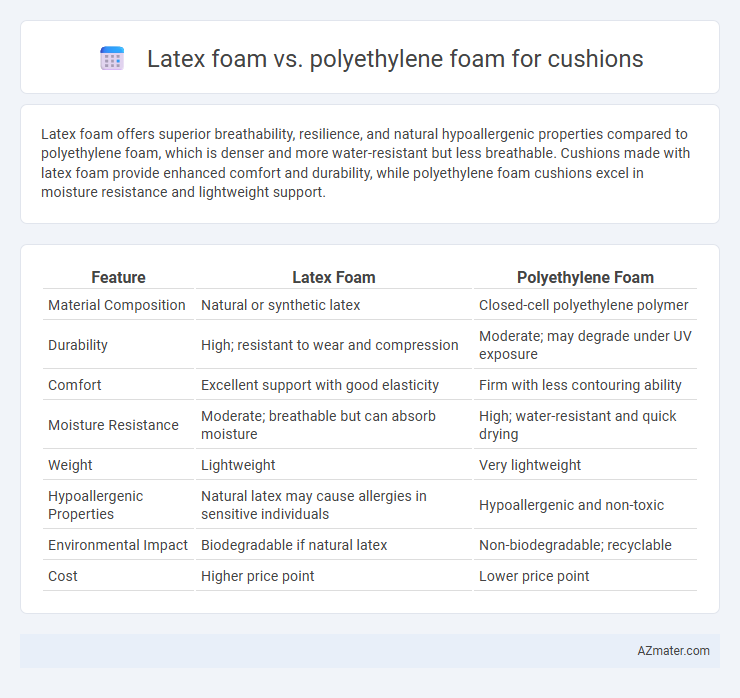
Latex foam offers superior breathability, resilience, and natural hypoallergenic properties compared to polyethylene foam, which is denser and more water-resistant but less breathable. Cushions made with latex foam provide enhanced comfort and durability, while polyethylene foam cushions excel in moisture resistance and lightweight support.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Latex Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic latex | Closed-cell polyethylene polymer |
| Durability | High; resistant to wear and compression | Moderate; may degrade under UV exposure |
| Comfort | Excellent support with good elasticity | Firm with less contouring ability |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate; breathable but can absorb moisture | High; water-resistant and quick drying |
| Weight | Lightweight | Very lightweight |
| Hypoallergenic Properties | Natural latex may cause allergies in sensitive individuals | Hypoallergenic and non-toxic |
| Environmental Impact | Biodegradable if natural latex | Non-biodegradable; recyclable |
| Cost | Higher price point | Lower price point |
Introduction: Latex Foam vs Polyethylene Foam in Cushion Applications
Latex foam offers superior elasticity, breathability, and resilience compared to polyethylene foam, making it ideal for high-comfort cushion applications requiring pressure relief and durability. Polyethylene foam, known for its lightweight, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness, is commonly used in outdoor or moisture-prone environments where cushioning protection is essential. Selecting between latex and polyethylene foam depends on application-specific needs such as comfort level, environmental exposure, and longevity.
Material Composition and Characteristics
Latex foam, derived from natural or synthetic latex, offers superior elasticity, breathable open-cell structure, and inherent resistance to dust mites and mold, making it ideal for cushioning applications requiring comfort and durability. Polyethylene foam, a closed-cell, polyethylene-based polymer, provides higher water resistance, excellent shock absorption, and lower density, which is beneficial for lightweight protective cushioning. The material composition influences performance: latex foam excels in pressure relief and breathability, while polyethylene foam delivers robust impact resistance and moisture barrier properties.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Latex foam offers superior comfort with its natural elasticity and breathability, contouring closely to the body while providing consistent support without sagging. Polyethylene foam, though less adaptive, delivers dense support and durability ideal for cushioning that requires firm resistance to compression. The balance between latex's pressure relief and polyethylene's firmness determines the ideal choice based on individual comfort and support preferences.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Latex foam offers superior durability with a typical lifespan of 8 to 10 years due to its natural elasticity and resistance to sagging, making it ideal for long-term cushion support. Polyethylene foam, while more affordable, tends to compress and degrade faster, usually lasting around 3 to 5 years under regular use, as its closed-cell structure is less resilient to repeated pressure. The longer lifespan of latex foam results in better cost-efficiency over time despite higher initial costs, especially in applications requiring consistent cushioning performance.
Breathability and Temperature Regulation
Latex foam offers superior breathability due to its natural open-cell structure, allowing enhanced air circulation and moisture-wicking properties, which prevents heat buildup and maintains a cooler seating surface. Polyethylene foam, typically denser and more closed-cell, provides limited airflow, causing heat retention and less effective temperature regulation in cushions. Choosing latex foam promotes a more comfortable, cool environment ideal for prolonged use, while polyethylene foam may result in increased warmth and reduced breathability.
Allergen and Toxicity Considerations
Latex foam, primarily made from natural or synthetic rubber, can cause allergic reactions in individuals sensitive to latex proteins, posing a significant allergen risk, whereas polyethylene foam is hypoallergenic and generally safe for most users. Polyethylene foam is chemically inert and free of volatile organic compounds (VOCs), resulting in low toxicity levels, while some latex foams might contain chemicals from processing that require careful attention to off-gassing and potential respiratory irritants. For allergy-sensitive environments, polyethylene foam offers superior safety by minimizing exposure to allergens and toxic substances compared to latex foam cushions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex foam, derived from natural rubber, offers superior biodegradability and renewable sourcing compared to polyethylene foam, which is petroleum-based and resistant to decomposition. The production of latex foam typically involves lower greenhouse gas emissions and reduced reliance on fossil fuels, enhancing its environmental sustainability credentials. In contrast, polyethylene foam's long degradation timeline and reliance on non-renewable resources contribute significantly to environmental pollution and landfill waste challenges.
Cost and Affordability Analysis
Latex foam cushions typically have higher upfront costs due to natural materials and durability, offering long-term value through longevity and resilience. Polyethylene foam provides a budget-friendly option with lower initial price points but may require more frequent replacement due to reduced durability. Analyzing cost-effectiveness, polyethylene foam suits short-term affordability, while latex foam excels in cost per use over extended periods.
Best Uses and Application Scenarios
Latex foam offers superior breathability and resilience, making it ideal for cushions in high-usage furniture like sofas and office chairs where comfort and durability are essential. Polyethylene foam excels in applications requiring lightweight support and impact absorption, such as outdoor seating cushions, boating, and sports equipment padding due to its water resistance and closed-cell structure. Selecting between latex and polyethylene foam depends on the need for comfort and pressure relief versus moisture resistance and shock absorption in specific environments.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Foam for Your Cushion
Latex foam offers superior durability, natural breathability, and resilience, making it ideal for cushions requiring long-term comfort and support. Polyethylene foam provides lightweight, cost-effective cushioning with good shock absorption, best suited for temporary or budget-friendly applications. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors such as comfort, durability, environmental impact, and budget to meet specific cushioning needs.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Polyethylene foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com