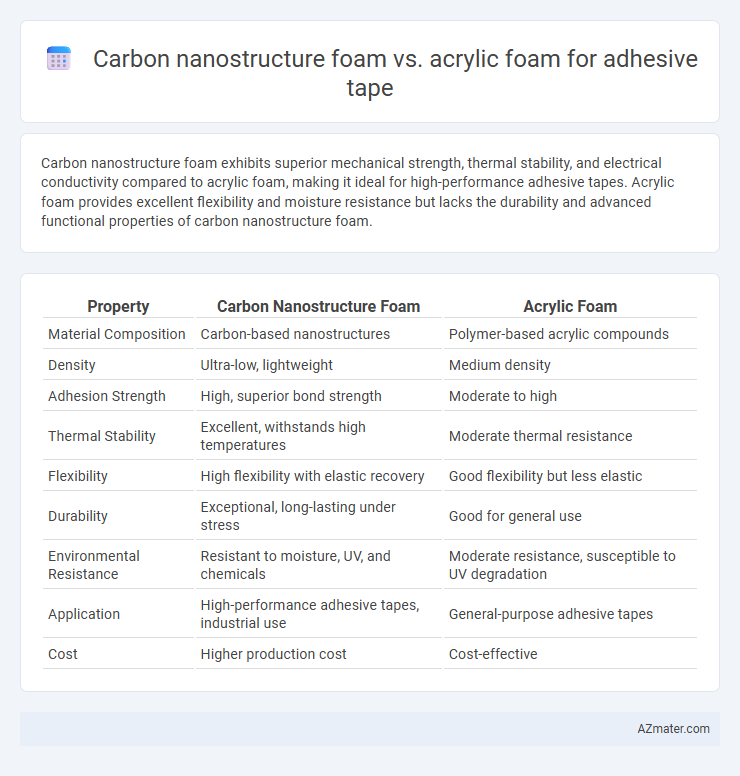
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior mechanical strength, thermal stability, and electrical conductivity compared to acrylic foam, making it ideal for high-performance adhesive tapes. Acrylic foam provides excellent flexibility and moisture resistance but lacks the durability and advanced functional properties of carbon nanostructure foam.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Carbon Nanostructure Foam | Acrylic Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based nanostructures | Polymer-based acrylic compounds |
| Density | Ultra-low, lightweight | Medium density |
| Adhesion Strength | High, superior bond strength | Moderate to high |
| Thermal Stability | Excellent, withstands high temperatures | Moderate thermal resistance |
| Flexibility | High flexibility with elastic recovery | Good flexibility but less elastic |
| Durability | Exceptional, long-lasting under stress | Good for general use |
| Environmental Resistance | Resistant to moisture, UV, and chemicals | Moderate resistance, susceptible to UV degradation |
| Application | High-performance adhesive tapes, industrial use | General-purpose adhesive tapes |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Cost-effective |
Introduction to Carbon Nanostructure Foam and Acrylic Foam in Adhesive Tapes
Carbon nanostructure foam in adhesive tapes offers exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, electrical conductivity, and thermal stability, enhancing tape performance in demanding industrial applications. Acrylic foam adhesive tapes provide superior elasticity, weather resistance, and strong bonding to various surfaces, making them ideal for automotive and construction uses. The advanced nanostructure of carbon foam enables innovative adhesive solutions focused on durability and multifunctionality compared to the versatile, cost-effective acrylic foam alternatives.
Chemical Composition and Structural Differences
Carbon nanostructure foam, composed primarily of interconnected carbon nanotubes and graphene sheets, offers superior chemical stability and electrical conductivity compared to acrylic foam, which is based on polymeric acrylate compounds with ester functional groups. Structurally, carbon nanostructure foam has a highly porous, lightweight matrix with nanometer-scale voids, enhancing mechanical strength and flexibility, whereas acrylic foam features a denser, closed-cell polymer structure that provides cushioning but less resilience under mechanical stress. The distinct chemical inertness of carbon nanostructure foam enables better resistance to oxidative degradation, outperforming the relatively hydrophilic and UV-sensitive acrylic foam in harsh environments.
