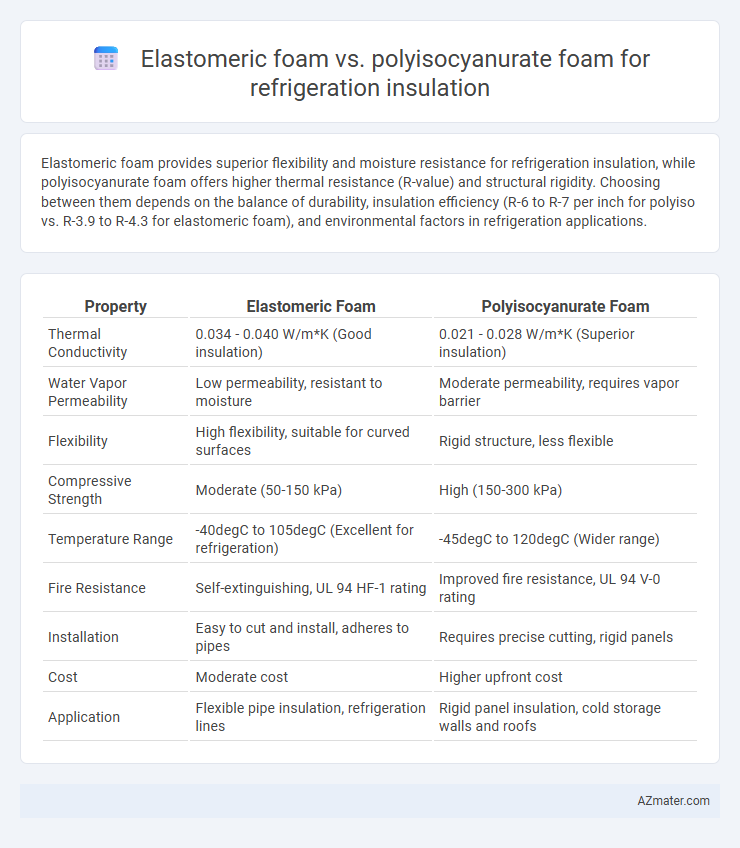
Elastomeric foam provides superior flexibility and moisture resistance for refrigeration insulation, while polyisocyanurate foam offers higher thermal resistance (R-value) and structural rigidity. Choosing between them depends on the balance of durability, insulation efficiency (R-6 to R-7 per inch for polyiso vs. R-3.9 to R-4.3 for elastomeric foam), and environmental factors in refrigeration applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Elastomeric Foam | Polyisocyanurate Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.034 - 0.040 W/m*K (Good insulation) | 0.021 - 0.028 W/m*K (Superior insulation) |
| Water Vapor Permeability | Low permeability, resistant to moisture | Moderate permeability, requires vapor barrier |
| Flexibility | High flexibility, suitable for curved surfaces | Rigid structure, less flexible |
| Compressive Strength | Moderate (50-150 kPa) | High (150-300 kPa) |
| Temperature Range | -40degC to 105degC (Excellent for refrigeration) | -45degC to 120degC (Wider range) |
| Fire Resistance | Self-extinguishing, UL 94 HF-1 rating | Improved fire resistance, UL 94 V-0 rating |
| Installation | Easy to cut and install, adheres to pipes | Requires precise cutting, rigid panels |
| Cost | Moderate cost | Higher upfront cost |
| Application | Flexible pipe insulation, refrigeration lines | Rigid panel insulation, cold storage walls and roofs |
Introduction to Refrigeration Insulation Materials
Elastomeric foam and polyisocyanurate foam are widely used refrigeration insulation materials, each offering distinct thermal performance and moisture resistance. Elastomeric foam excels in flexibility and closed-cell structure, preventing condensation and enhancing energy efficiency in cold storage. Polyisocyanurate foam provides higher R-values per inch, ensuring superior thermal insulation but may require protective coverings to address potential moisture absorption in refrigeration applications.
Overview of Elastomeric Foam
Elastomeric foam is a flexible, closed-cell insulation material widely used in refrigeration systems due to its excellent thermal resistance and vapor barrier properties. It offers superior resistance to moisture, mold, and mildew, making it ideal for maintaining energy efficiency and preventing condensation in cold storage environments. Its durability and ease of installation make elastomeric foam a preferred choice over rigid foams like polyisocyanurate in applications requiring flexibility and long-term reliability.
