | Cavity wall insulation, floor insulation, general purpose |
Introduction to Cavity Wall Insulation
Cavity wall insulation improves thermal efficiency by filling the gap between inner and outer walls, reducing heat loss and enhancing energy savings. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance, low thermal conductivity (around 0.021 W/mK), and moisture resistance, making it highly effective for cavity wall applications. Polystyrene foam, including expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) types, provides good insulation with thermal conductivity typically between 0.030 to 0.040 W/mK but has lower fire resistance compared to phenolic foam.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material known for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal conductivity, making it ideal for cavity wall insulation. Its closed-cell structure provides outstanding moisture resistance and long-term dimensional stability compared to polystyrene foam. Phenolic foam's exceptional thermal efficiency and fire-retardant properties often result in enhanced energy savings and increased safety for residential and commercial buildings.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in cavity wall insulation, offers excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 4.0 to 5.0 per inch. It is lightweight, moisture-resistant, and provides effective air barrier properties, making it suitable for reducing heat loss in building envelopes. Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) and Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) are the two main types, with XPS providing higher compressive strength and better moisture resistance.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Phenolic foam exhibits a lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.020-0.023 W/m*K, providing superior insulation performance compared to polystyrene foam, which ranges from 0.030-0.040 W/m*K. This enhanced thermal efficiency makes phenolic foam more effective in reducing heat loss and improving energy savings in cavity wall insulation applications. Polystyrene foam, while more cost-effective, generally requires greater thickness to match the thermal resistance offered by phenolic foam.
Fire Resistance and Safety
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam, with a higher ignition temperature and self-extinguishing properties that prevent flame spread in cavity wall insulation. Polystyrene foam tends to melt and emit toxic fumes when exposed to fire, posing greater safety hazards in building applications. Building regulations often favor phenolic foam for enhanced fire safety performance in cavity wall insulation systems.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Phenolic foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polystyrene foam, making it less prone to water absorption and mold growth in cavity wall insulation applications. Phenolic foam also offers higher durability due to its rigid cellular structure, which maintains thermal performance over time even in humid environments. Polystyrene foam, while cost-effective, tends to degrade faster when exposed to moisture, reducing its insulating lifespan.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Phenolic foam exhibits superior environmental performance due to its low Global Warming Potential (GWP) blowing agents and high thermal efficiency, reducing energy consumption in buildings. Polystyrene foam, while widely used, often involves higher carbon emissions during production and poses recycling challenges due to limited biodegradability and chemical additives. Sustainable cavity wall insulation increasingly favors phenolic foam for its long lifespan, reduced environmental footprint, and contribution to improved building energy ratings.
Installation Process and Practicality
Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal performance, making it easier to install in tight cavity walls due to its rigidity and lightweight nature, which reduces cutting and fitting time. Polystyrene foam, particularly expanded polystyrene (EPS), is less rigid and may require extra support or adhesives to remain in place, potentially complicating installation in irregular cavities. Both materials provide good insulation but phenolic foam's moisture resistance and smaller panel sizes enhance practicality for precise cavity wall applications.
Cost Effectiveness Analysis
Phenolic foam generally offers superior thermal insulation performance with a higher R-value per inch compared to polystyrene foam, leading to better energy savings over time despite its higher upfront cost. Polystyrene foam, particularly expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded polystyrene (XPS), is more cost-effective initially due to lower material and installation expenses but may have reduced long-term savings from lower insulation efficiency. A thorough cost-effectiveness analysis should consider both initial investment and lifecycle energy savings to determine the optimal choice for cavity wall insulation projects.
Choosing the Right Insulation for Your Project
Phenolic foam offers superior thermal performance with low thermal conductivity around 0.020 W/mK, making it highly effective for cavity wall insulation compared to polystyrene foam, which typically has a conductivity of 0.030-0.040 W/mK. Phenolic foam also provides better fire resistance and less air permeability, enhancing building safety and energy efficiency. Polystyrene foam remains a cost-effective option with good moisture resistance but may require additional fire protection measures depending on local building codes.
Infographic: Phenolic foam vs Polystyrene foam for Cavity wall insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com