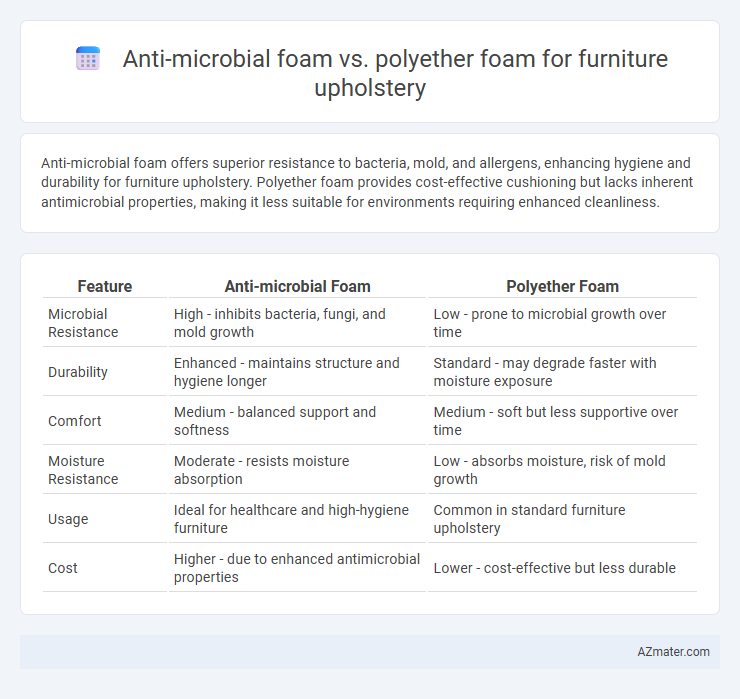
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to bacteria, mold, and allergens, enhancing hygiene and durability for furniture upholstery. Polyether foam provides cost-effective cushioning but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it less suitable for environments requiring enhanced cleanliness.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-microbial Foam | Polyether Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Microbial Resistance | High - inhibits bacteria, fungi, and mold growth | Low - prone to microbial growth over time |
| Durability | Enhanced - maintains structure and hygiene longer | Standard - may degrade faster with moisture exposure |
| Comfort | Medium - balanced support and softness | Medium - soft but less supportive over time |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate - resists moisture absorption | Low - absorbs moisture, risk of mold growth |
| Usage | Ideal for healthcare and high-hygiene furniture | Common in standard furniture upholstery |
| Cost | Higher - due to enhanced antimicrobial properties | Lower - cost-effective but less durable |
Introduction to Upholstery Foams
Upholstery foams such as anti-microbial foam and polyether foam play crucial roles in furniture comfort and durability. Anti-microbial foam incorporates agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and fungi, enhancing hygiene in high-use environments. Polyether foam offers resilience and cost-effectiveness with moderate durability, making it suitable for less intensive applications where microbial resistance is not a primary concern.
What is Anti-Microbial Foam?
Anti-microbial foam for furniture upholstery is engineered with agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and mold, enhancing hygiene and prolonging foam durability. Unlike polyether foam, which lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, this foam reduces odors and allergens, making it ideal for environments requiring high sanitation standards. Its applications are prevalent in healthcare settings, hospitality, and residential furniture where resistance to microbial contamination is essential.
Understanding Polyether Foam
Polyether foam is a widely used material in furniture upholstery due to its excellent flexibility, high resilience, and cost-effectiveness. Unlike anti-microbial foam, which is treated to resist bacterial growth, polyether foam offers superior breathability and cushioning comfort but may require additional treatments to prevent mold and odors. Its open-cell structure promotes airflow, making it an ideal choice for furniture where comfort and durability are priorities.
Key Differences Between Anti-Microbial and Polyether Foam
Anti-microbial foam is specifically treated to resist bacteria, fungi, and mold growth, making it ideal for maintaining hygiene in furniture upholstery. Polyether foam, known for its open-cell structure, offers excellent breathability and cushioning but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. The key difference lies in anti-microbial foam's protective coating versus polyether foam's focus on comfort and airflow without antimicrobial treatment.
Durability and Lifespan Comparison
Anti-microbial foam features enhanced resistance to mold, bacteria, and fungi, extending its durability in high-moisture or hygiene-sensitive environments, often surpassing the typical lifespan of standard polyether foam. Polyether foam, while cost-effective and offering moderate resilience, tends to degrade faster due to lower resistance to microbial growth and physical wear. The extended lifespan of anti-microbial foam makes it a preferred choice for upholstery in healthcare and commercial settings where long-term durability and cleanliness are critical.
Comfort and Support Levels
Anti-microbial foam provides enhanced hygiene by inhibiting bacterial growth, making it ideal for maintaining fabric freshness, while offering medium-firm comfort that balances softness and support. Polyether foam tends to have a firmer feel with lower durability but provides consistent support suitable for budget-friendly furniture upholstery. Selecting between these foams depends on prioritizing antimicrobial properties with moderate comfort or opting for cost-effective yet firmer support.
Health and Safety Considerations
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced protection against bacteria, mold, and allergens, significantly improving indoor air quality and reducing health risks for sensitive individuals. Polyether foam, while cost-effective and widely used, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it more susceptible to microbial growth and potential health hazards. Selecting anti-microbial foam for furniture upholstery prioritizes hygiene and safety, crucial for environments requiring stringent health standards such as healthcare and hospitality settings.
Cost Analysis: Anti-Microbial vs. Polyether Foam
Anti-microbial foam typically incurs higher initial costs compared to polyether foam due to specialized additives that inhibit microbial growth, enhancing durability and hygiene in upholstery applications. Polyether foam offers a more budget-friendly option, though it may require more frequent replacement due to lower resistance to bacteria and mold. When evaluating overall expenses, anti-microbial foam can lead to cost savings over time by reducing maintenance, cleaning frequency, and potential health-related issues associated with microbial contamination.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Anti-microbial foam is best suited for healthcare facilities, public seating, and environments requiring enhanced hygiene due to its resistance to bacteria, mold, and mildew. Polyether foam excels in residential and commercial furniture where cost-effectiveness and moderate durability are priorities, offering good resilience for everyday use. Selecting between these foams depends on the need for microbial resistance versus budget and comfort considerations in upholstery applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Upholstered Furniture
Selecting between anti-microbial foam and polyether foam hinges on the furniture's usage environment and durability needs. Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to bacteria, mold, and odors, making it ideal for healthcare settings or high-traffic areas requiring enhanced hygiene. Polyether foam provides cost-effective cushioning with moderate durability but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, suggesting it suits low-moisture, private spaces where budget considerations outweigh hygiene concerns.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Polyether foam for Furniture upholstery
 azmater.com
azmater.com