Polystyrene foam offers high insulation with low moisture absorption, ideal for lightweight building panels, while phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and thermal stability, making it suitable for fire-rated construction applications. Both materials optimize energy efficiency, but choice depends on prioritizing fire safety or cost-effectiveness.
Table of Comparison
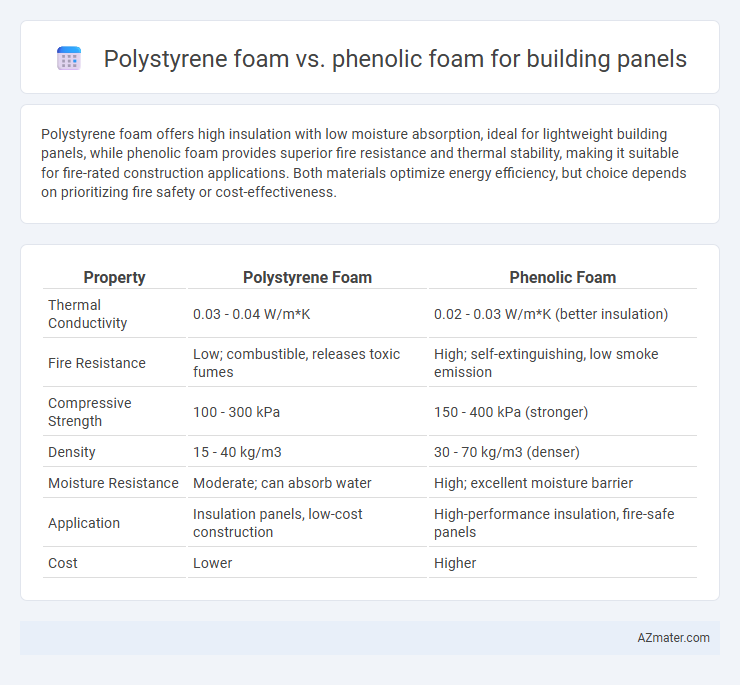
| Property | Polystyrene Foam | Phenolic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | 0.03 - 0.04 W/m*K | 0.02 - 0.03 W/m*K (better insulation) |
| Fire Resistance | Low; combustible, releases toxic fumes | High; self-extinguishing, low smoke emission |
| Compressive Strength | 100 - 300 kPa | 150 - 400 kPa (stronger) |
| Density | 15 - 40 kg/m3 | 30 - 70 kg/m3 (denser) |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate; can absorb water | High; excellent moisture barrier |
| Application | Insulation panels, low-cost construction | High-performance insulation, fire-safe panels |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Introduction to Building Panel Insulation Materials
Polystyrene foam and phenolic foam are widely used insulation materials for building panels due to their thermal performance and moisture resistance. Polystyrene foam offers excellent rigidity and cost-effectiveness with a typical R-value of 4 to 5 per inch, making it ideal for standard thermal insulation. Phenolic foam provides superior fire resistance and lower smoke emission while maintaining a comparable R-value, enhancing safety and energy efficiency in building envelope systems.
Overview of Polystyrene Foam
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in building panels, offers excellent thermal insulation properties with a typical R-value of about 4 per inch, making it efficient for energy conservation in construction. Its lightweight, moisture-resistant nature and ease of fabrication contribute to widespread use in both residential and commercial buildings. Compared to phenolic foam, polystyrene foam generally provides lower fire resistance but offers cost-effective insulation solutions with good structural performance.
Overview of Phenolic Foam
Phenolic foam is a high-performance insulation material characterized by its superior fire resistance, low smoke emission, and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for building panels in fire-sensitive environments. Compared to polystyrene foam, phenolic foam offers enhanced structural rigidity and better dimensional stability over time, ensuring long-lasting panel integrity. Its closed-cell structure provides excellent moisture resistance while maintaining a low environmental impact due to its formaldehyde-free resin composition.
Thermal Performance Comparison
Polystyrene foam exhibits a thermal conductivity of approximately 0.03-0.04 W/m*K, offering effective insulation for building panels but with moderate fire resistance. Phenolic foam demonstrates superior thermal performance with a lower thermal conductivity around 0.02-0.03 W/m*K, enhancing energy efficiency by reducing heat transfer more effectively. Its closed-cell structure and inherent fire-retardant properties make phenolic foam a preferred choice for high-performance thermal insulation in building applications.
Fire Resistance and Safety Analysis
Phenolic foam exhibits superior fire resistance compared to polystyrene foam, with a higher Limiting Oxygen Index (LOI) typically above 30%, indicating enhanced flame retardancy and self-extinguishing properties. Polystyrene foam, although lightweight and cost-effective, is highly combustible and produces toxic smoke and fumes during combustion, raising safety concerns in building panel applications. Building codes and safety standards, such as NFPA 285 and ASTM E84, often favor phenolic foam panels for critical fire safety requirements due to their lower heat release rate and reduced smoke development.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
Polystyrene foam offers moderate moisture resistance but can absorb water over time, compromising its insulation properties and structural integrity in building panels. Phenolic foam exhibits superior moisture resistance due to its closed-cell structure, maintaining durability and thermal performance even in high-humidity environments. The long-term durability of phenolic foam panels makes them ideal for applications requiring consistent performance against moisture exposure and potential mold growth.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Polystyrene foam, widely used in building panels, has significant environmental drawbacks due to its non-biodegradable nature and reliance on petrochemical resources, leading to persistent waste and higher carbon emissions during production. Phenolic foam offers superior sustainability benefits with its lower global warming potential, excellent thermal insulation reducing energy consumption, and greater fire resistance, which contributes to longer building lifespan and less material replacement. Incorporating phenolic foam panels supports eco-friendly construction by minimizing environmental footprint while enhancing building energy efficiency.
Cost Considerations and Value
Polystyrene foam panels generally offer lower upfront costs compared to phenolic foam, making them a budget-friendly insulation choice for building projects. Phenolic foam, while more expensive, provides superior thermal performance and fire resistance, potentially reducing long-term energy costs and enhancing building safety. Evaluating initial price against lifecycle energy savings and durability is crucial to determine the best value in insulation panel selection.
Installation and Handling Differences
Polystyrene foam panels are lightweight and easy to cut, allowing for faster installation but require careful handling due to their brittle nature. Phenolic foam panels offer superior fire resistance and dimensional stability, demanding precise fitting and skilled labor for seamless integration. Installation of phenolic foam often involves specialized adhesives and protective measures to maintain its integrity during handling.
Best Applications for Each Material
Polystyrene foam excels in insulation for residential walls, roofs, and floors due to its lightweight structure and moisture resistance, making it ideal for energy-efficient homes and commercial buildings. Phenolic foam offers superior fire resistance and thermal performance, perfectly suited for high-rise buildings, industrial facilities, and environments with stringent fire safety requirements. Choosing between polystyrene and phenolic foam depends on balancing insulation needs with fire code compliance and structural demands.
Infographic: Polystyrene foam vs Phenolic foam for Building Panel
 azmater.com
azmater.com