Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior impact absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for soundproofing applications requiring durability and moisture resistance. Melamine foam excels in high-frequency sound absorption due to its open-cell structure and thermal stability, providing enhanced acoustic treatment in environments sensitive to heat and fire.
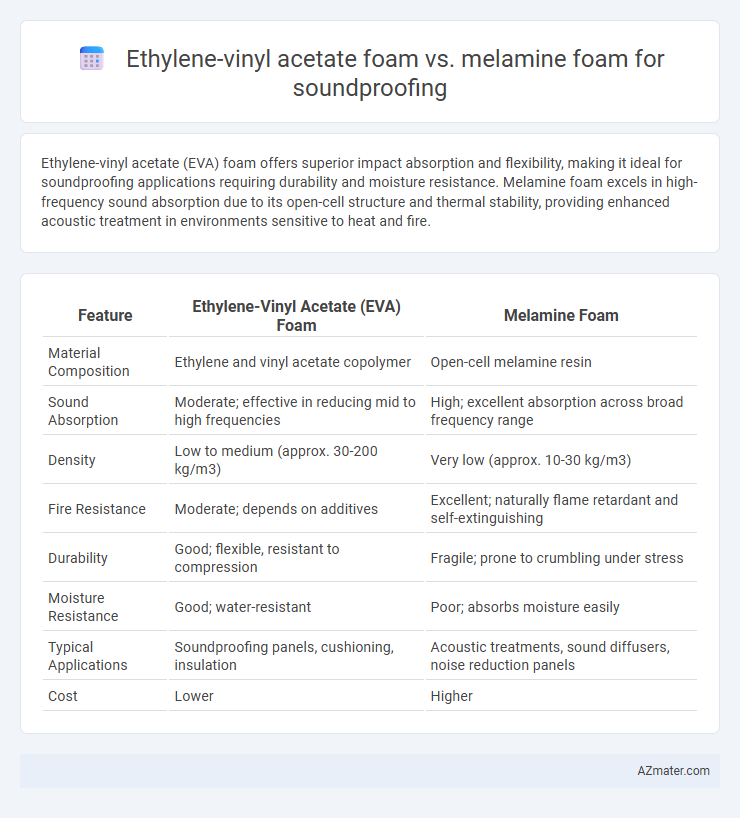
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Ethylene and vinyl acetate copolymer | Open-cell melamine resin |
| Sound Absorption | Moderate; effective in reducing mid to high frequencies | High; excellent absorption across broad frequency range |
| Density | Low to medium (approx. 30-200 kg/m3) | Very low (approx. 10-30 kg/m3) |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate; depends on additives | Excellent; naturally flame retardant and self-extinguishing |
| Durability | Good; flexible, resistant to compression | Fragile; prone to crumbling under stress |
| Moisture Resistance | Good; water-resistant | Poor; absorbs moisture easily |
| Typical Applications | Soundproofing panels, cushioning, insulation | Acoustic treatments, sound diffusers, noise reduction panels |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Soundproofing Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and melamine foam are widely used soundproofing materials due to their distinct acoustic properties. EVA foam offers excellent impact absorption and moderate sound insulation, making it ideal for vibration damping and noise reduction in residential and commercial spaces. Melamine foam provides superior sound absorption and fire resistance, which enhances room acoustics by minimizing echo and reverberation in studios and auditoriums.
Overview of Ethylene-vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is a closed-cell material known for its excellent impact absorption, flexibility, and durability, making it a popular choice in soundproofing applications where vibration damping and moderate noise reduction are required. Its closed-cell structure provides resistance to moisture and environmental factors, contributing to long-lasting acoustic insulation performance. Compared to melamine foam, EVA foam offers superior compression resistance but typically has lower sound absorption coefficients, making it more suitable for specific noise control scenarios involving low-frequency sounds and physical cushioning.
Overview of Melamine Foam
Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-celled material known for its excellent sound absorption properties, particularly in mid to high-frequency ranges. It offers superior thermal resistance and fire retardancy compared to Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, making it ideal for environments requiring both soundproofing and safety. Melamine foam's unique geometric structure enhances sound diffusion and minimizes reverberation, providing effective noise control in acoustic applications.
Acoustic Properties Comparison: EVA vs Melamine Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior sound absorption in mid to high-frequency ranges due to its closed-cell structure, effectively reducing echo and reverberation in indoor environments. Melamine foam demonstrates excellent broadband sound absorption, especially in high-frequency domains, thanks to its open-cell microstructure that dissipates sound waves efficiently. While EVA foam provides better impact resistance and durability, melamine foam excels in lightweight soundproofing applications requiring thermal insulation alongside acoustic performance.
Installation and Ease of Use
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a lightweight, flexible design that simplifies cutting and fitting during soundproofing installation, making it highly user-friendly for DIY applications. Melamine foam, while excellent for sound absorption due to its open-cell structure, tends to be more brittle and may require careful handling and specialized adhesives, complicating the installation process. EVA foam's durability and resilience provide easier repositioning without damage, whereas melamine foam demands precision to avoid crumbling or tearing during setup.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to melamine foam in soundproofing applications due to its resilience against compression, moisture, and chemical degradation. Melamine foam, while excellent for sound absorption, tends to degrade faster under physical stress and environmental exposure, leading to reduced effectiveness over time. EVA foam's robust polymer structure ensures prolonged performance and consistent acoustic insulation in a variety of settings.
Cost Analysis: EVA Foam vs Melamine Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam generally offers a lower cost per square foot compared to melamine foam, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale soundproofing projects. Melamine foam, while more expensive, provides superior noise absorption and fire resistance, justifying its higher price in critical acoustic applications. The choice between EVA foam and melamine foam depends on balancing upfront material costs with performance requirements and long-term durability.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers moderate fire resistance but can release toxic fumes when burned, while melamine foam is inherently fire-retardant with low smoke emission, making it safer in fire scenarios. Melamine foam's open-cell structure also provides excellent sound absorption while maintaining high thermal stability. For soundproofing applications requiring stringent fire safety standards, melamine foam is the superior choice due to its non-combustible properties and minimal toxic output during combustion.
Applications in Residential and Commercial Spaces
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent sound absorption and impact resistance, making it ideal for residential applications such as home theaters and music rooms where both comfort and noise reduction are desired. Melamine foam excels in commercial environments due to its superior acoustic absorption and fire-retardant properties, often used in offices, conference rooms, and public spaces requiring stringent fire safety standards. Both materials enhance soundproofing but are selected based on specific needs like durability, fire resistance, and acoustic performance in either residential or commercial settings.
Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Foam for Soundproofing
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers excellent impact absorption and moisture resistance, making it ideal for environments with high humidity and physical stress, but it provides moderate soundproofing mainly in mid-frequency ranges. Melamine foam excels in sound absorption across a broad frequency spectrum due to its open-cell structure and fire-resistant properties, making it a superior choice for acoustic treatment in studios and office spaces. For soundproofing applications prioritizing fire safety and wide-range noise reduction, melamine foam stands out, whereas EVA foam suits scenarios requiring durability and moisture resistance alongside noise control.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com