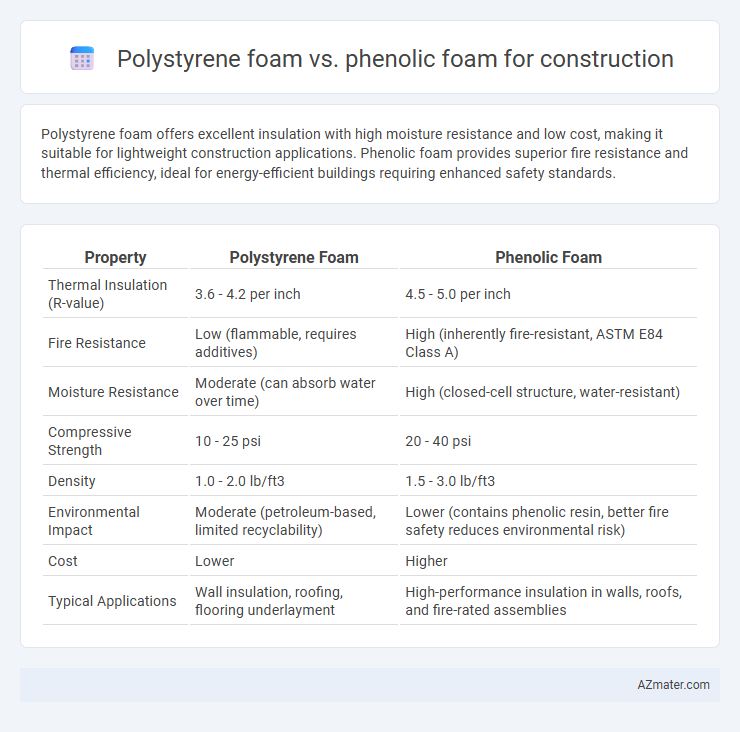
Polystyrene foam offers excellent insulation with high moisture resistance and low cost, making it suitable for lightweight construction applications. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and thermal efficiency, ideal for energy-efficient buildings requiring enhanced safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Polystyrene Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | 3.6 - 4.2 per inch | 4.5 - 5.0 per inch |
| Fire Resistance | Low (flammable, requires additives) | High (inherently fire-resistant, ASTM E84 Class A) |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate (can absorb water over time) | High (closed-cell structure, water-resistant) |
| Compressive Strength | 10 - 25 psi | 20 - 40 psi |
| Density | 1.0 - 2.0 lb/ft3 | 1.5 - 3.0 lb/ft3 |
| Environmental Impact | Moderate (petroleum-based, limited recyclability) | Lower (contains phenolic resin, better fire safety reduces environmental risk) |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Typical Applications | Wall insulation, roofing, flooring underlayment | High-performance insulation in walls, roofs, and fire-rated assemblies |
Introduction to Polystyrene and Phenolic Foams
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in construction, is a lightweight material known for its excellent insulation properties and moisture resistance. Phenolic foam stands out for its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance in building applications. Both foams serve critical roles in energy-efficient construction, with polystyrene favored for cost-effectiveness and phenolic foam preferred for enhanced safety and durability.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Polystyrene foam, a polymer made from styrene monomers, is produced through polymerization and expanded using pentane or other blowing agents to create a lightweight, rigid structure ideal for insulation. Phenolic foam derives from phenol-formaldehyde resin, polymerized through a condensation reaction and expanded with pentane or similar agents, resulting in a highly fire-resistant and low-smoke-emission insulation material. The chemical composition differences influence manufacturing processes, where polystyrene foam uses radical polymerization and physical blowing, while phenolic foam involves thermosetting chemical reactions, contributing to distinct thermal properties and fire performance in construction applications.
Thermal Insulation Performance
Polystyrene foam, including expanded (EPS) and extruded (XPS) types, offers moderate thermal insulation with R-values typically ranging from 3.6 to 5 per inch, making it effective for general building envelope applications. Phenolic foam delivers superior thermal insulation performance, boasting higher R-values around 4.2 to 5.4 per inch and excellent thermal stability, which minimizes heat transfer and reduces energy consumption in construction. Its low thermal conductivity and fire-resistant properties enhance overall building efficiency, outperforming polystyrene foam in demanding insulation scenarios.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Polystyrene foam, commonly used for insulation, has lower fire resistance due to its combustible nature and tendency to release toxic fumes when burned, making it less favorable for stringent fire safety standards in construction. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance, characterized by low flame spread, high char formation, and compliance with rigorous fire safety regulations such as ASTM E84 Class A ratings. Construction projects prioritizing fire safety often prefer phenolic foam for its ability to enhance building safety and reduce fire hazards.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Polystyrene foam offers moderate mechanical strength with good impact resistance but is less durable under prolonged UV exposure and moisture, making it suitable for applications requiring lightweight insulation. Phenolic foam provides superior mechanical strength, higher compressive strength, and excellent durability due to its fire-resistant and moisture-resistant properties, ensuring long-term structural integrity. In construction, phenolic foam is preferred for high-performance insulation where durability and safety are critical, while polystyrene foam is chosen for cost-effective, less demanding projects.
Moisture Resistance and Water Absorption
Polystyrene foam exhibits moderate moisture resistance but tends to absorb more water over time, leading to potential degradation in construction applications. Phenolic foam offers superior moisture resistance with minimal water absorption, maintaining its insulating properties and structural integrity even in high-humidity environments. This makes phenolic foam a preferred choice for projects requiring enhanced durability and long-term waterproof performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene foam, widely used for insulation, poses environmental concerns due to its non-biodegradability and reliance on petroleum-based raw materials, contributing to landfill waste and carbon emissions. Phenolic foam offers enhanced sustainability benefits with its superior fire resistance, lower smoke production, and potential for recycled content, making it a more eco-friendly choice in green building projects. Life cycle assessments reveal phenolic foam's lower global warming potential and better thermal performance, promoting energy efficiency and reducing long-term environmental impact in construction.
Cost Comparison and Economic Considerations
Polystyrene foam offers lower initial costs and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly option for insulation in construction projects. Phenolic foam, while typically more expensive upfront, provides superior thermal performance and fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term energy costs and improving safety. Economic considerations should include lifecycle costs, where phenolic foam's durability and energy savings can offset its higher initial investment.
Common Construction Applications
Polystyrene foam is widely used for insulation in walls, roofs, and flooring due to its excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and low smoke toxicity, which is essential for high-risk areas such as commercial buildings, hospitals, and schools. While polystyrene foam is preferred for general insulation needs, phenolic foam is favored in applications demanding enhanced fire safety and structural integrity.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Project
Polystyrene foam offers excellent thermal insulation with high compressive strength, making it ideal for walls, roofs, and under-slab applications where moisture resistance is crucial. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, suitable for projects with stringent fire safety requirements and high-performance insulation needs. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors such as thermal performance, fire rating, moisture resistance, and budget constraints to optimize building efficiency and safety.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Phenolic foam for Construction
 azmater.com
azmater.com