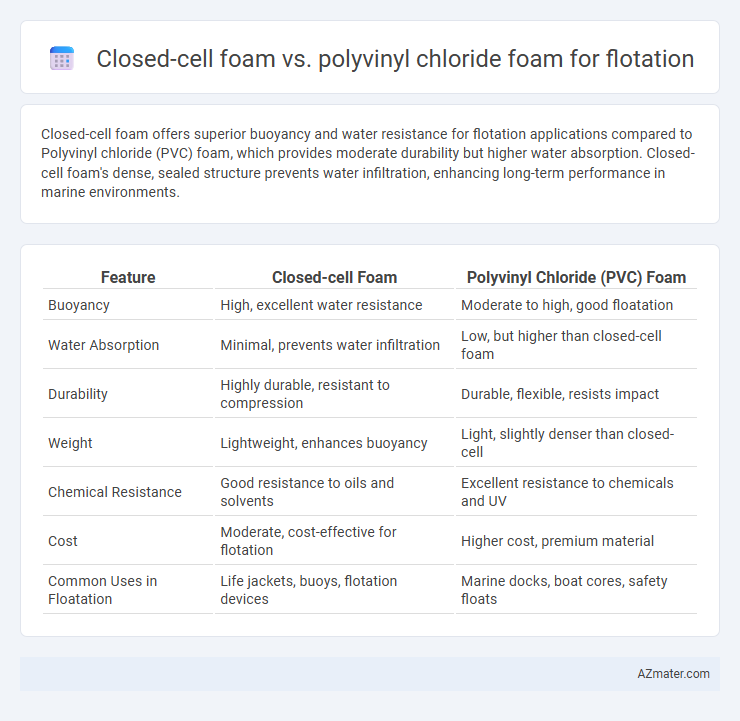
Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy and water resistance for flotation applications compared to Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which provides moderate durability but higher water absorption. Closed-cell foam's dense, sealed structure prevents water infiltration, enhancing long-term performance in marine environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-cell Foam | Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Buoyancy | High, excellent water resistance | Moderate to high, good floatation |
| Water Absorption | Minimal, prevents water infiltration | Low, but higher than closed-cell foam |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to compression | Durable, flexible, resists impact |
| Weight | Lightweight, enhances buoyancy | Light, slightly denser than closed-cell |
| Chemical Resistance | Good resistance to oils and solvents | Excellent resistance to chemicals and UV |
| Cost | Moderate, cost-effective for flotation | Higher cost, premium material |
| Common Uses in Floatation | Life jackets, buoys, flotation devices | Marine docks, boat cores, safety floats |
Introduction to Flotation Materials
Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy and water resistance due to its impermeable structure, making it ideal for flotation applications where durability and long-term performance are critical. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides lightweight and flexible properties with moderate buoyancy, commonly used in recreational and marine flotation devices. Selecting between these materials depends on specific requirements such as weight capacity, environmental exposure, and structural strength in flotation systems.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a type of foam characterized by its tightly packed, sealed cells that prevent water absorption, making it highly effective for flotation applications. This structure provides excellent buoyancy and durability compared to materials like polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, which is softer and more flexible but less resistant to water penetration. The rigid and waterproof nature of closed-cell foam ensures superior performance in maintaining flotation and structural integrity in marine environments.
What is Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) Foam?
Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a lightweight, closed-cell material widely used in flotation applications due to its excellent buoyancy and water resistance. Unlike traditional closed-cell foams, PVC foam offers superior chemical stability, durability, and resistance to UV radiation and saltwater corrosion, making it ideal for marine environments. Its rigid structure provides enhanced mechanical strength, ensuring reliable performance in boat decks, docks, and life-saving equipment.
Key Differences in Material Composition
Closed-cell foam consists of tiny, sealed gas pockets that provide high buoyancy and water resistance, making it ideal for flotation devices. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam is a synthetic polymer with a dense cellular structure, offering superior durability, chemical resistance, and moderate buoyancy compared to traditional closed-cell foams. The key difference lies in material composition: closed-cell foam relies on trapped gas bubbles for floatation, while PVC foam's polymer matrix enhances strength and longevity in marine environments.
Buoyancy Performance Comparison
Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy performance due to its sealed air pockets that prevent water absorption, maintaining consistent floatation over time. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides good buoyancy but tends to absorb moisture gradually, which can reduce its overall floatation efficiency in prolonged water exposure. The higher density and water resistance of closed-cell foam make it more reliable for applications requiring long-term, stable buoyancy.
Durability and Lifespan Analysis
Closed-cell foam offers superior durability and a longer lifespan for flotation applications due to its high resistance to water absorption, chemical corrosion, and physical compression. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while lightweight and resistant to many environmental factors, tends to degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure and mechanical stress, reducing its service life. The closed-cell structure in foam ensures enhanced buoyancy retention and structural integrity, making it a preferred choice for long-term flotation devices compared to PVC foam.
Water Absorption and Resistance
Closed-cell foam exhibits lower water absorption due to its tightly sealed cells, making it highly resistant to moisture infiltration and ideal for flotation applications requiring durability in wet environments. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam also offers excellent water resistance but tends to absorb slightly more water over extended exposure compared to closed-cell foam, potentially affecting its long-term buoyancy. The superior water absorption resistance of closed-cell foam ensures sustained flotation performance with minimal degradation in marine or aquatic conditions.
Cost Efficiency and Availability
Closed-cell foam offers superior cost efficiency for flotation applications due to its lower manufacturing expenses and widespread availability, making it a budget-friendly choice for large-scale projects. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, while often more expensive, provides enhanced durability and chemical resistance, which can justify the higher initial investment in long-term or specialized uses. Availability of PVC foam is generally more limited compared to closed-cell foam, impacting procurement speed and overall project timelines.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy and water resistance, making it highly efficient for flotation devices, while its environmental impact is generally lower due to lower toxic chemical emissions during production. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam, despite providing good flotation and structural strength, poses greater environmental concerns from the release of harmful chemicals such as dioxins during manufacturing and disposal. In terms of safety, closed-cell foam exhibits better resistance to water absorption and chemical exposure, reducing the risk of degradation and maintaining consistent flotation performance over time.
Choosing the Right Foam for Flotation Applications
Closed-cell foam offers superior buoyancy and water resistance, making it ideal for flotation applications that require durability and long-term exposure to moisture. Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) foam provides excellent structural strength and chemical resistance, suitable for marine environments where resistance to UV rays and saltwater is critical. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific application's buoyancy needs, environmental exposure, and mechanical requirements to ensure optimal floatation performance and longevity.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polyvinyl chloride foam for Floatation
 azmater.com
azmater.com