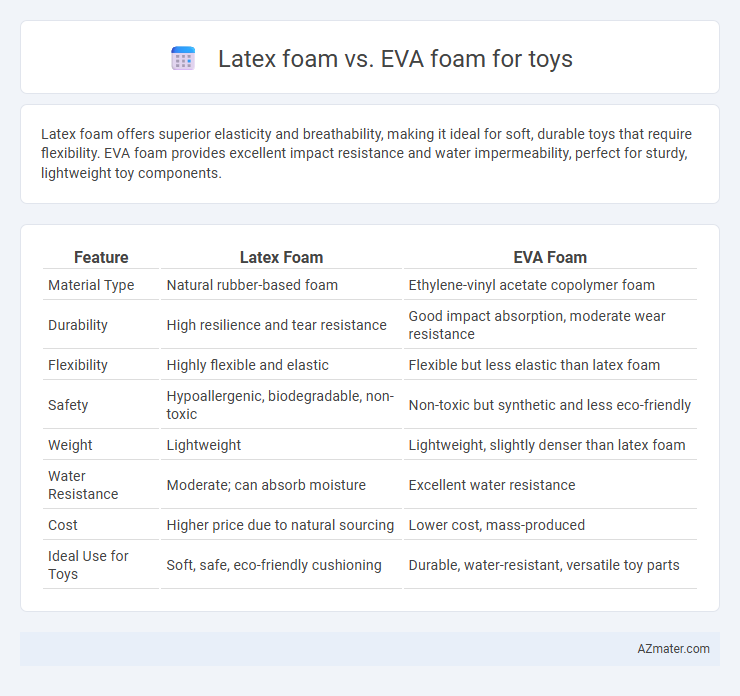
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and breathability, making it ideal for soft, durable toys that require flexibility. EVA foam provides excellent impact resistance and water impermeability, perfect for sturdy, lightweight toy components.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Latex Foam | EVA Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Natural rubber-based foam | Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer foam |
| Durability | High resilience and tear resistance | Good impact absorption, moderate wear resistance |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and elastic | Flexible but less elastic than latex foam |
| Safety | Hypoallergenic, biodegradable, non-toxic | Non-toxic but synthetic and less eco-friendly |
| Weight | Lightweight | Lightweight, slightly denser than latex foam |
| Water Resistance | Moderate; can absorb moisture | Excellent water resistance |
| Cost | Higher price due to natural sourcing | Lower cost, mass-produced |
| Ideal Use for Toys | Soft, safe, eco-friendly cushioning | Durable, water-resistant, versatile toy parts |
Introduction: Understanding Toy Foam Materials
Latex foam offers natural elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for toys requiring softness and durability, while EVA foam provides excellent shock absorption and water resistance, suitable for outdoor or water-based play. Both materials vary in density and flexibility, affecting the toy's comfort and safety features. Choosing between latex and EVA foam depends on the specific toy's functional requirements and user experience priorities.
What is Latex Foam?
Latex foam is a natural material derived from rubber tree sap, known for its exceptional elasticity, breathability, and durability. It offers superior cushioning and resilience, making it ideal for toys that require a soft, yet sturdy texture that can withstand repeated compression and movement. Compared to EVA foam, latex foam provides a more eco-friendly, hypoallergenic option with enhanced comfort and long-lasting performance.
What is EVA Foam?
EVA foam, or ethylene-vinyl acetate foam, is a lightweight, flexible material widely used in toy manufacturing due to its shock-absorbing properties and durability. Unlike latex foam, EVA foam is more resistant to water, chemicals, and UV radiation, making it ideal for outdoor and frequently handled toys. Its non-toxic nature and ease of molding into various shapes contribute to safer, more versatile toy designs.
Physical and Chemical Properties Compared
Latex foam exhibits higher elasticity and resilience, offering superior cushioning and durability compared to EVA foam, which is denser and stiffer with greater impact resistance but less flexibility. Chemically, latex foam is natural and biodegradable, composed primarily of polyisoprene polymers, whereas EVA foam is synthetic, made from ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymers, providing better chemical resistance but less environmental friendliness. Latex foam's porous structure allows for better breathability, while EVA foam's closed-cell structure enhances water resistance and longevity in toy applications.
Safety Considerations: Latex vs EVA Foam
Latex foam offers excellent biodegradability and natural hypoallergenic properties, reducing potential allergic reactions in children compared to synthetic EVA foam. EVA foam provides greater chemical stability and resistance to UV radiation, minimizing off-gassing and toxic emissions, which are critical safety factors in toy manufacturing. Both materials must comply with stringent safety standards such as EN 71 and ASTM F963 to ensure non-toxicity and durability under vigorous play conditions.
Durability and Longevity in Toys
Latex foam offers superior durability for toys due to its natural elasticity and resistance to wear, maintaining shape and softness over prolonged use. EVA foam, while lightweight and flexible, tends to compress and degrade faster under frequent handling or rough play conditions. For long-lasting toys, latex foam is often preferred as it withstands friction and repeated stress better than EVA foam.
Comfort and Sensory Experience
Latex foam offers superior softness and resilience, providing a plush, natural feel that enhances comfort and delivers a gentle cushioning ideal for toys designed for tactile engagement. EVA foam, while durable and lightweight, provides firmer support and a bouncier texture, contributing to a different sensory experience that emphasizes responsiveness and impact absorption. Both foams serve distinct purposes: latex foam is optimal for toys prioritizing soothing touch and flexibility, whereas EVA foam suits products requiring robustness and dynamic feedback.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Latex foam is derived from natural rubber, making it biodegradable and more eco-friendly compared to EVA foam, which is synthetic and non-biodegradable. The production of latex foam has a lower carbon footprint due to its renewable source, while EVA foam relies on petrochemicals, contributing to environmental pollution. Choosing latex foam for toys supports sustainability through reduced waste and less reliance on fossil fuels.
Cost and Manufacturing Differences
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and biodegradability, but it incurs higher material and production costs due to its natural origin and more complex processing requirements. EVA foam is cost-effective and easier to manufacture, with faster molding processes and lower raw material expenses, making it ideal for mass-produced toys. The choice between latex and EVA foam significantly impacts the manufacturing budget and scalability in toy production.
Choosing the Right Foam for Toy Applications
Latex foam offers superior elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for toys requiring softness and durability under repeated compression. EVA foam provides excellent shock absorption and is resistant to water and chemicals, suitable for toys exposed to outdoor or wet conditions. Selecting between latex and EVA foam depends on the toy's intended use, durability needs, and environmental exposure to ensure safety and longevity.
Infographic: Latex foam vs EVA foam for Toy
 azmater.com
azmater.com