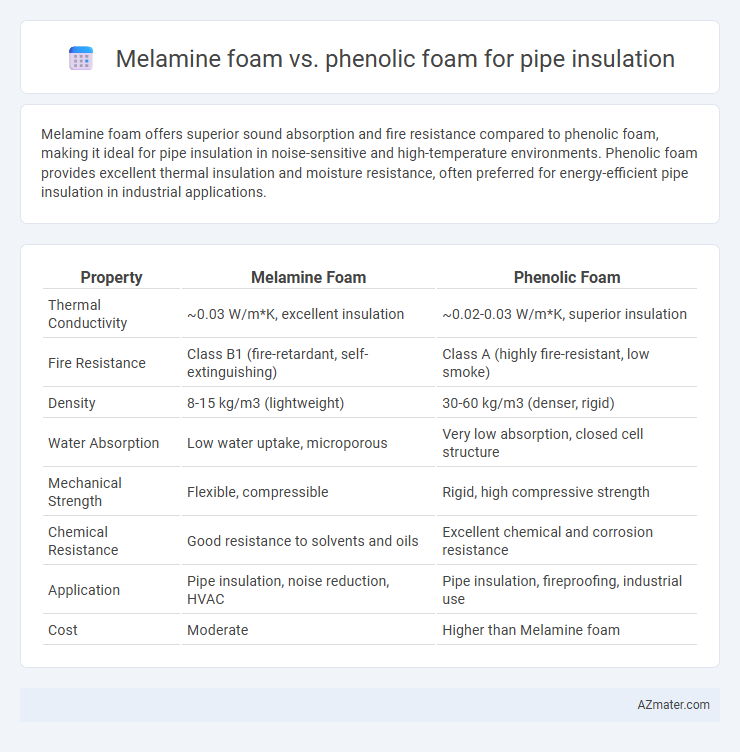
Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption and fire resistance compared to phenolic foam, making it ideal for pipe insulation in noise-sensitive and high-temperature environments. Phenolic foam provides excellent thermal insulation and moisture resistance, often preferred for energy-efficient pipe insulation in industrial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Melamine Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | ~0.03 W/m*K, excellent insulation | ~0.02-0.03 W/m*K, superior insulation |
| Fire Resistance | Class B1 (fire-retardant, self-extinguishing) | Class A (highly fire-resistant, low smoke) |
| Density | 8-15 kg/m3 (lightweight) | 30-60 kg/m3 (denser, rigid) |
| Water Absorption | Low water uptake, microporous | Very low absorption, closed cell structure |
| Mechanical Strength | Flexible, compressible | Rigid, high compressive strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to solvents and oils | Excellent chemical and corrosion resistance |
| Application | Pipe insulation, noise reduction, HVAC | Pipe insulation, fireproofing, industrial use |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher than Melamine foam |
Introduction to Pipe Insulation Materials
Melamine foam and phenolic foam are popular materials used for pipe insulation due to their thermal resistance and fire-retardant properties. Melamine foam offers excellent sound absorption and is lightweight with a high melting point, making it suitable for environments requiring acoustic control and thermal insulation. Phenolic foam provides superior thermal insulation with low smoke emissions and high fire resistance, commonly applied in industrial and commercial piping systems to enhance energy efficiency and safety.
Overview of Melamine Foam
Melamine foam is a lightweight, flexible material known for its excellent thermal insulation, sound absorption, and fire resistance, making it ideal for pipe insulation applications. Its open-cell structure provides superior acoustic attenuation and moisture resistance compared to phenolic foam, enhancing durability in various environments. Melamine foam also offers chemical stability and low smoke emission, contributing to safer and more efficient thermal management in piping systems.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a rigid, closed-cell insulation material known for its excellent thermal performance and fire resistance, making it ideal for pipe insulation in commercial and industrial applications. It offers low smoke emission and high dimensional stability under heat exposure, enhancing safety and durability compared to other foams like melamine. Phenolic foam's inherent resistance to moisture and chemicals further extends its lifespan, providing effective insulation in harsh environments.
Thermal Insulation Properties Comparison
Melamine foam offers low thermal conductivity around 0.033 W/m*K, providing effective insulation at temperatures up to 150degC, making it suitable for moderate thermal barriers in pipe insulation. Phenolic foam demonstrates superior thermal resistance with conductivity values near 0.020 W/m*K and excellent performance at higher temperatures reaching 180degC, ensuring better energy efficiency and fire resistance in industrial piping. The choice between melamine and phenolic foam depends on the required operating temperature and insulation thickness, with phenolic foam preferred for more demanding thermal insulation applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Melamine foam offers superior fire resistance with a high limiting oxygen index (LOI) above 32%, making it self-extinguishing and resistant to flames, which enhances safety in pipe insulation applications. Phenolic foam also provides excellent fire-resistant properties due to its char-forming nature and low smoke emissions, securing a Class 1 fire rating under ASTM E84 standards. Both materials ensure enhanced safety, but melamine foam's low smoke toxicity and flame-retardant characteristics make it especially suitable for environments where fire safety and occupant health are critical.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to melamine foam, making it more suitable for humid or wet pipe insulation environments. Melamine foam, while effective for thermal insulation, tends to absorb more moisture, which can compromise its insulating properties over time. Phenolic foam also exhibits enhanced chemical resistance, providing better durability against exposure to harsh chemicals and solvents commonly encountered in industrial pipe insulation.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Melamine foam provides moderate mechanical strength but excels in fire resistance and flexibility, making it suitable for applications requiring lightweight insulation with basic durability. Phenolic foam offers superior mechanical strength and higher compressive resistance, ensuring long-term durability and structural integrity under mechanical stress in pipe insulation. The enhanced thermal stability of phenolic foam further contributes to its prolonged performance in demanding industrial environments.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Melamine foam offers superior flexibility and ease of installation compared to phenolic foam, allowing it to conform smoothly to irregular pipe shapes and reducing the need for additional cutting or tools. Its lightweight and compressible nature enable faster application with minimal labor, while phenolic foam, being more rigid, requires precise measurement and scoring, which can extend installation time. Melamine foam also provides better resilience against deformation during handling, making it an ideal choice for complex piping systems where quick and adaptable insulation is essential.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Melamine foam offers a lower initial purchase cost compared to phenolic foam, making it a budget-friendly option for pipe insulation projects with tight cost constraints. Phenolic foam, while more expensive upfront, provides superior thermal insulation and higher fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term energy expenses and maintenance costs. Evaluating total cost of ownership including durability, energy savings, and safety compliance is essential to determine the most economically viable material for specific insulation applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Melamine foam offers lower environmental impact due to its non-toxic, formaldehyde-free composition and greater recyclability compared to phenolic foam, which contains phenol and formaldehyde resins that raise concerns over emissions during manufacturing and disposal. Phenolic foam typically exhibits superior fire resistance and thermal stability but has a higher carbon footprint and limited recyclability, affecting long-term sustainability. Choosing melamine foam for pipe insulation supports eco-friendly building practices with reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and enhanced potential for circular waste management.
Infographic: Melamine foam vs Phenolic foam for Pipe insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com