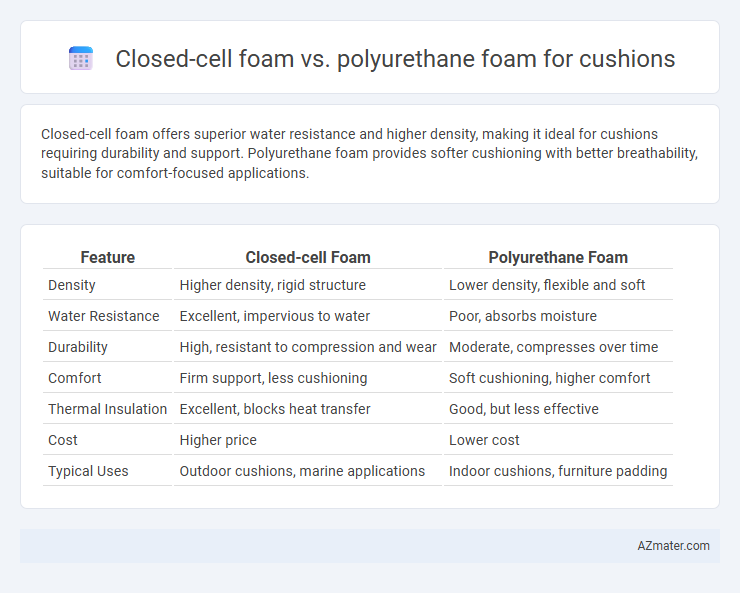
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and higher density, making it ideal for cushions requiring durability and support. Polyurethane foam provides softer cushioning with better breathability, suitable for comfort-focused applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-cell Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Higher density, rigid structure | Lower density, flexible and soft |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, impervious to water | Poor, absorbs moisture |
| Durability | High, resistant to compression and wear | Moderate, compresses over time |
| Comfort | Firm support, less cushioning | Soft cushioning, higher comfort |
| Thermal Insulation | Excellent, blocks heat transfer | Good, but less effective |
| Cost | Higher price | Lower cost |
| Typical Uses | Outdoor cushions, marine applications | Indoor cushions, furniture padding |
Introduction to Cushion Foams
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and structural rigidity, making it ideal for cushions requiring durability and moisture protection. Polyurethane foam provides excellent comfort and flexibility with a softer feel, suitable for general-purpose cushioning applications. Both foams enhance cushioning performance but differ significantly in density, breathability, and impact absorption properties.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a dense, rigid material composed of cells that are completely enclosed and packed tightly together, preventing water absorption and enhancing insulation properties. It offers superior durability, moisture resistance, and high compressive strength, making it ideal for cushions requiring firm support and long-term resilience. Compared to polyurethane foam, closed-cell foam provides better structural integrity and is more effective in outdoor or high-moisture environments.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile, open-cell or closed-cell polymer widely used in cushions due to its excellent durability, flexibility, and cushioning properties. It offers superior shock absorption and comfort by trapping air within its cellular structure, making it ideal for furniture and bedding applications. Its lightweight nature and resistance to moisture enhance longevity, distinguishing it from closed-cell foam, which is denser and less breathable.
Key Differences Between Closed-Cell and Polyurethane Foam
Closed-cell foam has a dense structure with cells that are fully enclosed, providing superior durability, moisture resistance, and firm support compared to polyurethane foam, which is open-celled and more flexible. Polyurethane foam offers better breathability and softness, making it ideal for cushioning applications requiring comfort and pressure relief. The primary differences lie in their density, water absorption properties, and resilience, with closed-cell foam favored for heavy-duty, moisture-prone environments and polyurethane foam preferred for comfort and lightweight cushioning.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Closed-cell foam provides firmer support with higher density, offering excellent durability and resistance to compression, ideal for maintaining shape and long-term comfort. Polyurethane foam is softer and more flexible, delivering superior cushioning and pressure relief but with less structural support over time. Selection depends on balancing comfort preferences with the need for consistent support and longevity in cushioning applications.
Durability and Lifespan of Cushion Foams
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and longer lifespan due to its dense structure that resists moisture, compression, and wear, making it ideal for cushions subjected to frequent use. Polyurethane foam, while softer and more flexible, tends to degrade faster over time from repeated compression and exposure to environmental factors. The robust cellular makeup of closed-cell foam ensures cushions maintain shape and support, whereas polyurethane foam cushions may require replacement more frequently due to faster breakdown and loss of resilience.
Water Resistance: Closed-Cell vs Polyurethane
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance due to its dense, impermeable structure that prevents water absorption, making it ideal for cushions exposed to moisture or outdoor environments. Polyurethane foam, being more porous, tends to absorb water, which can lead to reduced cushioning performance and faster degradation. For applications where water resistance is crucial, closed-cell foam cushions provide enhanced durability and longevity compared to polyurethane alternatives.
Applications in Cushioning Solutions
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and higher density, making it ideal for outdoor cushions and marine applications requiring durability and moisture protection. Polyurethane foam provides excellent softness and cushioning, commonly used in indoor furniture, mattresses, and ergonomic seating where comfort and pressure relief are priorities. Both materials serve distinct roles in cushioning solutions, with closed-cell foam emphasizing resilience and polyurethane foam enhancing comfort.
Cost Considerations for Each Foam Type
Closed-cell foam generally has a higher upfront cost compared to polyurethane foam due to its dense structure and superior durability. Polyurethane foam offers a more budget-friendly option with lower initial expenses but may incur higher replacement costs over time due to faster wear and tear. Evaluating long-term cost efficiency requires balancing the initial investment of closed-cell foam against the potential maintenance and replacement frequency of polyurethane foam.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Cushion Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and durability, making it ideal for outdoor cushions or high-moisture environments, while polyurethane foam provides greater softness and breathability, suited for indoor seating comfort. Choosing the right foam depends on factors like usage environment, desired firmness, and longevity; closed-cell foam excels in structural support and resilience, whereas polyurethane foam enhances cushioning and flexibility. Assessing these key attributes ensures selecting the optimal foam that balances comfort with durability for your specific cushion needs.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polyurethane foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com