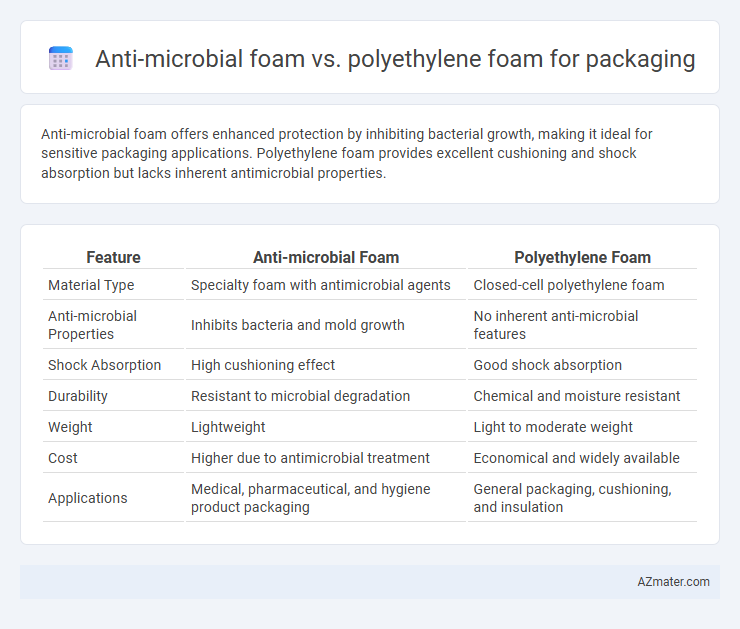
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced protection by inhibiting bacterial growth, making it ideal for sensitive packaging applications. Polyethylene foam provides excellent cushioning and shock absorption but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-microbial Foam | Polyethylene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Specialty foam with antimicrobial agents | Closed-cell polyethylene foam |
| Anti-microbial Properties | Inhibits bacteria and mold growth | No inherent anti-microbial features |
| Shock Absorption | High cushioning effect | Good shock absorption |
| Durability | Resistant to microbial degradation | Chemical and moisture resistant |
| Weight | Lightweight | Light to moderate weight |
| Cost | Higher due to antimicrobial treatment | Economical and widely available |
| Applications | Medical, pharmaceutical, and hygiene product packaging | General packaging, cushioning, and insulation |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Packaging foams, including anti-microbial foam and polyethylene foam, serve crucial roles in protecting goods by providing cushioning and shock absorption. Anti-microbial foam integrates agents that inhibit bacterial growth, ideal for sensitive or medical products requiring hygiene control. Polyethylene foam offers excellent durability, water resistance, and cost-effectiveness, making it a widely used option for general packaging needs.
Understanding Anti-Microbial Foam
Anti-microbial foam incorporates agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, fungi, and mold, enhancing hygiene and product safety during packaging and storage. Polyethylene foam, while excellent for cushioning and shock absorption, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, making it less effective in environments where contamination control is critical. Understanding the benefits of anti-microbial foam is essential for industries like pharmaceuticals, food, and electronics, where maintaining sterile conditions extends product shelf life and reduces health risks.
Key Properties of Polyethylene Foam
Polyethylene foam offers excellent impact resistance, lightweight cushioning, and moisture resistance, making it an ideal choice for protective packaging. Its closed-cell structure provides superior durability and prevents absorption of liquids, unlike some anti-microbial foams that focus primarily on inhibiting microbial growth. The chemical stability and flexibility of polyethylene foam also contribute to its widespread use in packaging delicate electronics and fragile items.
Performance Comparison: Durability and Protection
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced protection against bacteria and mold, making it ideal for packaging sensitive medical and food products. Polyethylene foam provides superior durability through high impact resistance and cushioning, effectively protecting heavy or fragile items during transport. While polyethylene foam excels in shock absorption and longevity, anti-microbial foam adds a critical layer of hygienic safety without compromising basic protective functions.
Anti-Microbial Capabilities: Why They Matter
Anti-microbial foam offers superior protection against bacteria, fungi, and mold, making it ideal for packaging sensitive products like medical devices and food items. This foam type contains embedded antimicrobial agents that inhibit microbial growth, thereby extending product shelf life and maintaining hygiene standards. Polyethylene foam lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, posing higher risks of contamination in environments requiring stringent cleanliness.
Cost Analysis: Which Foam Offers Better Value?
Anti-microbial foam typically commands a higher upfront cost due to its specialized treatment and enhanced protection against bacterial growth, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and food packaging sectors. Polyethylene foam, being more affordable and widely available, offers cost-effective cushioning and protection for general packaging needs without antimicrobial properties. When balancing price versus functionality, polyethylene foam provides better value for standard applications, whereas anti-microbial foam justifies its premium price through added hygiene benefits crucial for sensitive or sterile product shipments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Anti-microbial foam often contains chemical additives that can hinder biodegradability and complicate recycling processes, resulting in a higher environmental footprint compared to polyethylene foam. Polyethylene foam, while traditionally derived from non-renewable petroleum sources, offers better recyclability and lower toxicity, making it a more sustainable choice when recycled within circular economy frameworks. Innovations in bio-based polyethylene foam further enhance sustainability by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and improving end-of-life environmental outcomes.
Industry Applications and Suitability
Anti-microbial foam offers superior protection in medical, pharmaceutical, and food packaging industries by inhibiting microbial growth, making it ideal for sensitive and sterile product transportation. Polyethylene foam excels in cushioning, impact absorption, and moisture resistance, often utilized in electronics, automotive, and consumer goods packaging due to its durability and lightweight nature. The choice between these foams depends on application-specific requirements such as hygiene standards, protection levels, and environmental conditions.
Health and Safety Considerations
Anti-microbial foam packaging incorporates agents that inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and fungi, reducing the risk of contamination and enhancing product hygiene during storage and transport. Polyethylene foam, while offering excellent cushioning and moisture resistance, lacks inherent antimicrobial properties, potentially allowing microbial growth on its surface in certain environments. Choosing anti-microbial foam over polyethylene foam improves health and safety by minimizing microbial hazards, especially critical for medical, pharmaceutical, and food packaging applications.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Anti-microbial foam provides enhanced protection by inhibiting the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew, making it ideal for packaging sensitive items such as medical devices and food products. Polyethylene foam offers excellent shock absorption, water resistance, and durability, suited for general packaging of electronics and fragile goods. Selecting the right foam depends on the specific requirements of your product, including hygiene, cushioning, and environmental conditions.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Polyethylene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com