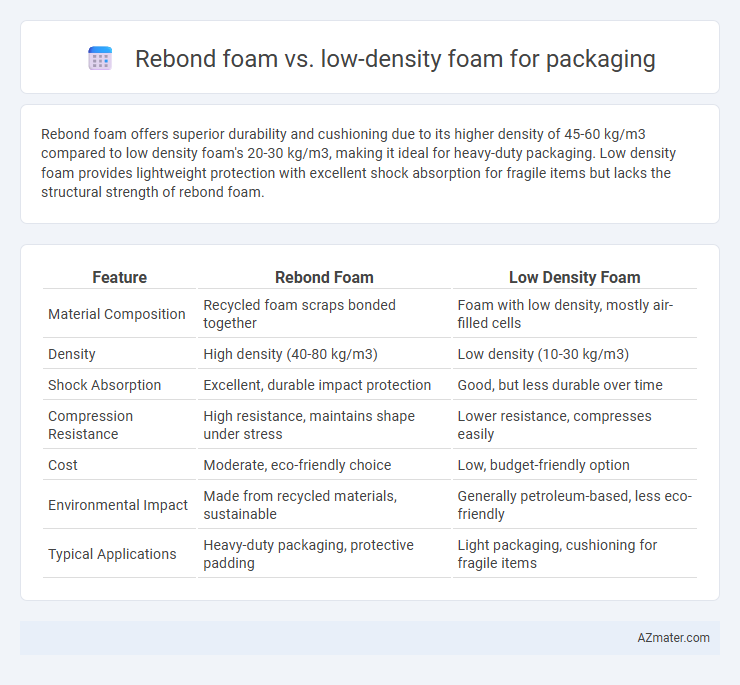
Rebond foam offers superior durability and cushioning due to its higher density of 45-60 kg/m3 compared to low density foam's 20-30 kg/m3, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging. Low density foam provides lightweight protection with excellent shock absorption for fragile items but lacks the structural strength of rebond foam.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Rebond Foam | Low Density Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Recycled foam scraps bonded together | Foam with low density, mostly air-filled cells |
| Density | High density (40-80 kg/m3) | Low density (10-30 kg/m3) |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent, durable impact protection | Good, but less durable over time |
| Compression Resistance | High resistance, maintains shape under stress | Lower resistance, compresses easily |
| Cost | Moderate, eco-friendly choice | Low, budget-friendly option |
| Environmental Impact | Made from recycled materials, sustainable | Generally petroleum-based, less eco-friendly |
| Typical Applications | Heavy-duty packaging, protective padding | Light packaging, cushioning for fragile items |
Introduction to Foam Packaging Materials
Rebond foam and low-density foam serve distinct roles in packaging, with rebond foam offering high durability through compressed recycled foam particles ideal for heavy-duty protection. Low-density foam provides lightweight cushioning suitable for fragile and lightweight items, optimizing space and reducing shipping costs. Both materials enhance product safety but differ in compression resistance, density, and ideal application environments.
What is Rebond Foam?
Rebond foam is a high-density material created by compressing and bonding shredded foam scraps, resulting in a durable and firm product ideal for heavy-duty packaging applications. It offers superior impact absorption and structural support compared to low density foam, which is softer, lighter, and primarily used for cushioning delicate items. The resilience and versatility of rebond foam make it suitable for protecting heavy machinery, electronics, and fragile goods during transportation.
What is Low Density Foam?
Low density foam is a flexible, lightweight cushioning material commonly used in packaging to protect fragile items from impact and vibrations during transportation. It offers excellent shock absorption and compression resistance, making it ideal for delicate electronics and glassware. Compared to rebond foam, low density foam provides softer padding with better cushioning performance but less structural support and durability.
Key Differences Between Rebond and Low Density Foam
Rebond foam is made from shredded and reprocessed foam scraps, resulting in higher density and greater durability compared to low density foam, which is typically softer and less resilient due to its cellular structure. Key differences include rebond foam's superior impact absorption and heavier weight, making it ideal for protective packaging that requires cushioning heavy or delicate items, while low density foam offers lighter protection with more flexibility and cost-effectiveness for less fragile goods. The compression resistance of rebond foam exceeds that of low density foam, providing longer-lasting support and enhanced shock absorption in packaging applications.
Durability Comparison for Packaging
Rebond foam offers superior durability compared to low density foam due to its higher density and resilience, making it more resistant to compression and impact during shipping. Low density foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to degrade faster under pressure and repeated use, providing less protection for fragile items. Choosing rebond foam enhances long-term structural integrity and shock absorption in packaging applications.
Shock Absorption and Cushioning Performance
Rebond foam offers superior shock absorption and cushioning performance compared to low density foam due to its denser structure made from recycled foam scraps compressed together, providing enhanced impact resistance and durability. Low density foam, while lightweight and flexible, typically absorbs less impact and compresses more easily under pressure, making it less effective for heavy-duty packaging protection. Rebond foam's resilience makes it ideal for safeguarding fragile items during shipping, reducing damage risks significantly.
Cost Analysis: Rebond Foam vs Low Density Foam
Rebond foam typically incurs higher upfront costs due to its complex manufacturing process involving recycled foam scrap, but offers superior durability and resilience, potentially reducing replacement frequency in packaging applications. Low density foam, while more affordable initially, may compromise on long-term protection and require more frequent replacements, which can increase overall expenditure over time. Evaluating total cost of ownership favors rebond foam for heavy-duty packaging, whereas low density foam suits budget-sensitive projects with less rigorous protection needs.
Sustainability and Eco-Friendliness
Rebond foam is made from recycled foam scrap, significantly reducing landfill waste and lowering environmental impact compared to low density foam, which is typically petroleum-based and less biodegradable. Its durability and compressive strength allow for longer reusability in packaging applications, enhancing sustainability by reducing material consumption. Low density foam, while lightweight, often lacks recyclability and contributes more to plastic pollution, making rebond foam a more eco-friendly choice for sustainable packaging solutions.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Rebond foam, made from shredded polyurethane foam, offers excellent durability and cushioning, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging and protective inserts for industrial equipment or machinery. Low density foam provides superior flexibility and shock absorption, perfect for fragile electronics, delicate glassware, and lightweight consumer goods that require gentle protection during transit. Choosing the right foam depends on the product's weight, fragility, and the level of impact resistance needed in shipping conditions.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Rebond foam offers superior durability and resilience, making it ideal for heavy-duty packaging that requires high impact absorption and long-term protection. Low density foam provides lightweight cushioning suited for delicate, low-impact items, optimizing shipping costs without compromising basic protection. Selecting the right foam depends on the package contents' fragility, weight, and shipping conditions to ensure efficient, cost-effective safeguarding.
Infographic: Rebond foam vs Low density foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com