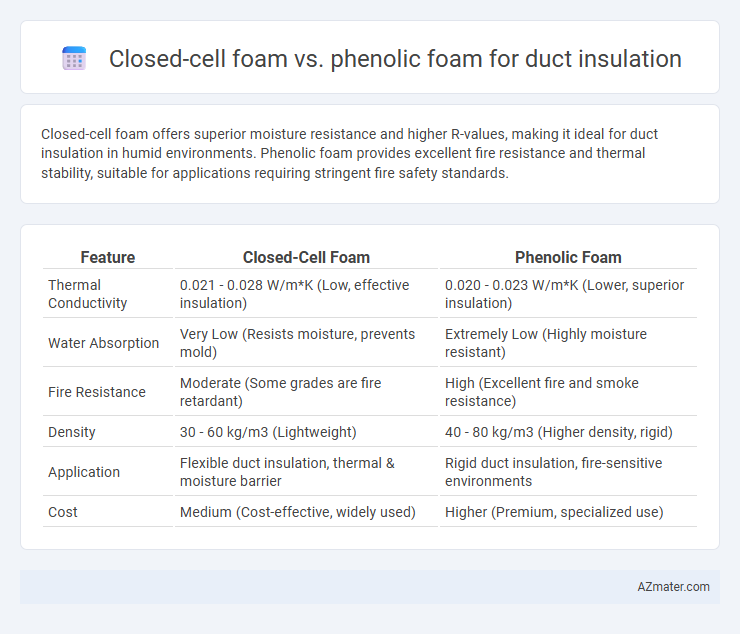
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and higher R-values, making it ideal for duct insulation in humid environments. Phenolic foam provides excellent fire resistance and thermal stability, suitable for applications requiring stringent fire safety standards.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Closed-Cell Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.021 - 0.028 W/m*K (Low, effective insulation) | 0.020 - 0.023 W/m*K (Lower, superior insulation) |
| Water Absorption | Very Low (Resists moisture, prevents mold) | Extremely Low (Highly moisture resistant) |
| Fire Resistance | Moderate (Some grades are fire retardant) | High (Excellent fire and smoke resistance) |
| Density | 30 - 60 kg/m3 (Lightweight) | 40 - 80 kg/m3 (Higher density, rigid) |
| Application | Flexible duct insulation, thermal & moisture barrier | Rigid duct insulation, fire-sensitive environments |
| Cost | Medium (Cost-effective, widely used) | Higher (Premium, specialized use) |
Introduction to Duct Insulation Materials
Closed-cell foam offers high thermal resistance and moisture impermeability, making it ideal for HVAC duct insulation in both residential and commercial applications. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and low smoke emission, which enhances safety in duct systems within industrial environments. Selecting between these materials depends on specific insulation performance requirements, fire safety standards, and environmental conditions of the installation site.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a rigid, high-density insulation material composed of numerous sealed cells that provide superior thermal resistance and moisture barrier properties, making it ideal for duct insulation applications. Its closed-cell structure prevents water absorption and offers enhanced structural stability compared to phenolic foam, which is semi-rigid with open-cell properties. The superior R-value per inch of closed-cell foam ensures efficient energy savings and improved HVAC system performance in both commercial and residential ductwork.
What is Phenolic Foam?
Phenolic foam is a rigid, high-performance insulation material characterized by its low thermal conductivity and excellent fire resistance properties, making it ideal for duct insulation. Unlike closed-cell foam, phenolic foam offers superior smoke and flame retardancy due to its unique chemical structure derived from phenol-formaldehyde resin. Its closed-cell composition also provides effective moisture resistance and structural integrity, enhancing energy efficiency and safety in HVAC systems.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Closed-cell foam insulation offers superior thermal performance due to its low thermal conductivity, typically around 0.02-0.03 W/m*K, which minimizes heat transfer and improves energy efficiency in duct systems. Phenolic foam also provides excellent thermal resistance with thermal conductivity values ranging from 0.021 to 0.027 W/m*K, but its closed-cell structure combined with inherent fire-retardant properties makes it ideal for applications demanding higher fire safety. When comparing both, closed-cell foam excels in moisture resistance and durability, while phenolic foam balances thermal insulation with enhanced fire performance, influencing the choice based on specific duct insulation requirements.
Fire Resistance and Safety Properties
Closed-cell foam for duct insulation offers good thermal resistance but has moderate fire resistance, often producing toxic smoke during combustion. Phenolic foam excels in fire safety with superior fire retardant properties, low smoke emission, and self-extinguishing characteristics, making it ideal for high fire safety requirements. The choice between the two depends on balancing insulation efficiency with stringent fire resistance and safety standards in HVAC systems.
Moisture and Water Vapor Resistance
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture and water vapor resistance due to its dense, impermeable structure, effectively preventing condensation and mold growth in duct insulation applications. Phenolic foam also provides excellent thermal insulation with moderate vapor resistance but tends to absorb more moisture over time, potentially compromising its performance. Selecting closed-cell foam is preferred in high-humidity environments to ensure long-term durability and moisture control in HVAC duct systems.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior mechanical strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for duct insulation in environments requiring robust physical protection. Phenolic foam offers excellent fire resistance and thermal insulation but generally has lower mechanical strength and is more brittle compared to closed-cell foam. For long-term durability in high-stress applications, closed-cell foam is preferred due to its resilience against compression and deformation.
Cost Analysis and Long-Term Value
Closed-cell foam typically offers lower upfront costs compared to phenolic foam, making it a budget-friendly option for duct insulation. Phenolic foam, despite higher initial expenses, provides superior thermal insulation and fire resistance, resulting in reduced energy bills and maintenance over time. The long-term value of phenolic foam often outweighs its cost due to enhanced durability and efficiency, leading to greater savings in lifecycle costs.
Installation and Handling Considerations
Closed-cell foam offers easy handling due to its lightweight and flexible nature, allowing quick and secure installation around complex ductwork without requiring specialized tools. Phenolic foam, while rigid and brittle, demands careful handling to avoid cracking and typically requires additional protective coverings during installation to prevent damage and maintain thermal performance. Both materials necessitate proper personal protective equipment (PPE) to ensure safety from dust and fibers during cutting and fitting processes.
Which Foam is Best for Duct Insulation?
Closed-cell foam offers superior thermal insulation with an R-value typically between 5 to 7 per inch, providing excellent moisture resistance and structural rigidity ideal for duct insulation. Phenolic foam features a high R-value around 4.5 to 7 per inch and exceptional fire resistance due to its low smoke and flame spread characteristics, making it suitable for duct systems requiring enhanced fire safety. Choosing the best foam depends on specific duct insulation needs: closed-cell foam excels in moisture control and durability, while phenolic foam is preferred where fire performance is paramount.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Phenolic foam for Duct insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com