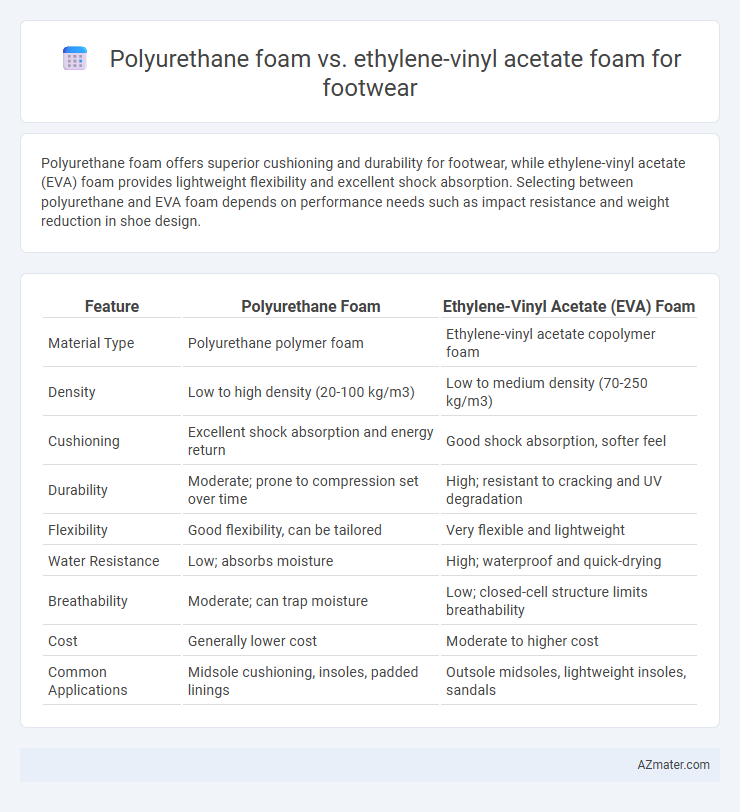
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and durability for footwear, while ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides lightweight flexibility and excellent shock absorption. Selecting between polyurethane and EVA foam depends on performance needs such as impact resistance and weight reduction in shoe design.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Polyurethane polymer foam | Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer foam |
| Density | Low to high density (20-100 kg/m3) | Low to medium density (70-250 kg/m3) |
| Cushioning | Excellent shock absorption and energy return | Good shock absorption, softer feel |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to compression set over time | High; resistant to cracking and UV degradation |
| Flexibility | Good flexibility, can be tailored | Very flexible and lightweight |
| Water Resistance | Low; absorbs moisture | High; waterproof and quick-drying |
| Breathability | Moderate; can trap moisture | Low; closed-cell structure limits breathability |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Moderate to higher cost |
| Common Applications | Midsole cushioning, insoles, padded linings | Outsole midsoles, lightweight insoles, sandals |
Introduction to PU Foam and EVA Foam in Footwear
Polyurethane (PU) foam and Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam are widely utilized materials in footwear manufacturing due to their unique cushioning properties and durability. PU foam offers high resilience, excellent energy absorption, and superior wear resistance, making it ideal for midsoles and insoles in performance and casual shoes. EVA foam is lightweight, flexible, and provides good shock absorption and compression resistance, commonly used in midsoles and outsole components for enhanced comfort and shock protection.
Composition and Material Properties
Polyurethane foam, composed of flexible polymers formed by the reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, offers excellent cushioning, durability, and abrasion resistance in footwear applications. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam consists of a copolymer of ethylene and vinyl acetate, providing lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties ideal for midsoles and insoles. The higher resilience and compression set resistance of polyurethane foam contrast with EVA's superior moisture resistance and ease of molding, influencing their specific uses in shoe manufacturing.
Comfort and Cushioning Performance
Polyurethane foam offers superior durability and high-density cushioning, providing excellent shock absorption and long-lasting comfort in footwear applications. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam delivers lightweight flexibility and enhanced softness, ideal for responsive cushioning and reduced foot fatigue during prolonged wear. The choice between polyurethane and EVA foam largely depends on the desired balance between resilience and lightweight comfort for specific footwear designs.
Durability and Longevity
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam in footwear applications due to its higher resistance to compression set and abrasion. EVA foam offers excellent cushioning and flexibility but tends to break down faster under prolonged stress and environmental exposure. Footwear designed for high-impact or long-term use primarily benefits from polyurethane foam's robust structural integrity and extended lifespan.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning with moderate weight, making it slightly heavier but more durable than ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which is lighter and enhances overall footwear flexibility. EVA foam provides excellent shock absorption and flexibility, ideal for lightweight shoes that require high mobility and comfort. The choice between polyurethane and EVA foam depends on balancing the need for durability versus lightweight performance and flexibility in footwear applications.
Shock Absorption Capabilities
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior shock absorption capabilities due to its high resilience and ability to compress and rebound quickly under pressure, making it ideal for footwear requiring sustained cushioning and impact resistance. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight flexibility with moderate shock absorption, often preferred in casual or athletic shoes where comfort and shock attenuation are balanced. The denser cellular structure of polyurethane foam provides enhanced energy return and durability compared to EVA, which tends to compress more over time.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Polyurethane foam offers superior breathability and moisture-wicking properties in footwear, enhancing comfort by allowing air circulation and quickly dispersing sweat. Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam, while lightweight and durable, tends to retain moisture due to its closed-cell structure, which can reduce breathability. Selecting polyurethane foam is ideal for applications requiring efficient moisture management and ventilation to prevent odor and skin irritation.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
Polyurethane foam in footwear offers excellent cushioning but poses environmental challenges due to its reliance on petroleum-based chemicals and difficulty in recycling, leading to significant landfill waste and greenhouse gas emissions. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is often considered more sustainable because it contains fewer toxic compounds and is more easily recyclable, though its production still depends on non-renewable fossil fuels and generates volatile organic compounds. Innovations in bio-based and recycled EVA aim to reduce its carbon footprint, making it a progressively eco-friendlier option compared to traditional polyurethane foams.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Polyurethane foam offers a high durability-to-cost ratio, making it a cost-effective choice for mass-produced footwear, while Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is generally more expensive due to its specialized processing requirements. Manufacturing polyurethane foam involves simpler chemical reactions and faster curing times, reducing production costs and improving scalability in footwear applications. EVA foam requires precise temperature controls and longer curing periods, increasing manufacturing complexity and overall expenses in shoe production.
Application Suitability in Different Footwear Types
Polyurethane foam offers high durability and excellent cushioning, making it ideal for athletic and casual footwear requiring long-lasting comfort and impact absorption. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides lightweight flexibility and superior shock absorption, suited for running shoes and lightweight sandals where flexibility and responsiveness are crucial. EVA's resistance to cracking in cold conditions also makes it favorable for casual and outdoor shoes exposed to varying weather.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Footwear
 azmater.com
azmater.com