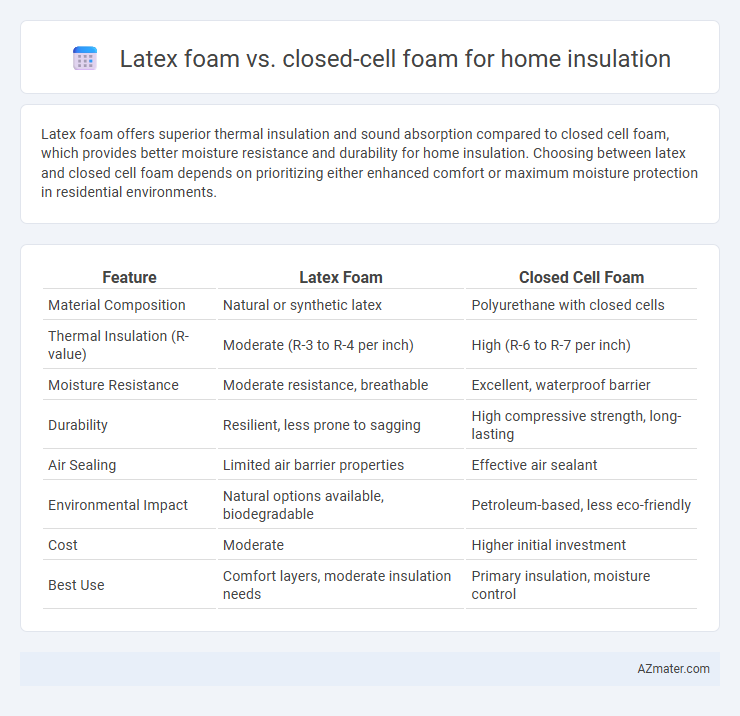
Latex foam offers superior thermal insulation and sound absorption compared to closed cell foam, which provides better moisture resistance and durability for home insulation. Choosing between latex and closed cell foam depends on prioritizing either enhanced comfort or maximum moisture protection in residential environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Latex Foam | Closed Cell Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Natural or synthetic latex | Polyurethane with closed cells |
| Thermal Insulation (R-value) | Moderate (R-3 to R-4 per inch) | High (R-6 to R-7 per inch) |
| Moisture Resistance | Moderate resistance, breathable | Excellent, waterproof barrier |
| Durability | Resilient, less prone to sagging | High compressive strength, long-lasting |
| Air Sealing | Limited air barrier properties | Effective air sealant |
| Environmental Impact | Natural options available, biodegradable | Petroleum-based, less eco-friendly |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher initial investment |
| Best Use | Comfort layers, moderate insulation needs | Primary insulation, moisture control |
Understanding Latex Foam and Closed Cell Foam
Latex foam offers superior breathability and flexibility, making it an excellent choice for home insulation where moisture control and comfort are priorities. Closed cell foam provides a high R-value per inch and acts as both an insulator and an air barrier, effectively preventing air leaks and moisture infiltration in tight building envelopes. Understanding these differences helps in selecting the right foam type based on insulation performance, moisture resistance, and installation requirements.
Key Differences Between Latex Foam and Closed Cell Foam
Latex foam offers superior breathability and natural hypoallergenic properties, making it ideal for maintaining indoor air quality in home insulation. Closed cell foam provides higher R-value per inch, exceptional moisture resistance, and structural rigidity, which enhances energy efficiency and prevents water infiltration. The primary differences lie in latex foam's flexibility and eco-friendly composition versus closed cell foam's durability and enhanced insulation performance.
Insulation Performance: R-Value Comparison
Latex foam typically has an R-value of around 3.5 to 4.0 per inch, providing moderate thermal resistance suitable for home insulation. Closed cell foam offers a higher R-value, usually between 6.0 and 7.0 per inch, making it more effective at reducing heat transfer and improving energy efficiency. The superior density and low permeability of closed cell foam contribute to its enhanced insulation performance compared to latex foam.
Moisture Resistance: Which Foam Protects Better?
Latex foam offers superior moisture resistance compared to closed cell foam, making it more effective in preventing mold and mildew growth in home insulation. Its natural elasticity and open-cell structure allow it to repel water while maintaining breathability. Closed cell foam, although denser and resistant to water absorption, can trap moisture over time, potentially leading to reduced insulation performance and structural damage.
Air Sealing Capability: Keeping Your Home Airtight
Latex foam offers moderate air sealing properties due to its open-cell structure, allowing some air movement and moisture vapor transmission, which can help regulate indoor humidity. Closed cell foam provides superior air sealing capabilities by creating a dense, impermeable barrier that prevents air infiltration and exfiltration, enhancing energy efficiency and indoor comfort. Its high R-value per inch and moisture resistance make closed cell foam an ideal choice for airtight home insulation applications.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Savings
Latex foam insulation offers superior energy efficiency due to its excellent thermal resistance (R-value) and natural elasticity, reducing heat transfer and maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Closed cell foam, with a higher R-value per inch and its dense structure, provides robust air and moisture barriers that enhance energy savings by minimizing heat loss and preventing drafts. While closed cell foam has a higher upfront cost, its long-term energy savings and durability often outweigh the initial investment compared to latex foam's moderate cost and performance benefits.
Installation Process and Considerations
Latex foam installation for home insulation requires precise cutting and fitting due to its flexible, porous structure that allows for breathability and moisture regulation, making it ideal for interior walls and soundproofing. Closed cell foam demands professional spray application to create a dense, rigid barrier that offers superior thermal resistance and moisture protection, suitable for exterior walls and foundations. Consider the latex foam's ease of DIY installation versus the closed cell foam's superior durability and potential higher cost and complexity in application.
Health and Environmental Impact
Latex foam insulation is derived from natural rubber, offering superior breathability and hypoallergenic properties that reduce indoor air pollutants and mold growth, thus enhancing indoor air quality and occupant health. Closed cell foam, typically made from petroleum-based materials like polyurethane, provides excellent moisture and air barriers but may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that can affect respiratory health during and shortly after installation. Environmentally, latex foam is more sustainable due to its biodegradability and renewable material sources, whereas closed cell foam has a higher carbon footprint and slower decomposition, posing long-term environmental concerns.
Longevity and Maintenance Requirements
Latex foam offers superior longevity due to its natural resistance to mold, mildew, and degradation, making it ideal for home insulation with minimal maintenance. Closed cell foam provides excellent moisture resistance and structural strength but may degrade faster under prolonged UV exposure, requiring occasional inspection and maintenance to ensure optimal performance. Both foams enhance energy efficiency, but latex foam typically demands less upkeep over time, resulting in lower long-term maintenance costs.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Home Insulation Needs
Latex foam offers excellent breathability and flexibility, making it ideal for cushioning and sound insulation in residential settings. Closed cell foam provides superior thermal resistance with its high R-value per inch and moisture resistance, ensuring effective energy efficiency and protection against water infiltration. Choosing the right foam depends on prioritizing moisture control and insulation performance, where closed cell excels for damp environments, while latex foam suits applications requiring comfort and airflow.
Infographic: Latex foam vs Closed cell foam for Home Insulation
 azmater.com
azmater.com