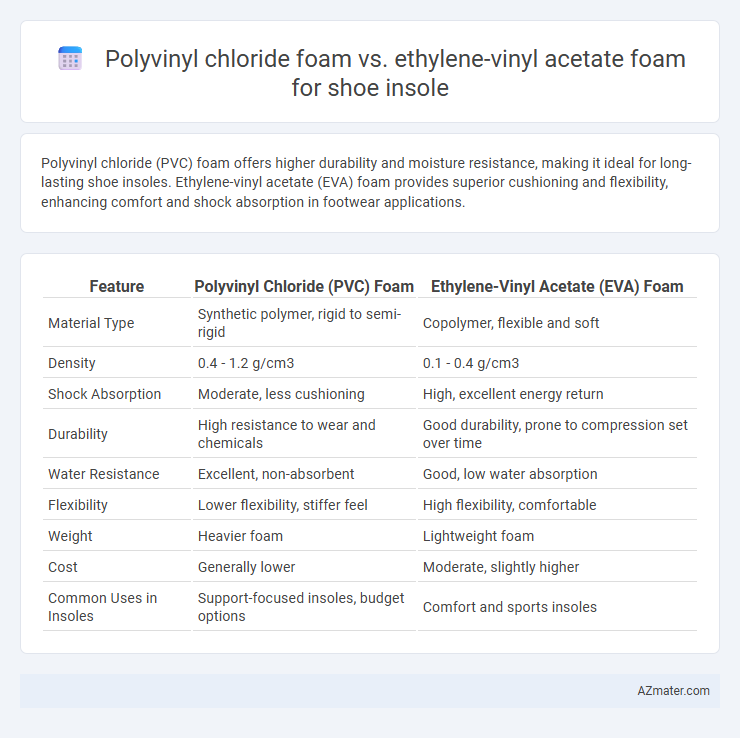
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers higher durability and moisture resistance, making it ideal for long-lasting shoe insoles. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior cushioning and flexibility, enhancing comfort and shock absorption in footwear applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Synthetic polymer, rigid to semi-rigid | Copolymer, flexible and soft |
| Density | 0.4 - 1.2 g/cm3 | 0.1 - 0.4 g/cm3 |
| Shock Absorption | Moderate, less cushioning | High, excellent energy return |
| Durability | High resistance to wear and chemicals | Good durability, prone to compression set over time |
| Water Resistance | Excellent, non-absorbent | Good, low water absorption |
| Flexibility | Lower flexibility, stiffer feel | High flexibility, comfortable |
| Weight | Heavier foam | Lightweight foam |
| Cost | Generally lower | Moderate, slightly higher |
| Common Uses in Insoles | Support-focused insoles, budget options | Comfort and sports insoles |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high durability, excellent cushioning, and resistance to compression, making it suitable for shoe insoles requiring sturdy support and longevity. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior flexibility, lightweight comfort, and shock absorption, commonly used in athletic and casual footwear for enhanced foot mobility. Both materials serve distinct functional roles in shoe insole technology, balancing factors such as resilience, comfort, and cost-effectiveness to optimize foot support.
What is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, durable material characterized by its closed-cell structure, providing excellent cushioning and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Used in shoe insoles, PVC foam offers firm support and shock absorption, ideal for long-term wear in various footwear types. Its versatility and resilience make it a popular choice compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which tends to be softer but less durable under heavy use.
Understanding Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is widely favored for shoe insoles due to its superior cushioning, flexibility, and shock absorption properties compared to Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) foam. EVA's closed-cell structure offers excellent resilience and durability, making it ideal for impact protection and long-term comfort in athletic and casual footwear. Its lightweight and hypoallergenic characteristics further enhance foot support and overall insole performance.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers high durability and firmness, providing stable support but less breathable comfort compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which excels in lightweight cushioning and shock absorption for enhanced comfort during prolonged wear. EVA foam's superior flexibility and softer texture allow for better foot contouring, reducing pressure points and improving overall insole comfort in shoes. The closed-cell structure of EVA foam also ensures effective moisture management, making it preferable for athletic and casual footwear focused on comfort and impact cushioning.
Durability and Longevity
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior durability and resistance to wear, making it ideal for long-lasting shoe insoles exposed to heavy use. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning but tends to compress and degrade faster under continuous pressure, reducing its lifespan compared to PVC foam. PVC's structural integrity ensures prolonged performance and maintains shape over time, while EVA excels in lightweight comfort but may require more frequent replacement.
Shock Absorption and Support Performance
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers superior shock absorption due to its dense cellular structure, effectively reducing impact forces during walking or running. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, known for its lightweight and flexible nature, provides excellent cushioning while enhancing foot support through its resilient energy return properties. EVA foam generally outperforms PVC in overall comfort and support, making it a preferred choice for insoles requiring both shock absorption and ergonomic performance.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam insoles are heavier and less flexible compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which offers a lightweight and highly flexible cushioning ideal for shoe comfort. EVA foam's lower density enhances shock absorption and allows greater foot movement, making it preferable for athletic and casual footwear. In contrast, PVC foam provides firmer support but may compromise flexibility and increase insole weight, impacting overall shoe comfort during extended wear.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers durability and cushioning but generally exhibits lower breathability and moisture management compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam provides superior breathability due to its open-cell structure, allowing better air circulation and moisture evaporation, critical for maintaining foot comfort during prolonged wear. The enhanced moisture-wicking properties of EVA foam help reduce sweat accumulation and odor, making it a preferred choice for shoe insoles focused on breathability and moisture control.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam insoles pose significant environmental concerns due to their release of toxic chemicals during production and difficulty in recycling, contributing to long-term pollution. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a more sustainable option with lower toxicity and better biodegradability, although it remains a petroleum-based material with limited recyclability. Sustainable footwear brands increasingly favor EVA foam for insoles, promoting eco-friendlier manufacturing processes and reduced environmental footprint.
Choosing the Right Insole Material for Your Needs
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam offers excellent durability and support, making it ideal for high-impact activities and prolonged use, while ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides superior cushioning and flexibility, enhancing comfort for everyday wear. EVA foam's lightweight and shock-absorption properties reduce foot fatigue, especially beneficial for running and walking, whereas PVC foam excels in maintaining structural integrity under heavy pressure. Selecting the right insole material depends on balancing durability with comfort needs, considering factors like activity level, foot sensitivity, and desired arch support.
Infographic: Polyvinyl chloride foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Shoe insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com