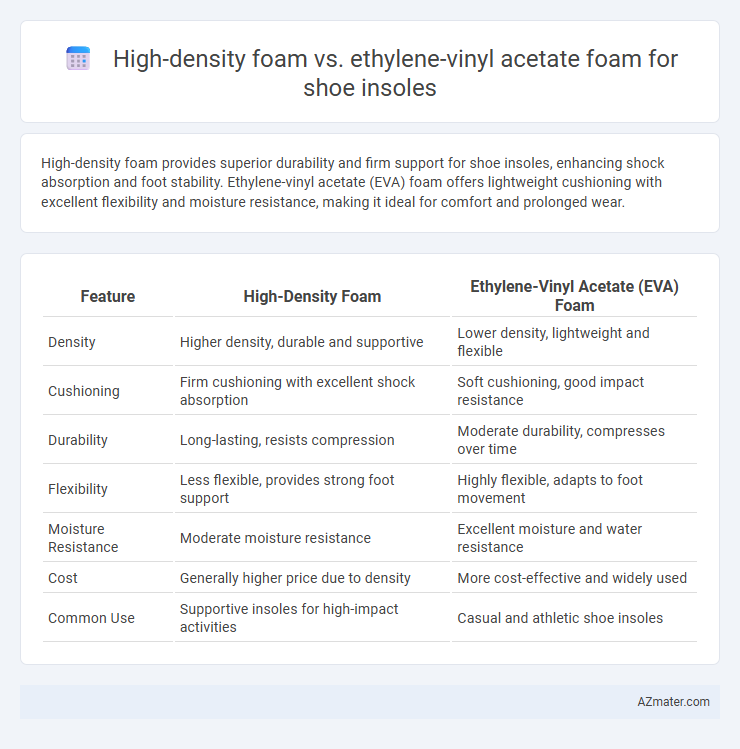
High-density foam provides superior durability and firm support for shoe insoles, enhancing shock absorption and foot stability. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight cushioning with excellent flexibility and moisture resistance, making it ideal for comfort and prolonged wear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | High-Density Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Density | Higher density, durable and supportive | Lower density, lightweight and flexible |
| Cushioning | Firm cushioning with excellent shock absorption | Soft cushioning, good impact resistance |
| Durability | Long-lasting, resists compression | Moderate durability, compresses over time |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, provides strong foot support | Highly flexible, adapts to foot movement |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture resistance | Excellent moisture and water resistance |
| Cost | Generally higher price due to density | More cost-effective and widely used |
| Common Use | Supportive insoles for high-impact activities | Casual and athletic shoe insoles |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
High-density foam and ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam are widely used materials for shoe insoles, each offering distinct properties that enhance comfort and durability. High-density foam provides superior support and pressure distribution, making it ideal for individuals needing extra cushioning and stability during prolonged wear. EVA foam boasts lightweight flexibility and excellent shock absorption, commonly favored in athletic and casual footwear for its balance of comfort and resilience.
What is High-Density Foam?
High-density foam is a type of polyurethane foam characterized by its compact cellular structure and superior durability, making it ideal for shoe insoles that require firm support and long-lasting cushioning. It offers excellent shock absorption and pressure distribution, which helps reduce foot fatigue during extended wear. In comparison to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, high-density foam provides enhanced structural stability and resistance to compression over time.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible, and durable material commonly used in shoe insoles for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties. This closed-cell foam enhances comfort by distributing pressure evenly across the foot, reducing fatigue during prolonged wear. EVA foam's resistance to cracking and its moisture-wicking ability make it a preferred choice over high-density foam for maintaining long-lasting support and foot health.
Durability Comparison: High-Density Foam vs EVA
High-density foam offers superior durability for shoe insoles due to its increased density and resistance to compression, maintaining structural integrity over extended use. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning but tends to break down faster under repeated stress, showing more significant deformation and loss of support. For long-lasting insoles, high-density foam outperforms EVA in retaining shape and shock absorption capabilities over time.
Cushioning and Comfort Analysis
High-density foam offers superior firmness and long-lasting support, making it ideal for individuals needing structured cushioning in shoe insoles, while ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides enhanced shock absorption and lightweight comfort due to its flexible and resilient properties. EVA foam contours more effectively to the foot's shape, reducing pressure points and enhancing overall comfort during prolonged wear. High-density foam typically excels in durability and maintaining shape under heavy use, whereas EVA foam prioritizes softness and responsive cushioning for everyday activities.
Shock Absorption Capabilities
High-density foam offers superior shock absorption due to its firm structure that evenly distributes pressure and reduces impact forces during walking or running. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning with a lightweight and flexible composition, enhancing comfort but with slightly less impact resistance compared to high-density foam. Choosing between the two depends on the need for durability and shock absorption intensity versus the preference for lighter, more flexible shoe insoles.
Breathability and Moisture Management
High-density foam insoles provide moderate breathability due to their closed-cell structure, which limits airflow and moisture evaporation, potentially leading to increased foot perspiration. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior moisture management through its lightweight, open-cell design that enhances ventilation and allows sweat to dissipate more effectively. Choosing EVA foam insoles significantly improves breathability and helps maintain a dry, comfortable environment for the feet during prolonged wear.
Weight and Flexibility Differences
High-density foam insoles are heavier due to their compact cell structure, providing firmer support but less flexibility compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam offers a lightweight feel with excellent shock absorption and enhanced flexibility, making it ideal for dynamic movements and prolonged wear. The weight advantage of EVA foam contributes to overall shoe comfort, especially in athletic and casual footwear.
Cost Efficiency and Value
High-density foam offers superior durability and support for shoe insoles, making it cost-efficient over the long term despite a slightly higher initial price compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam. EVA foam provides excellent cushioning and flexibility at a lower upfront cost but may compress faster, reducing its lifespan and overall value. Choosing between the two depends on balancing upfront expenses against long-term performance and comfort needs for specific footwear applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Footwear
High-density foam offers superior support and durability, making it ideal for long-lasting shoe insoles that require firmness and impact resistance. Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam provides excellent cushioning, flexibility, and lightweight comfort, suitable for athletic shoes and everyday wear. Selecting the right foam depends on activity level, foot arch type, and desired balance between shock absorption and structural support.
Infographic: High-density foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Shoe insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com