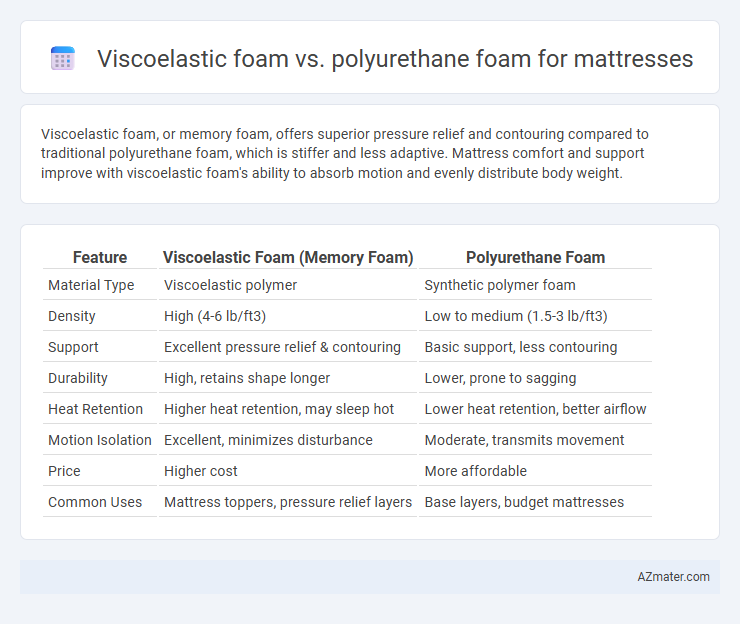
Viscoelastic foam, or memory foam, offers superior pressure relief and contouring compared to traditional polyurethane foam, which is stiffer and less adaptive. Mattress comfort and support improve with viscoelastic foam's ability to absorb motion and evenly distribute body weight.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Viscoelastic Foam (Memory Foam) | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Viscoelastic polymer | Synthetic polymer foam |
| Density | High (4-6 lb/ft3) | Low to medium (1.5-3 lb/ft3) |
| Support | Excellent pressure relief & contouring | Basic support, less contouring |
| Durability | High, retains shape longer | Lower, prone to sagging |
| Heat Retention | Higher heat retention, may sleep hot | Lower heat retention, better airflow |
| Motion Isolation | Excellent, minimizes disturbance | Moderate, transmits movement |
| Price | Higher cost | More affordable |
| Common Uses | Mattress toppers, pressure relief layers | Base layers, budget mattresses |
Introduction to Mattress Foam Materials
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, is engineered with polyurethane but enhanced by added chemicals to increase viscosity and density, providing superior contouring and pressure relief properties compared to traditional polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam comes in various densities and firmness levels, offering affordable and lightweight support but generally less conforming than viscoelastic foam. Mattress manufacturers often select viscoelastic foam for its ability to reduce motion transfer and improve spinal alignment, while polyurethane foam is favored for its durability and breathability in base foam layers.
What is Viscoelastic Foam?
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, is a type of polyurethane foam enhanced with viscoelastic polymers that provide slow recovery and high conformability to body shape. Its unique cell structure offers superior pressure relief and motion isolation compared to traditional polyurethane foam, making it ideal for mattresses that promote better spinal alignment and comfort. Viscoelastic foam responds to heat and pressure, creating a personalized sleep surface that adapts precisely to the sleeper's body.
What is Polyurethane Foam?
Polyurethane foam is a versatile synthetic material widely used in mattresses for its lightweight and cushioning properties. It is created through the chemical reaction of polyols and diisocyanates, forming a durable and flexible cellular structure that provides consistent support and pressure relief. Unlike viscoelastic foam, polyurethane foam offers faster response to body movement and typically has a more affordable price point while maintaining good breathability and resilience.
Key Differences Between Viscoelastic and Polyurethane Foam
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, offers superior contouring and pressure relief by responding to body heat and weight, whereas polyurethane foam tends to be firmer and less adaptive. Viscoelastic foam typically provides better motion isolation and durability, making it ideal for reducing partner disturbance and long-term support. Polyurethane foam is generally more affordable and available in varying densities but lacks the viscoelastic foam's ability to conform closely to the sleeper's body shape.
Comfort and Support Comparison
Viscoelastic foam, also known as memory foam, offers superior comfort by conforming closely to body contours and relieving pressure points, making it ideal for individuals seeking personalized support and pain relief. Polyurethane foam provides a firmer, more buoyant support with quicker response time, which benefits those who prefer a traditional mattress feel and enhanced spinal alignment. The key difference lies in viscoelastic foam's ability to absorb and distribute weight evenly, whereas polyurethane foam delivers consistent resilience and durability for long-term support.
Durability and Longevity of Each Foam
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, offers superior durability due to its dense structure and ability to return to its original shape after compression, typically lasting between 7 to 10 years. Polyurethane foam, although more affordable and lightweight, tends to degrade faster under constant use, often showing signs of wear such as sagging and loss of support within 3 to 5 years. The high-density variants of polyurethane foam improve lifespan but generally do not match the longevity and resilience of viscoelastic foam used in premium mattresses.
Temperature Regulation and Breathability
Viscoelastic foam, also known as memory foam, typically retains heat due to its dense structure, which can lead to reduced breathability and warmer sleeping conditions. Polyurethane foam, especially open-cell varieties, offers better air circulation and temperature regulation by allowing heat to dissipate more effectively throughout the mattress. Choosing polyurethane foam enhances breathability and cooler sleep, while viscoelastic foam excels in contouring but may require gel infusions or ventilation technology to improve temperature control.
Motion Isolation Capabilities
Viscoelastic foam, commonly known as memory foam, excels in motion isolation by contouring to the body's shape and absorbing movement, minimizing disturbances from a sleeping partner. Polyurethane foam, while adaptable and supportive, typically lacks the same degree of motion absorption due to its denser and more elastic structure. For sleepers prioritizing reduced motion transfer, viscoelastic foam mattresses offer superior performance, enhancing overall sleep quality.
Price and Value Considerations
Viscoelastic foam mattresses typically cost 20-30% more than polyurethane foam due to superior pressure relief and contouring properties. Polyurethane foam offers a budget-friendly option with decent durability, but it lacks the adaptive comfort and motion isolation that viscoelastic foam provides. For buyers prioritizing long-term value, viscoelastic foam delivers enhanced sleep quality and longevity, justifying the higher initial investment despite the price difference.
Choosing the Best Foam for Your Mattress Needs
Viscoelastic foam, known for its superior pressure relief and contouring ability, adapts to body shape and temperature, making it ideal for individuals seeking enhanced comfort and support. Polyurethane foam offers a firmer, more affordable option with quicker response times and greater durability, suitable for those who prefer a sturdier mattress with less motion transfer. Selecting the best foam involves considering factors such as sleeping position, weight distribution, and desired firmness to ensure optimal spinal alignment and personalized comfort.
Infographic: Viscoelastic foam vs Polyurethane foam for Mattress
 azmater.com
azmater.com