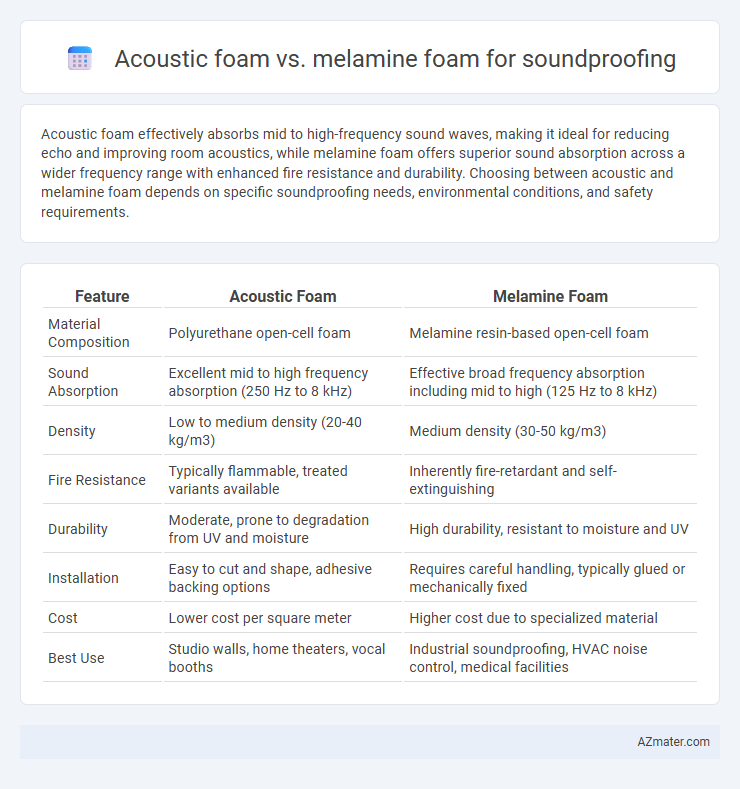
Acoustic foam effectively absorbs mid to high-frequency sound waves, making it ideal for reducing echo and improving room acoustics, while melamine foam offers superior sound absorption across a wider frequency range with enhanced fire resistance and durability. Choosing between acoustic and melamine foam depends on specific soundproofing needs, environmental conditions, and safety requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acoustic Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Polyurethane open-cell foam | Melamine resin-based open-cell foam |
| Sound Absorption | Excellent mid to high frequency absorption (250 Hz to 8 kHz) | Effective broad frequency absorption including mid to high (125 Hz to 8 kHz) |
| Density | Low to medium density (20-40 kg/m3) | Medium density (30-50 kg/m3) |
| Fire Resistance | Typically flammable, treated variants available | Inherently fire-retardant and self-extinguishing |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to degradation from UV and moisture | High durability, resistant to moisture and UV |
| Installation | Easy to cut and shape, adhesive backing options | Requires careful handling, typically glued or mechanically fixed |
| Cost | Lower cost per square meter | Higher cost due to specialized material |
| Best Use | Studio walls, home theaters, vocal booths | Industrial soundproofing, HVAC noise control, medical facilities |
Introduction to Acoustic and Melamine Foam
Acoustic foam is a porous, polyurethane material designed to absorb mid to high-frequency sound waves, reducing echo and reverberation in recording studios and home theaters. Melamine foam, composed of a melamine resin, features an open-cell structure that offers superior fire resistance along with effective sound absorption across a broader frequency range, especially in higher frequencies. Both materials enhance soundproofing by controlling noise reflections, but melamine foam's enhanced thermal and fire-retardant properties make it suitable for environments with stricter safety requirements.
Key Differences Between Acoustic and Melamine Foam
Acoustic foam and melamine foam differ primarily in material composition and sound absorption capabilities; acoustic foam is typically polyurethane-based, offering effective mid-to-high frequency absorption, while melamine foam, made from a thermoset resin, provides broader frequency absorption including lower frequencies. Melamine foam is more fire-resistant and water-repellent, making it suitable for environments requiring stringent safety standards compared to the generally combustible acoustic foam. Cost and durability also vary, with melamine foam being more expensive but longer-lasting and less prone to deformation over time, unlike acoustic foam which may degrade faster under frequent use.
