Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and environmental sustainability compared to polystyrene foam, making it an advanced alternative for protective packaging. Its lightweight nature and enhanced shock absorption properties significantly reduce damage risks during shipping while supporting eco-friendly disposal.
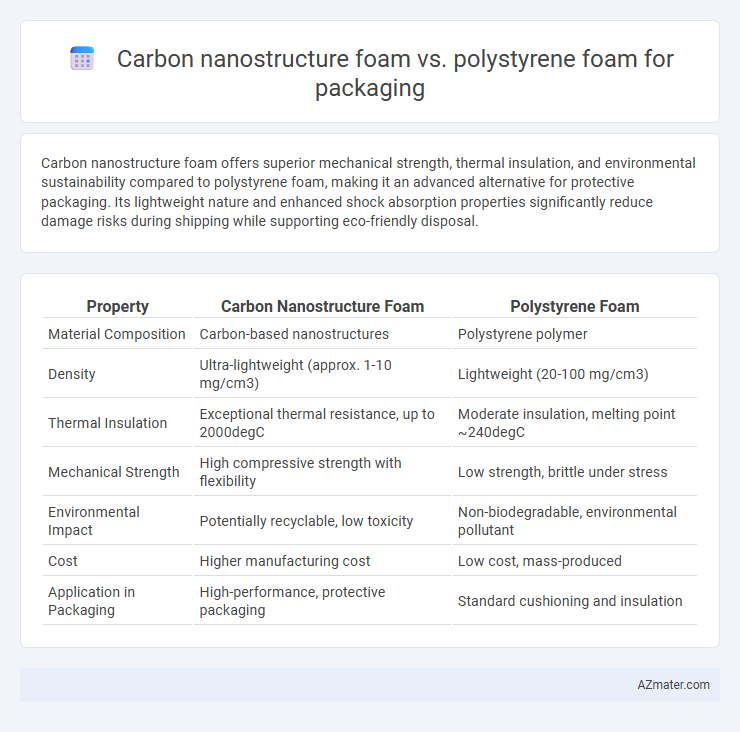
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based nanostructures | Polystyrene polymer |
| Density | Ultra-lightweight (approx. 1-10 mg/cm3) | Lightweight (20-100 mg/cm3) |
| Thermal Insulation | Exceptional thermal resistance, up to 2000degC | Moderate insulation, melting point ~240degC |
| Mechanical Strength | High compressive strength with flexibility | Low strength, brittle under stress |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially recyclable, low toxicity | Non-biodegradable, environmental pollutant |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Low cost, mass-produced |
| Application in Packaging | High-performance, protective packaging | Standard cushioning and insulation |
Introduction to Advanced Packaging Materials
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and lightweight properties compared to traditional polystyrene foam, making it an innovative solution in advanced packaging materials. Its unique nanoscale architecture enhances durability and impact resistance, reducing product damage during transportation and storage. Polystyrene foam remains widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacture, but carbon nanostructure foam represents a significant advancement in sustainable and high-performance packaging solutions.
Overview of Carbon Nanostructure Foam
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and superior thermal insulation compared to traditional polystyrene foam, making it ideal for advanced packaging solutions. Its unique interconnected network of carbon nanotubes provides enhanced mechanical resilience, electrical conductivity, and environmental sustainability. This foam's ability to withstand extreme temperatures and resist chemical degradation positions it as a revolutionary material in protective packaging applications.
Properties of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam is a lightweight, rigid material known for its excellent shock absorption and thermal insulation properties, making it widely used in packaging applications to protect fragile items. Its closed-cell structure provides resistance to moisture and chemicals, ensuring durability during transportation and storage. Despite its advantages, polystyrene foam has limited environmental biodegradability compared to emerging materials like carbon nanostructure foam.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits significantly higher mechanical strength compared to polystyrene foam, with tensile strength values often surpassing 50 MPa, whereas polystyrene typically ranges between 0.2 to 0.7 MPa. The superior stiffness and impact resistance of carbon nanostructure foam make it ideal for protecting fragile and high-value items during transportation. Moreover, its lightweight yet robust framework provides enhanced durability, reducing the risk of damage from compression and shock forces in packaging applications.
Thermal Insulation Capabilities
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal insulation capabilities compared to polystyrene foam due to its low thermal conductivity and high thermal stability, effectively minimizing heat transfer in packaging applications. The porous structure of carbon nanomaterials enhances thermal resistance by trapping air within nanoscale cavities, outperforming the relatively higher thermal conductivity and lower temperature tolerance of polystyrene foam. These properties make carbon nanostructure foam a more efficient and sustainable choice for thermal insulation in protective packaging solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior biodegradability and lower carbon footprint compared to traditional polystyrene foam, which is non-biodegradable and contributes significantly to plastic pollution. Polystyrene foam's persistence in landfills and ecosystems raises environmental concerns, while carbon nanostructure foam's advanced materials enable easier recycling and reduced waste accumulation. The sustainable lifecycle of carbon nanostructure foam aligns with increasing regulatory pressures to adopt eco-friendly packaging alternatives.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Analysis
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical properties and thermal insulation compared to traditional polystyrene foam, potentially reducing material volume and shipping costs. Despite higher initial production costs, the enhanced durability and recyclability of carbon nanostructure foam lead to lower long-term expenses and waste management fees. Economic analyses highlight improved lifecycle cost efficiency in industries prioritizing sustainability and performance over upfront savings.
Customization and Manufacturing Flexibility
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior customization and manufacturing flexibility compared to polystyrene foam due to its tunable nanostructure properties and ability to be engineered at the molecular level for specific packaging requirements. Advanced fabrication techniques such as chemical vapor deposition allow precise control over density, porosity, and mechanical strength, enabling bespoke design adaptations not achievable with traditional polystyrene foam. In contrast, polystyrene foam manufacturing relies on standardized molding processes with limited scope for material property modifications, restricting its customization potential for specialty packaging applications.
Safety and Regulatory Considerations
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior fire resistance and lower toxicity compared to polystyrene foam, significantly reducing health hazards during manufacturing and disposal. Polystyrene foam is well-documented for its flammability and release of harmful styrene monomers, which raise concerns under various environmental and safety regulations such as the U.S. EPA and EU REACH guidelines. Regulatory agencies increasingly scrutinize polystyrene's environmental impact, whereas carbon nanostructure foam faces emerging standards focusing on nanomaterial safety, requiring thorough risk assessments for safe commercial use in packaging.
Future Trends in Packaging Foams
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical strength, thermal insulation, and biodegradability compared to traditional polystyrene foam, making it a promising material for sustainable packaging solutions. Emerging trends highlight an increased investment in carbon-based foams that enhance recyclability and reduce environmental impact while maintaining lightweight protection. Advances in nanotechnology enable scalable production methods, positioning carbon nanostructure foam as a key innovation in future eco-friendly packaging developments.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com