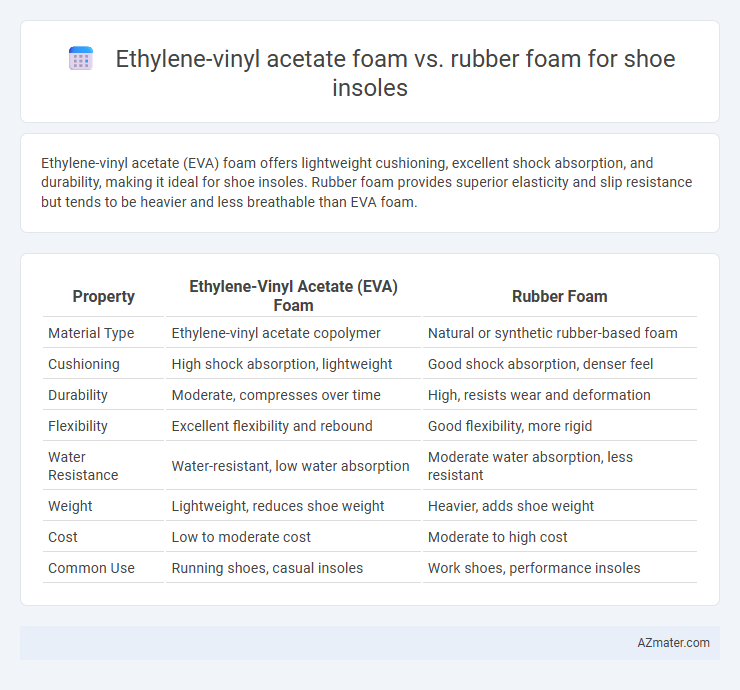
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers lightweight cushioning, excellent shock absorption, and durability, making it ideal for shoe insoles. Rubber foam provides superior elasticity and slip resistance but tends to be heavier and less breathable than EVA foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam | Rubber Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Ethylene-vinyl acetate copolymer | Natural or synthetic rubber-based foam |
| Cushioning | High shock absorption, lightweight | Good shock absorption, denser feel |
| Durability | Moderate, compresses over time | High, resists wear and deformation |
| Flexibility | Excellent flexibility and rebound | Good flexibility, more rigid |
| Water Resistance | Water-resistant, low water absorption | Moderate water absorption, less resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight, reduces shoe weight | Heavier, adds shoe weight |
| Cost | Low to moderate cost | Moderate to high cost |
| Common Use | Running shoes, casual insoles | Work shoes, performance insoles |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam and rubber foam are popular materials used in shoe insoles due to their cushioning and shock-absorbing properties. EVA foam offers lightweight flexibility and excellent energy return, making it suitable for athletic and casual footwear, while rubber foam provides superior durability and slip resistance, often preferred in work and outdoor shoes. Choosing between EVA and rubber foam depends on the required comfort, support, and specific application within the footwear industry.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible material known for its excellent shock absorption and cushioning properties, making it ideal for shoe insoles. Compared to rubber foam, EVA offers superior compression resistance and resilience, enhancing comfort and durability in footwear applications. EVA foam's closed-cell structure also provides better water resistance and breathability, contributing to overall foot comfort.
Understanding Rubber Foam Properties
Rubber foam offers superior resilience, durability, and excellent abrasion resistance, making it ideal for shoe insoles that require long-lasting cushioning and impact absorption. Its closed-cell structure provides enhanced water resistance and thermal insulation compared to ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam, which is softer but less durable. Rubber foam's elasticity supports better energy return during movement, contributing to improved comfort and foot support in athletic and casual footwear applications.
Cushioning and Comfort Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning with its lightweight, flexible structure that effectively absorbs shock, making it ideal for shoe insoles requiring enhanced comfort during prolonged wear. Rubber foam provides excellent durability and resilience but tends to be denser and less responsive, which may result in heavier insoles with reduced cushioning performance. EVA foam's higher energy return and softness contribute significantly to improved comfort, especially in athletic and casual footwear applications.
Durability and Longevity Differences
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior resilience and long-term cushioning, maintaining its shape and shock absorption over extended use, making it highly durable for shoe insoles. Rubber foam, while providing excellent initial comfort and grip, tends to compress and degrade faster under repetitive stress, resulting in reduced longevity compared to EVA. The chemical stability and lightweight nature of EVA contribute significantly to its enhanced durability, making it a preferred choice for high-performance insoles.
Shock Absorption in EVA vs Rubber Foam
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption compared to rubber foam due to its lightweight and flexible cellular structure, which efficiently disperses impact forces during walking or running. EVA's closed-cell composition provides excellent cushioning and energy return, reducing joint stress more effectively than the denser, less compressible rubber foam. Rubber foam, while durable and resilient, typically absorbs less shock and can feel stiffer, making EVA the preferred choice for enhanced comfort and impact protection in shoe insoles.
Breathability and Moisture Management
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior breathability and moisture management compared to rubber foam, due to its open-cell structure that enhances air circulation and wicks away sweat effectively. EVA foam's lightweight and flexible nature allows for better ventilation inside the shoe, reducing heat buildup and keeping feet dry. In contrast, rubber foam typically has a closed-cell structure, limiting airflow and trapping moisture, which can lead to discomfort and increased odor in shoe insoles.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a lightweight solution for shoe insoles, typically weighing less than rubber foam, which enhances overall comfort and reduces foot fatigue. EVA foam exhibits superior flexibility due to its cellular structure, allowing better shock absorption and cushioning compared to the denser, more rigid rubber foam. This flexibility in EVA foam supports dynamic foot movement, while rubber foam, although durable, tends to provide stiffer support with less adaptability to foot contours.
Cost and Environmental Impact
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam insoles generally offer a lower-cost option compared to rubber foam, making them popular for budget-friendly footwear manufacturing. EVA foam is lightweight and recyclable, contributing to a reduced environmental footprint, whereas rubber foam, often derived from natural or synthetic rubber, may involve more resource-intensive production and limited recyclability. Cost-efficiency combined with better sustainability profiles positions EVA foam as a more eco-friendly choice for shoe insoles in mass production.
Choosing the Right Foam: EVA or Rubber for Shoe Insoles
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning, lightweight durability, and excellent shock absorption, making it ideal for athletic and casual shoe insoles. Rubber foam provides Greater density, enhanced resilience, and excellent slip resistance, suitable for heavy-duty or work shoe applications. Selecting between EVA or rubber foam depends on the balance of comfort, support, and durability required for specific footwear needs.
Infographic: Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam vs Rubber foam for Shoe insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com