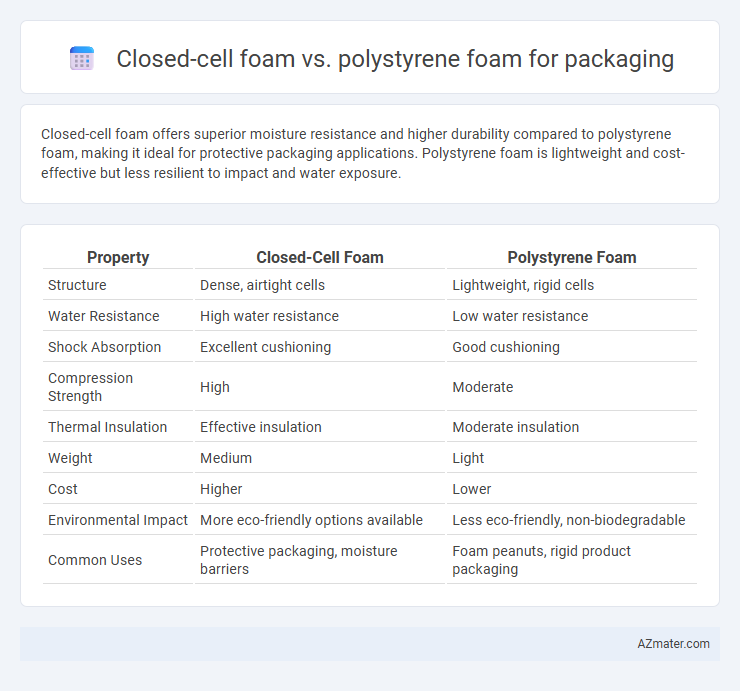
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and higher durability compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for protective packaging applications. Polystyrene foam is lightweight and cost-effective but less resilient to impact and water exposure.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Closed-Cell Foam | Polystyrene Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Dense, airtight cells | Lightweight, rigid cells |
| Water Resistance | High water resistance | Low water resistance |
| Shock Absorption | Excellent cushioning | Good cushioning |
| Compression Strength | High | Moderate |
| Thermal Insulation | Effective insulation | Moderate insulation |
| Weight | Medium | Light |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Environmental Impact | More eco-friendly options available | Less eco-friendly, non-biodegradable |
| Common Uses | Protective packaging, moisture barriers | Foam peanuts, rigid product packaging |
Introduction to Packaging Foams
Closed-cell foam and polystyrene foam are widely used materials in packaging due to their excellent cushioning and insulation properties. Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance, higher compressive strength, and better durability compared to polystyrene, making it ideal for delicate or heavy items. Polystyrene foam is lightweight, cost-effective, and provides good thermal insulation, often preferred for disposable packaging and thermal protection of products during transit.
What is Closed-Cell Foam?
Closed-cell foam is a type of insulation material characterized by its dense, compact structure where each cell is completely enclosed and isolated from neighboring cells, providing superior moisture resistance and high compressive strength. Unlike polystyrene foam, which is often rigid but less flexible, closed-cell foam offers enhanced durability and excellent thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for protective packaging that requires shock absorption and moisture barriers. Its versatility includes applications in cushioning delicate items and protecting electronics due to its ability to resist deformation under pressure.
What is Polystyrene Foam?
Polystyrene foam, commonly used in packaging, is a lightweight, rigid material made from expanded polystyrene beads, offering excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties. It provides superior thermal insulation and moisture resistance compared to many other foams, making it ideal for protecting delicate items during shipping. Unlike closed-cell foam, polystyrene foam maintains its shape under pressure but is less flexible and more brittle, which can influence packaging choices based on product requirements.
Key Differences: Closed-Cell vs. Polystyrene Foam
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and higher tensile strength compared to polystyrene foam, making it ideal for packaging sensitive or fragile items requiring advanced protection. Polystyrene foam, often found in expanded (EPS) or extruded (XPS) forms, provides excellent cushioning but is more rigid and less moisture-resistant, suitable for lightweight packaging with cost-efficiency. The key differences lie in density, durability, and water absorption, with closed-cell foams delivering enhanced insulation and structural integrity over polystyrene counterparts.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Closed-cell foam exhibits superior durability and strength compared to polystyrene foam, offering enhanced resistance to impact and compression, making it ideal for protecting fragile items during shipping. Polystyrene foam, while lightweight and cost-effective, tends to be more brittle and prone to cracking under pressure, reducing its effectiveness in high-stress packaging scenarios. The denser structure of closed-cell foam provides better cushioning and long-term resilience, significantly improving product safety in transit.
Insulation and Protective Qualities
Closed-cell foam offers superior insulation due to its dense structure that prevents heat transfer and provides excellent moisture resistance, making it ideal for temperature-sensitive packaging. Polystyrene foam, known for its lightweight and rigid cell structure, excels at shock absorption and impact protection but has lower insulation effectiveness compared to closed-cell foam. Both materials provide cushioning, yet closed-cell foam's enhanced thermal insulation and water resistance make it better suited for packaging that requires temperature control and durability.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Closed-cell foam typically offers better insulation and moisture resistance compared to polystyrene foam, but its environmental impact varies based on material composition, often relying on non-biodegradable plastics. Polystyrene foam, widely used for lightweight packaging, contributes significantly to plastic pollution due to its low biodegradability and difficulty in recycling, raising concerns for sustainability. Choosing closed-cell foam with biodegradable or recycled content can improve environmental outcomes by reducing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices in packaging.
Cost Analysis: Closed-Cell Foam vs. Polystyrene
Closed-cell foam generally incurs higher initial costs than polystyrene foam due to its superior durability and insulation properties, which reduce long-term packaging expenses by minimizing product damage. Polystyrene foam offers a more cost-effective option upfront, making it suitable for bulk packaging where protection needs are moderate and budget constraints are critical. Evaluating total cost of ownership, including material, handling, and waste management, reveals that closed-cell foam often delivers better value for fragile or high-value items despite its higher price point.
Best Applications for Each Foam Type
Closed-cell foam offers superior moisture resistance and cushioning, making it ideal for packaging delicate electronics, medical devices, and perishable goods. Polystyrene foam excels in lightweight protection and thermal insulation, commonly used for packaging appliances, food containers, and shipping fragile items. Selecting the right foam depends on factors like impact absorption, environmental exposure, and temperature sensitivity specific to the product being packaged.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Packaging Needs
Closed-cell foam offers superior water resistance and cushioning, making it ideal for packaging sensitive electronics or moisture-sensitive items. Polystyrene foam, known for its lightweight and rigid structure, excels in protecting fragile products during shipping due to its high impact absorption. Selecting the right foam depends on balancing factors like product fragility, environmental exposure, and cost efficiency to ensure optimal protection and performance.
Infographic: Closed-cell foam vs Polystyrene foam for Packaging
 azmater.com
azmater.com