Overview of Polyisocyanurate Foam
Polyisocyanurate foam, commonly used in refrigeration insulation, offers superior thermal resistance with an R-value typically around 6.5 to 8 per inch, making it highly effective in minimizing heat transfer. Its rigid cellular structure and closed-cell composition provide excellent moisture resistance and structural stability, crucial for maintaining insulation performance in cold environments. Compared to elastomeric foam, polyisocyanurate foam delivers enhanced fire resistance and durability, optimizing energy efficiency and longevity in refrigeration systems.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Elastomeric foam offers superior thermal insulation with low thermal conductivity values typically around 0.030 to 0.040 W/m*K, making it highly effective for refrigeration applications by minimizing heat transfer. Polyisocyanurate foam exhibits slightly lower thermal conductivity, often in the range of 0.022 to 0.028 W/m*K, which provides enhanced thermal resistance and energy efficiency in cold storage environments. Both materials ensure reliable thermal performance, but Polyisocyanurate foam generally achieves better insulation efficiency, contributing to reduced energy consumption in refrigeration systems.
Moisture Resistance and Water Vapor Permeability
Elastomeric foam offers superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, significantly minimizing water absorption and preventing condensation in refrigeration insulation applications. Polyisocyanurate foam, while providing good thermal insulation, exhibits higher water vapor permeability, which can lead to increased risk of moisture intrusion and degradation over time. Selecting elastomeric foam enhances durability and maintains thermal performance by effectively controlling moisture infiltration and vapor diffusion in cold storage environments.
Fire Resistance and Safety Standards
Elastomeric foam offers excellent fire resistance with low flame spread and smoke generation, complying with UL 94 HB and NFPA 255 standards, making it a preferred choice for refrigeration insulation in safety-critical environments. Polyisocyanurate foam provides superior thermal insulation but tends to have higher flame spread and smoke development, requiring additional fire retardant treatments to meet ASTM E84 and NFPA 286 regulations. Selecting between these materials involves balancing fire safety compliance with thermal performance specific to refrigeration applications.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility and ease of installation, conforming well to irregular surfaces and allowing for quick, seamless application without the need for adhesives or specialized tools. Polyisocyanurate foam, while providing excellent thermal insulation, requires more precise cutting and fitting, often demanding adhesives or mechanical fasteners to secure panels, resulting in a less adaptable installation process. The inherent flexibility of elastomeric foam reduces the risk of gaps and thermal bridging, making it an ideal choice for refrigeration insulation systems where efficient sealing and vibration resistance are critical.
Longevity and Maintenance Considerations
Elastomeric foam offers superior resistance to moisture absorption and UV degradation, extending its lifespan in refrigeration insulation applications compared to polyisocyanurate foam. Polyisocyanurate foam provides higher initial R-value but may require more frequent inspections and maintenance due to potential brittleness and susceptibility to moisture damage over time. Selecting elastomeric foam reduces long-term maintenance costs and enhances durability in cold storage environments.
Cost Analysis and Return on Investment
Elastomeric foam typically offers a lower initial cost compared to Polyisocyanurate foam, leading to reduced upfront expenditure for refrigeration insulation projects. Polyisocyanurate foam's higher R-value per inch enhances thermal efficiency, resulting in greater energy savings and faster return on investment over the insulation's lifespan. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals that despite the higher upfront cost, Polyisocyanurate foam often delivers superior long-term economic benefits due to decreased energy consumption and extended durability.
Choosing the Right Foam for Refrigeration Applications
Elastomeric foam offers superior flexibility, excellent thermal insulation, and moisture resistance, making it ideal for refrigeration systems requiring tight seals and vibration dampening. Polyisocyanurate foam provides higher R-values and rigid structural support, suitable for insulating large refrigeration units where maximizing thermal efficiency is critical. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing flexibility needs against insulation performance, moisture resistance, and mechanical strength within specific refrigeration environments.
Infographic: Elastomeric foam vs Polyisocyanurate foam for Refrigeration insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com