Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high durability and water resistance, making it ideal for mattresses in humid environments. Memory foam provides superior pressure relief and contouring comfort, enhancing sleep quality through body heat and weight responsiveness.
Table of Comparison
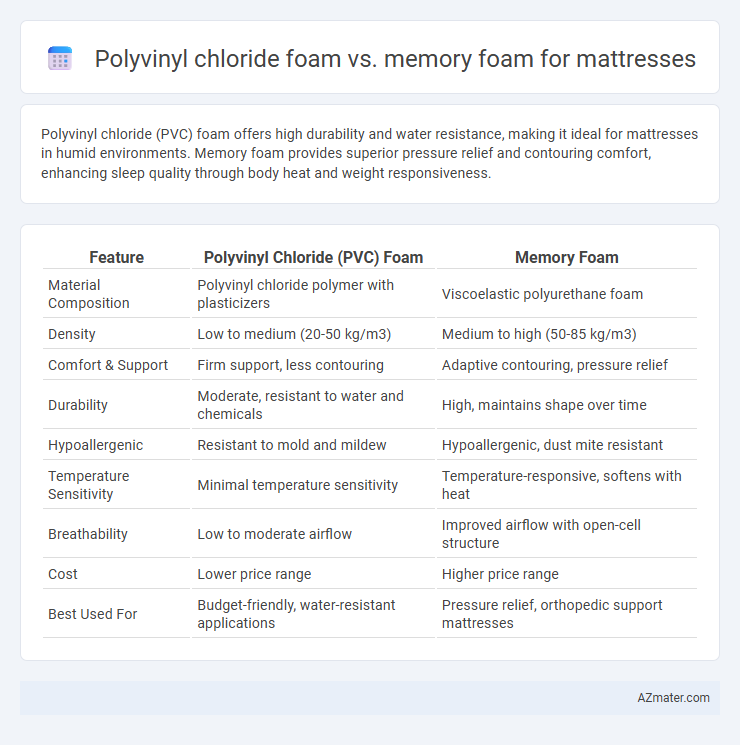
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Memory Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyvinyl chloride polymer with plasticizers | Viscoelastic polyurethane foam |
| Density | Low to medium (20-50 kg/m3) | Medium to high (50-85 kg/m3) |
| Comfort & Support | Firm support, less contouring | Adaptive contouring, pressure relief |
| Durability | Moderate, resistant to water and chemicals | High, maintains shape over time |
| Hypoallergenic | Resistant to mold and mildew | Hypoallergenic, dust mite resistant |
| Temperature Sensitivity | Minimal temperature sensitivity | Temperature-responsive, softens with heat |
| Breathability | Low to moderate airflow | Improved airflow with open-cell structure |
| Cost | Lower price range | Higher price range |
| Best Used For | Budget-friendly, water-resistant applications | Pressure relief, orthopedic support mattresses |
Introduction to Polyvinyl Chloride Foam and Memory Foam
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a durable, lightweight material known for its resistance to moisture, chemicals, and wear, making it suitable for mattress support layers that require firmness and longevity. Memory foam, composed of viscoelastic polyurethane, is recognized for its contouring ability and pressure relief, responding to body heat and weight to offer customized comfort. Choosing between PVC foam and memory foam depends on desired mattress properties such as support, durability, and pressure distribution.
Composition and Material Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a synthetic material made from polymerized vinyl chloride, characterized by its closed-cell structure, durability, and resistance to moisture and chemicals, making it denser and firmer than memory foam. Memory foam, composed primarily of polyurethane with added viscoelastic compounds, responds to heat and pressure by conforming to body shape, providing superior comfort and pressure relief due to its open-cell structure. The fundamental difference lies in PVC foam's rigid, resilient nature for support and longevity versus memory foam's adaptive, contouring properties designed for enhanced cushioning and ergonomic support.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers firm support and durability but lacks the adaptive contouring that memory foam provides, making it less effective for pressure relief and body alignment. Memory foam excels in comfort by responding to body heat and weight, evenly distributing pressure, and reducing motion transfer, which enhances spinal support and sleep quality. While PVC foam is resistant to moisture and suitable for budget-conscious buyers, memory foam's superior cushioning and ergonomic benefits make it the preferred choice for long-term comfort and support in mattresses.
Durability and Longevity
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses exhibit superior durability due to their resistance to wear, moisture, and chemicals, making them ideal for long-term use in various environments. Memory foam mattresses, while renowned for comfort and pressure relief, tend to degrade faster under constant stress and heat, leading to reduced longevity compared to PVC foam. The structural integrity of PVC foam combined with its resilience to external factors significantly enhances mattress lifespan over memory foam alternatives.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattress offers limited breathability due to its dense cell structure, often trapping heat and moisture, which can lead to discomfort during sleep. Memory foam mattresses feature an open-cell design with enhanced airflow channels that improve breathability and temperature regulation by dissipating body heat more effectively. Advanced memory foam models incorporate gel infusions or phase-change materials to further optimize cooling, making them superior to PVC foam in maintaining a comfortable sleep environment.
Health and Safety Considerations
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and contain chemical additives like phthalates, raising concerns about indoor air quality and potential respiratory irritation. Memory foam mattresses are generally made from polyurethane and can off-gas compounds such as benzene and formaldehyde, which may affect sensitive individuals, though CertiPUR-US certified options ensure reduced chemical emissions. Both materials require careful selection to minimize exposure to harmful substances, with memory foam often favored for hypoallergenic properties and superior breathability contributing to healthier sleep environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses pose significant environmental concerns due to their production process involving toxic chemicals and limited recyclability, contributing to long-lasting landfill waste and potential release of harmful dioxins. In contrast, memory foam mattresses, primarily made from polyurethane, have a lower environmental footprint when produced with bio-based or plant-derived materials, though traditional formulations still rely on petroleum-based components and can off-gas volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Sustainable memory foam options featuring CertiPUR-US certification and biodegradable additives offer improved eco-friendliness, whereas PVC foam lacks widely recognized sustainability certifications and remains problematic for green consumers.
Cost and Value Analysis
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam mattresses offer a significantly lower upfront cost compared to memory foam, making them an economical choice for budget-conscious consumers. While PVC foam provides basic support and durability, memory foam excels in pressure relief and contouring to the body, delivering superior comfort and long-term value despite its higher price point. Evaluating cost-effectiveness involves balancing initial investment against longevity and sleep quality, where memory foam generally provides better return on investment due to enhanced durability and comfort benefits.
Best Applications and Use Cases
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam excels in outdoor and high-moisture environments due to its water resistance, durability, and ease of cleaning, making it ideal for camping pads, gym mats, and marine cushions. Memory foam offers superior comfort and pressure relief, making it the best choice for mattresses aimed at reducing joint pain and improving sleep quality in residential and healthcare settings. Each foam type's unique properties align with distinct applications, with PVC foam suited for rugged, moisture-prone use and memory foam tailored for ergonomic support and comfort.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Mattress
Polyvinyl chloride foam offers durability, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it ideal for budget-friendly mattresses and moisture-prone environments. Memory foam excels in pressure relief, body contouring, and motion isolation, providing superior comfort for individuals with joint pain or sleep disturbances. Selecting the right foam depends on personal preferences for support, comfort, budget, and specific health needs.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Memory foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com