Manufacturing Processes of Carbon Nanostructure Foam vs. Acrylic Foam
Carbon nanostructure foam manufacturing involves advanced techniques such as chemical vapor deposition (CVD) and templating methods, enabling precise control over pore size and morphology to enhance adhesive properties. Acrylic foam is typically produced through polymerization and cross-linking processes, resulting in a soft, flexible structure with consistent density ideal for general adhesive applications. The high-temperature and catalyst-driven synthesis of carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical strength and thermal stability compared to the simpler, solvent-based curing methods used for acrylic foam.
Adhesion Mechanisms: How Each Foam Type Binds
Carbon nanostructure foam enhances adhesive tape performance through its high surface area and nanoscale porosity, enabling strong van der Waals forces and mechanical interlocking with substrates. Acrylic foam relies on its viscoelastic properties and tackifiers to create adhesive bonds through molecular entanglement and surface wetting, ensuring durable contact on smooth and rough surfaces. The carbon nanostructure's unique nanofiber network provides superior load distribution and resilience compared to the more uniform but less intricate acrylic foam matrix.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Carbon nanostructure foam offers superior mechanical strength due to its high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance compared to acrylic foam, which tends to degrade under prolonged stress. The nano-scale architecture of carbon foam enhances load distribution and maintains structural integrity in extreme conditions, resulting in greater durability for adhesive tape applications. Acrylic foam, while flexible and cushioning, generally exhibits lower resistance to temperature fluctuations and aging, reducing its lifespan in demanding environments.
Performance Under Extreme Temperatures and Environments
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior thermal stability and maintains adhesive strength under extreme temperatures ranging from -196degC to over 1000degC, outperforming acrylic foam which typically degrades above 120degC. Its chemical resistance and mechanical robustness in harsh environments such as high radiation or corrosive conditions make it ideal for aerospace and industrial applications. Acrylic foam offers good flexibility and initial tack but loses performance in prolonged exposure to UV radiation and extreme moisture, limiting its use in severe environments.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Differences
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits significantly higher electrical and thermal conductivity compared to acrylic foam, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and electrical grounding in adhesive tapes. Acrylic foam acts as an excellent electrical insulator with low thermal conductivity, suitable for insulating components in electronic assemblies. The choice between these foams depends on the need for conductive properties versus insulation in adhesive tape applications.
Applications in Industry: Where Each Foam Excels
Carbon nanostructure foam excels in high-performance adhesive tapes used in aerospace and electronics industries due to its exceptional thermal conductivity, electrical properties, and lightweight structure, enabling superior heat dissipation and electromagnetic interference shielding. Acrylic foam is widely favored in automotive and construction applications for its excellent weather resistance, strong adhesion to diverse substrates, and durability under varying environmental conditions. Each foam type serves distinct industrial needs, with carbon nanostructure foam prioritizing advanced functional properties and acrylic foam providing reliable, versatile bonding solutions.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability Considerations
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits superior environmental benefits compared to acrylic foam due to its potential for enhanced recyclability and reduced carbon footprint during production. Acrylic foam, derived from petrochemical sources, often poses challenges in biodegradability and generates higher volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions. Sustainable adhesive tape solutions increasingly favor carbon nanostructure foams for their durability, lower environmental impact, and ability to integrate with eco-friendly manufacturing processes.
Cost Analysis and Market Trends in Adhesive Tape Foams
Carbon nanostructure foam exhibits higher initial costs compared to acrylic foam due to advanced material synthesis and limited large-scale production. Acrylic foam remains dominant in the adhesive tape market, driven by affordability, versatility, and established supply chains. Market trends indicate growing interest in carbon nanostructure foams for specialized applications requiring superior mechanical and thermal properties, potentially increasing their cost justification over time.
Infographic: Carbon nanostructure foam vs Acrylic foam for Adhesive tape
 azmater.com
azmater.com