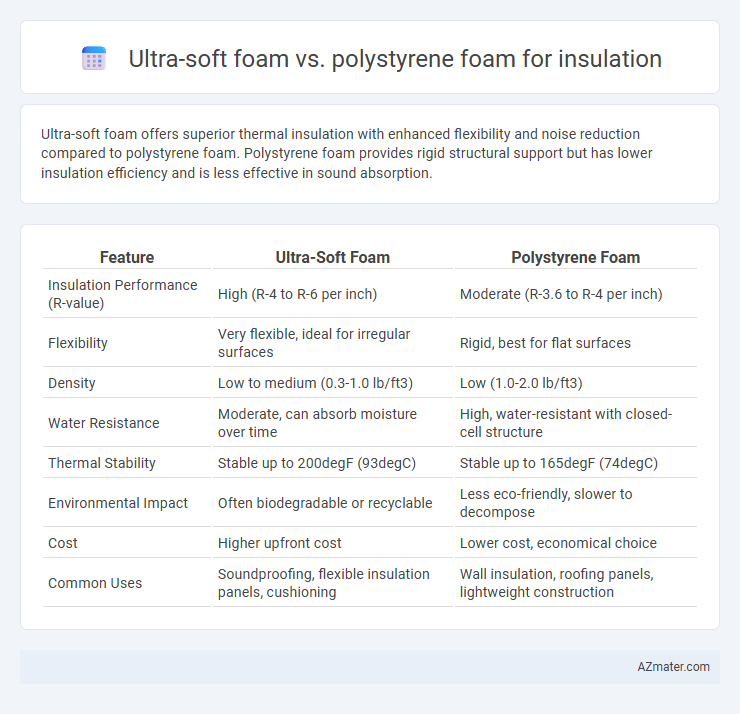
Ultra-soft foam offers superior thermal insulation with enhanced flexibility and noise reduction compared to polystyrene foam. Polystyrene foam provides rigid structural support but has lower insulation efficiency and is less effective in sound absorption.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ultra-Soft Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Insulation Performance (R-value) | High (R-4 to R-6 per inch) | Moderate (R-3.6 to R-4 per inch) |
| Flexibility | Very flexible, ideal for irregular surfaces | Rigid, best for flat surfaces |
| Density | Low to medium (0.3-1.0 lb/ft3) | Low (1.0-2.0 lb/ft3) |
| Water Resistance | Moderate, can absorb moisture over time | High, water-resistant with closed-cell structure |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 200degF (93degC) | Stable up to 165degF (74degC) |
| Environmental Impact | Often biodegradable or recyclable | Less eco-friendly, slower to decompose |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower cost, economical choice |
| Common Uses | Soundproofing, flexible insulation panels, cushioning | Wall insulation, roofing panels, lightweight construction |
Introduction to Foam Insulation Materials
Ultra-soft foam, characterized by its flexible cellular structure, offers superior thermal insulation and sound absorption compared to rigid polystyrene foam. Polystyrene foam, widely used for its high compressive strength and moisture resistance, provides excellent thermal insulation but lacks the same level of flexibility and acoustic benefits. Both materials are essential in building insulation, with ultra-soft foam ideal for areas requiring cushioning and noise reduction, while polystyrene foam excels in structural insulation and moisture-prone environments.
What is Ultra-Soft Foam?
Ultra-soft foam is a highly flexible and compressible insulation material characterized by its low density and superior thermal resistance properties, making it ideal for soundproofing and thermal insulation in residential and commercial buildings. Unlike polystyrene foam, which is rigid and brittle, ultra-soft foam adapts easily to irregular surfaces and provides exceptional cushioning, reducing energy loss through superior air sealing. Its closed-cell structure offers enhanced moisture resistance, preventing mold growth and improving indoor air quality compared to polystyrene foam.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam, a popular insulation material, offers excellent thermal resistance with an R-value typically ranging from 4 to 5 per inch, making it highly efficient for reducing heat transfer in buildings. This rigid foam is available in two forms: expanded polystyrene (EPS) and extruded polystyrene (XPS), with XPS providing superior moisture resistance and compressive strength. Its lightweight nature, affordability, and durability make polystyrene foam a preferred choice for walls, roofs, and foundations in energy-efficient construction projects.
Thermal Insulation Performance Comparison
Ultra-soft foam exhibits superior thermal insulation performance due to its lower thermal conductivity, typically around 0.02 W/m*K, which minimizes heat transfer effectively. Polystyrene foam, with a thermal conductivity ranging from 0.03 to 0.04 W/m*K, provides decent insulation but allows more heat flow compared to ultra-soft foam. The denser cell structure of ultra-soft foam enhances its insulating capabilities, making it a preferred choice for energy-efficient building applications.
Moisture Resistance: Which Foam Prevails?
Ultra-soft foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to polystyrene foam, effectively preventing water absorption and mold growth in insulation applications. Polystyrene foam, although widely used for its thermal properties, tends to absorb moisture under prolonged exposure, which can reduce its insulating efficiency and durability. The higher closed-cell structure density of ultra-soft foam ensures enhanced protection against moisture infiltration, making it the preferred choice for damp or humid environments.
Durability and Longevity Analysis
Ultra-soft foam insulation offers superior durability with enhanced resistance to compression and deformation, maintaining its insulating properties over extended periods. Polystyrene foam, while cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under environmental stressors such as moisture and UV exposure, leading to reduced longevity. The long-term performance of ultra-soft foam makes it a more reliable choice for insulation in demanding applications requiring sustained thermal efficiency.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Ultra-soft foam insulation typically offers improved environmental benefits compared to polystyrene foam due to its higher recyclability and lower carbon footprint during production. Polystyrene foam, while effective for thermal insulation, contributes significantly to plastic pollution and is less biodegradable, posing challenges for sustainable waste management. Choosing ultra-soft foam supports long-term sustainability goals by reducing environmental pollution and promoting energy efficiency throughout its lifecycle.
Cost-Effectiveness: Ultra-Soft vs. Polystyrene
Ultra-soft foam insulation offers higher initial costs but excels in long-term energy savings due to superior thermal resistance and air sealing properties. Polystyrene foam insulation is more budget-friendly upfront, providing effective moisture resistance and moderate insulating performance, making it suitable for cost-sensitive projects. Evaluating project scale and energy efficiency goals is crucial to determine if ultra-soft foam's enhanced durability and R-value justify the premium over polystyrene foam's affordability.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Ultra-soft foam excels in applications requiring sound absorption, cushioning, and thermal insulation in residential and commercial interiors, particularly in walls, ceilings, and flooring underlays due to its flexibility and compressibility. Polystyrene foam, available in expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) forms, is best suited for structural insulation, including exterior wall sheathing, foundation insulation, and roofing, where high compressive strength and moisture resistance are critical. Choosing between these foams depends on specific insulation needs: ultra-soft foam for acoustic and comfort-focused applications, and polystyrene foam for robust, moisture-resistant thermal barriers.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam Insulation
Ultra-soft foam offers superior flexibility and better air sealing properties, making it ideal for irregular spaces and enhancing overall energy efficiency, while polystyrene foam provides high compressive strength and excellent moisture resistance suited for foundation and below-grade insulation. Evaluating project-specific needs such as thermal performance, installation environment, and budget helps determine the optimal foam type. Selecting the appropriate foam insulation maximizes thermal comfort, energy savings, and long-term durability.
Infographic: Ultra-soft foam vs Polystyrene foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com