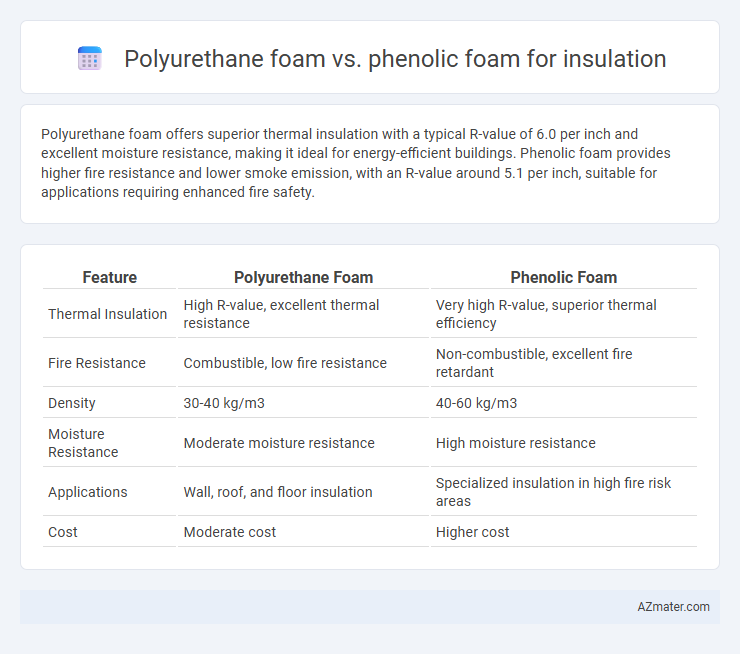
Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation with a typical R-value of 6.0 per inch and excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for energy-efficient buildings. Phenolic foam provides higher fire resistance and lower smoke emission, with an R-value around 5.1 per inch, suitable for applications requiring enhanced fire safety.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Polyurethane Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | High R-value, excellent thermal resistance | Very high R-value, superior thermal efficiency |
| Fire Resistance | Combustible, low fire resistance | Non-combustible, excellent fire retardant |
| Density | 30-40 kg/m3 | 40-60 kg/m3 |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate moisture resistance | High moisture resistance |
| Applications | Wall, roof, and floor insulation | Specialized insulation in high fire risk areas |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Polyurethane and Phenolic Foam Insulation
Polyurethane foam insulation is a versatile material known for its excellent thermal resistance, lightweight properties, and high R-value per inch, making it ideal for energy-efficient building envelopes. Phenolic foam insulation offers superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and dimensional stability, making it a preferred choice in applications requiring stringent fire safety standards. Both foams provide effective thermal insulation but differ significantly in chemical composition and performance characteristics, influencing their suitability for specific construction needs.
Understanding the Composition of Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam consists of a polymer matrix formed by reacting polyols and isocyanates, creating a cellular structure that provides excellent thermal insulation and high flexibility. Its chemical composition allows for low thermal conductivity, making it highly efficient for insulating walls, roofs, and refrigeration systems. Compared to phenolic foam, polyurethane foam offers superior moisture resistance and mechanical strength, enhancing long-term durability in various environmental conditions.
Overview of Phenolic Foam Structure and Properties
Phenolic foam features a closed-cell structure with fine, uniform cells that provide excellent thermal insulation and fire resistance. Its rigid, lightweight composition offers superior dimensional stability, low smoke emission, and high thermal performance compared to many other insulation materials. The foam's inherent chemical makeup delivers enhanced resistance to heat and flame, making it ideal for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value typically ranging from 6 to 7 per inch, making it highly effective in reducing heat transfer. Phenolic foam provides competitive insulating properties with an R-value around 4 to 5 per inch, though it excels in fire resistance and low smoke emissions. The choice between these foams depends on balancing thermal performance needs with fire safety requirements in building insulation applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Considerations
Polyurethane foam offers superior thermal insulation but has limited fire resistance, often requiring flame retardant additives to meet safety standards. Phenolic foam exhibits excellent fire resistance due to its inherent chemical structure, releasing low smoke and toxic gases during combustion, making it a safer choice in fire-critical applications. Safety considerations favor phenolic foam in environments demanding stringent fire performance, while polyurethane foam suits less fire-sensitive settings where high insulation is prioritized.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Polyurethane foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, effectively preventing water absorption and maintaining thermal performance over time. Phenolic foam offers excellent fire resistance and thermal stability but is more prone to moisture absorption, which can compromise its insulating properties and durability. Polyurethane foam's robustness under humid conditions typically ensures longer-lasting insulation compared to phenolic foam, which may require additional protective barriers in moist environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polyurethane foam exhibits higher global warming potential due to its use of isocyanates and blowing agents with significant greenhouse gas emissions, whereas phenolic foam generally has lower environmental impact due to its composition of formaldehyde-based resins and less harmful blowing agents. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs), supporting healthier indoor air quality and sustainability goals. Life cycle assessments highlight phenolic foam's potential for better end-of-life recyclability and reduced carbon footprint compared to polyurethane foam.
Cost Analysis and Installation Differences
Polyurethane foam typically offers lower material costs compared to phenolic foam, making it a more budget-friendly option for insulation projects. Installation of polyurethane foam is generally faster due to its spray application method, which expands rapidly to fill gaps and irregular spaces. Phenolic foam, while more expensive, provides superior fire resistance and dimensional stability but requires more specialized handling and longer curing times during installation.
Application Areas: Best Uses for Each Foam
Polyurethane foam excels in residential and commercial building insulation due to its superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for walls, roofs, and HVAC systems. Phenolic foam is preferred in industrial and high-temperature applications such as petrochemical plants, cold storage facilities, and fire-resistant insulation because of its excellent fire retardancy and low smoke emission. Each foam's unique chemical structure and performance characteristics dictate its suitability, with polyurethane offering flexibility and phenolic providing enhanced safety in demanding environments.
Choosing the Right Insulation: Key Factors to Consider
When choosing between polyurethane foam and phenolic foam for insulation, consider thermal conductivity, fire resistance, and environmental impact as key factors. Polyurethane foam offers low thermal conductivity and excellent air sealing properties, making it ideal for energy-efficient applications, while phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low smoke emissions suitable for high-risk environments. Evaluating project-specific requirements such as budget, building codes, and long-term durability will ensure the optimal insulation material selection.
Infographic: Polyurethane foam vs Phenolic foam for Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com