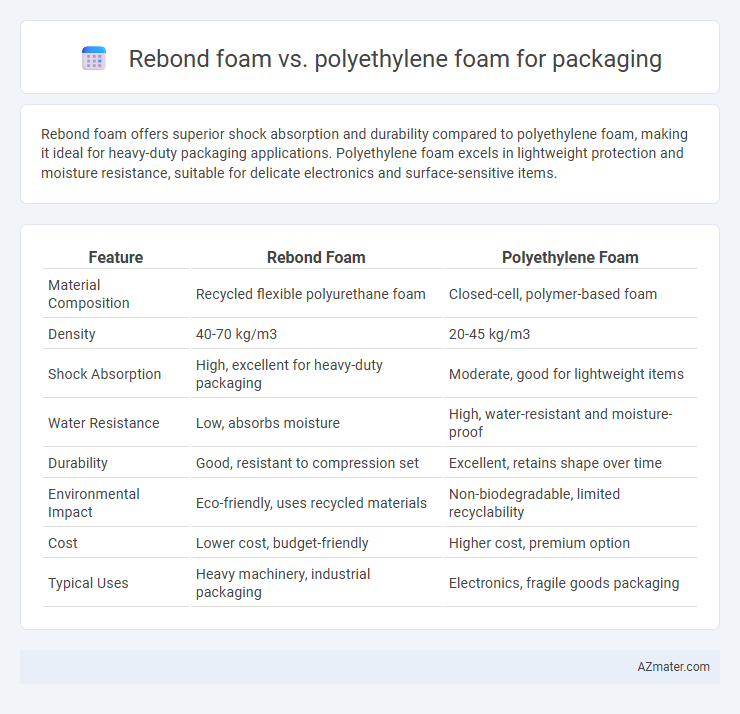
Rebond foam offers superior shock absorption and durability compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications. Polyethylene foam excels in lightweight protection and moisture resistance, suitable for delicate electronics and surface-sensitive items.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled flexible polyurethane foam | Closed-cell, polymer-based foam |
| Density | 40-70 kg/m3 | 20-45 kg/m3 |
| Shock Absorption | High, excellent for heavy-duty packaging | Moderate, good for lightweight items |
| Water Resistance | Low, absorbs moisture | High, water-resistant and moisture-proof |
| Durability | Good, resistant to compression set | Excellent, retains shape over time |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, uses recycled materials | Non-biodegradable, limited recyclability |
| Cost | Lower cost, budget-friendly | Higher cost, premium option |
| Typical Uses | Heavy machinery, industrial packaging | Electronics, fragile goods packaging |
Introduction to Packaging Foam Materials
Rebond foam, made from recycled polyurethane scraps, offers high durability and cushioning, ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications requiring impact resistance and longevity. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell material, provides lightweight, moisture-resistant protection with excellent shock absorption, suitable for delicate and moisture-sensitive items. Both materials enhance product safety during transit, with rebond foam favored for heavy impact scenarios and polyethylene foam preferred for lightweight, moisture-sensitive packaging needs.
What is Rebond Foam?
Rebond foam is a durable cushioning material made by shredding and bonding scrap polyurethane foam pieces with adhesive under heat and pressure, creating a dense and resilient final product. It offers excellent impact absorption, making it ideal for protective packaging applications requiring high durability and shock resistance. Compared to polyethylene foam, rebond foam provides superior compression strength and long-term resilience, especially for heavy or delicate items.
What is Polyethylene Foam?
Polyethylene foam is a closed-cell, durable material widely used in packaging for its excellent shock absorption and moisture resistance properties. Its lightweight structure provides cushioning that protects fragile items from impact and vibration during shipping and storage. Compared to rebond foam, polyethylene foam offers superior water resistance and chemical stability, making it ideal for protecting sensitive products in diverse environments.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Rebond foam exhibits higher density and superior compression resistance compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for heavy-duty protective packaging. Polyethylene foam offers excellent flexibility, moisture resistance, and impact absorption with a lower density, suitable for lightweight, cushioning applications. Both materials differ significantly in tensile strength and resilience, impacting their effectiveness based on the packaging requirements.
Shock Absorption and Cushioning Capabilities
Rebond foam, made from shredded polyurethane foam bonded together, offers superior shock absorption due to its high density and resilience, making it ideal for heavy or delicate items requiring enhanced cushioning. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning with its closed-cell structure that resists compression and moisture, but generally delivers less shock absorption compared to rebond foam. For packaging applications demanding maximum impact protection, rebond foam's energy-dissipating properties outperform the lighter, more flexible polyethylene foam.
Durability and Longevity
Rebond foam exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to polyethylene foam due to its dense composition and resilience under repeated stress, making it ideal for heavy-duty protective packaging. Polyethylene foam offers good cushioning but tends to compress and degrade faster over time, especially under continuous impact or pressure. For packaging applications requiring long-term protection and resistance to wear, rebond foam provides a more robust and enduring solution.
Moisture and Chemical Resistance
Rebond foam exhibits moderate moisture resistance but is more susceptible to absorbing chemicals due to its recycled content, making it less ideal for packaging sensitive items exposed to harsh environments. Polyethylene foam offers superior moisture resistance and excellent chemical resistance, preventing water absorption and degradation from solvents or acids during transportation and storage. Choosing polyethylene foam enhances protection for products requiring durable, moisture-proof, and chemically stable packaging solutions.
Cost-Effectiveness for Packaging Solutions
Rebond foam offers superior cost-effectiveness for packaging solutions due to its recycled material composition, significantly reducing production expenses without compromising cushioning performance. Polyethylene foam, while providing excellent moisture resistance and durability, generally incurs higher costs because of its petroleum-based manufacturing process. Choosing rebond foam can lower overall packaging costs, especially for bulk shipments requiring sustainable and impact-absorbing materials.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Rebond foam, made from recycled foam scraps, offers a sustainable packaging solution by reducing landfill waste and lowering raw material consumption compared to polyethylene foam, which is typically derived from non-renewable petroleum resources. Polyethylene foam poses greater environmental challenges due to its low biodegradability and limited recycling facilities, whereas rebond foam's composition allows for easier reuse and repurposing in various applications. Both materials present durability benefits, but rebond foam's emphasis on recyclability and use of reclaimed materials positions it as the more eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Rebond foam offers high durability and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging that requires impact resistance and cushioning for delicate items. Polyethylene foam provides a lightweight, moisture-resistant solution with superior flexibility and surface protection, perfect for packaging electronic components and fragile goods. Selecting the right foam depends on factors like weight, fragility of the product, environmental conditions, and budget constraints to ensure optimal protection during transport and storage.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com