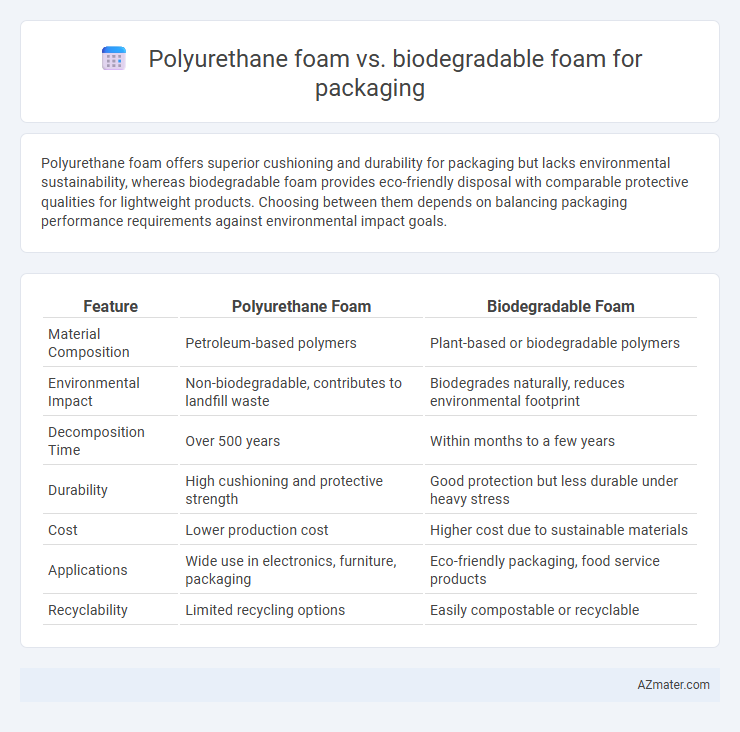
Polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and durability for packaging but lacks environmental sustainability, whereas biodegradable foam provides eco-friendly disposal with comparable protective qualities for lightweight products. Choosing between them depends on balancing packaging performance requirements against environmental impact goals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Biodegradable Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Petroleum-based polymers | Plant-based or biodegradable polymers |
| Environmental Impact | Non-biodegradable, contributes to landfill waste | Biodegrades naturally, reduces environmental footprint |
| Decomposition Time | Over 500 years | Within months to a few years |
| Durability | High cushioning and protective strength | Good protection but less durable under heavy stress |
| Cost | Lower production cost | Higher cost due to sustainable materials |
| Applications | Wide use in electronics, furniture, packaging | Eco-friendly packaging, food service products |
| Recyclability | Limited recycling options | Easily compostable or recyclable |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Packaging foams such as polyurethane foam and biodegradable foam serve critical roles in cushioning, protecting, and preserving goods during transportation and storage. Polyurethane foam offers superior impact resistance, flexibility, and durability, making it a standard choice for heavy or fragile items. Biodegradable foams, derived from renewable resources like starch or polylactic acid (PLA), prioritize environmental sustainability by decomposing naturally, reducing long-term landfill accumulation in packaging applications.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile synthetic material widely used in packaging for its excellent cushioning, durability, and impact resistance. It is made through a chemical reaction between polyols and isocyanates, resulting in a lightweight and flexible foam that provides superior protection for fragile items during shipping. Despite its effectiveness, polyurethane foam is non-biodegradable and poses environmental challenges due to its long decomposition time and potential toxicity.
Defining Biodegradable Foam
Biodegradable foam is an eco-friendly packaging material derived from renewable resources such as cornstarch or sugarcane, designed to break down naturally through microbial activity within a short timeframe. Unlike traditional polyurethane foam, which is petroleum-based and non-degradable, biodegradable foam significantly reduces environmental impact by decomposing into non-toxic components. This sustainable alternative offers comparable cushioning and protection for fragile items while aligning with increasing global demands for green packaging solutions.
Material Composition and Production
Polyurethane foam is composed primarily of petrochemical-based polyols and isocyanates, produced through a chemical reaction resulting in a durable, flexible material widely used for protective packaging. Biodegradable foam typically utilizes natural polymers such as starch, cellulose, or polylactic acid (PLA), created through processes that promote eco-friendly degradation and reduced environmental impact. Production of polyurethane foam involves energy-intensive reactions and synthetic chemicals, whereas biodegradable foam manufacturing often incorporates renewable resources and lower energy inputs to enhance sustainability.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Polyurethane foam, derived from petrochemicals, contributes significantly to environmental pollution due to its non-biodegradable nature and the release of toxic substances during production and disposal. In contrast, biodegradable foam, often made from plant-based materials like cornstarch or sugarcane, decomposes naturally within months, reducing landfill volume and minimizing ecological harm. The shift towards biodegradable foam offers a sustainable alternative, lowering carbon footprints and promoting circular economy principles in packaging industries.
Performance and Protective Qualities
Polyurethane foam provides superior cushioning with high impact resistance and excellent durability, making it ideal for long-term protection in packaging applications. Biodegradable foam, often made from plant-based materials, offers eco-friendly disposal options but generally exhibits lower resilience and may degrade faster under stress. Choosing between polyurethane and biodegradable foam depends on balancing performance needs with environmental considerations in packaging protection.
Cost Analysis: Polyurethane vs Biodegradable Foam
Polyurethane foam offers lower initial material costs compared to biodegradable foam, making it a cost-effective choice for large-scale packaging operations. However, biodegradable foam may reduce long-term expenses through lower waste management fees and compliance with environmental regulations. When evaluating total cost of ownership, firms should consider production volume, disposal costs, and potential tax incentives for eco-friendly materials.
End-of-Life Disposal and Recycling Options
Polyurethane foam poses significant challenges for end-of-life disposal due to its non-biodegradable nature and limited recycling options, often resulting in landfill accumulation or incineration. Biodegradable foam, typically made from plant-based materials like polylactic acid (PLA), offers enhanced compostability and breaks down under industrial composting conditions, reducing environmental impact. Recycling efforts for biodegradable foams are expanding but remain less established than traditional polymer recycling systems.
Industry Trends and Consumer Preferences
Polyurethane foam remains widely used in packaging due to its durability, cushioning properties, and cost-effectiveness, but growing environmental concerns drive a shift towards biodegradable foam alternatives derived from natural materials like starch or cornstarch. Industry trends indicate increasing adoption of eco-friendly packaging solutions to meet stricter regulations and consumer demand for sustainable products, with biodegradable foam gaining traction in sectors such as electronics, food, and cosmetics. Consumer preferences favor packaging that balances protection with environmental impact, making biodegradable foam a key innovation in reducing plastic waste and enhancing corporate social responsibility.
Future Outlook for Sustainable Packaging
Polyurethane foam remains a widely used packaging material due to its durability and cushioning properties, but growing environmental concerns are accelerating the shift towards biodegradable foam alternatives derived from natural polymers like starch, cellulose, and plant-based oils. Innovations in biodegradable foam formulations aim to enhance performance characteristics such as moldability, water resistance, and biodegradability rates to meet increasing regulatory standards and consumer demand for eco-friendly packaging. The future outlook for sustainable packaging strongly favors biodegradable foams as they align with circular economy principles, reduce landfill waste, and support brand sustainability goals in sectors ranging from electronics to food packaging.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Biodegradable foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com