Sound Absorption Performance Comparison
Acoustic foam typically offers superior sound absorption, especially in mid to high-frequency ranges, due to its open-cell polyurethane structure that effectively traps sound waves. Melamine foam, while lighter and more fire-resistant, provides moderate absorption but excels in higher frequencies and has a more rigid composition that can reflect lower frequencies. For optimal soundproofing, acoustic foam is generally preferred for absorbing a wider spectrum of frequencies, whereas melamine foam is suited for environments requiring lightweight, fire-retardant materials with focused acoustic treatment.
Durability and Lifespan
Acoustic foam typically offers greater durability and a longer lifespan compared to melamine foam due to its denser, open-cell polyurethane structure that resists compression and deformation over time. Melamine foam, while effective for sound absorption and fire resistance, tends to degrade faster under prolonged exposure to moisture and physical wear, reducing its overall longevity. For long-term soundproofing applications, acoustic foam provides a more resilient solution that maintains performance stability and structural integrity.
Fire Resistance and Safety Features
Acoustic foam typically features open-cell polyurethane, which is highly flammable and releases toxic fumes when burned, whereas melamine foam boasts superior fire resistance with a Class A (ASTM E84) rating, making it safer for soundproofing in fire-sensitive environments. Melamine foam's inherent self-extinguishing properties reduce the risk of fire spread, offering enhanced safety for residential and commercial applications. Choosing melamine foam significantly improves compliance with fire safety codes and minimizes hazardous smoke production compared to conventional acoustic foam.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Acoustic foam typically requires precise placement and adhesive application to ensure optimal sound absorption, while melamine foam can be easily cut and installed using staples or spray adhesives due to its lightweight, rigid structure. Maintenance for acoustic foam involves careful dusting and avoidance of moisture to prevent degradation, whereas melamine foam is more resistant to mold and moisture, making it easier to clean with a damp cloth. Both materials benefit from regular inspection to maintain effectiveness, but melamine foam's durability often results in lower long-term upkeep costs.
Cost Comparison and Budget Considerations
Acoustic foam typically costs between $20 to $50 per panel, making it a more affordable option for sound absorption compared to melamine foam, which ranges from $40 to $80 per panel due to its enhanced fire resistance and durability. Budget considerations favor acoustic foam for larger projects or DIY setups, while melamine foam suits environments requiring stricter safety standards despite higher expenses. Selecting between the two depends largely on the balance between cost efficiency and performance requirements in soundproofing applications.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Settings
Acoustic foam is widely used in residential studios and home theaters for its ability to absorb mid to high-frequency sound waves, enhancing speech clarity and reducing echo. Melamine foam, known for its lightweight structure and fire-resistant properties, is favored in commercial settings such as offices and recording studios for broad-spectrum sound absorption and compliance with strict fire safety standards. Both materials contribute to improved acoustic comfort, but melamine foam often serves well in environments requiring stringent fire codes and durability.
Eco-Friendliness and Material Composition
Acoustic foam is typically made from polyurethane or melamine resin, offering effective sound absorption but often involves petrochemical-based materials with limited biodegradability. Melamine foam, derived from melamine resin, is lighter, more fire-resistant, and generally considered more environmentally friendly due to its formaldehyde-free composition and potential recyclability. Both materials provide soundproofing benefits, but melamine foam's eco-friendlier production and disposal profile make it a sustainable choice for green building projects.
Which Foam is Best for Your Soundproofing Needs?
Acoustic foam excels in absorbing mid to high-frequency sound waves, making it ideal for reducing echoes and improving room acoustics, especially in studios and home theaters. Melamine foam offers superior fire resistance and better performance across a broader frequency range, including low frequencies, which is beneficial for industrial settings and soundproofing walls. Choose acoustic foam for targeted frequency control and cost efficiency, while melamine foam suits environments requiring enhanced safety and wider sound absorption capabilities.
Infographic: Acoustic foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com