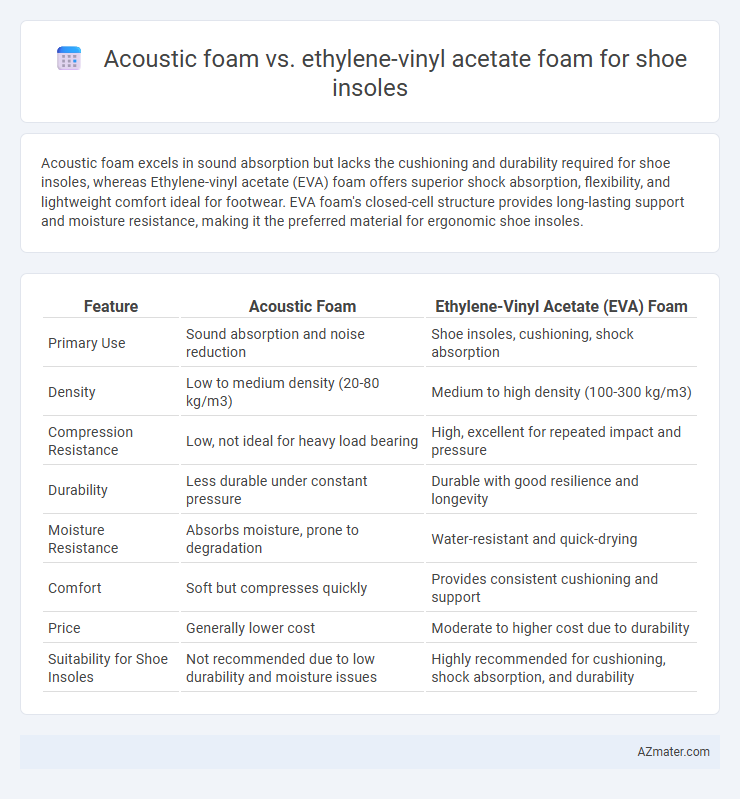
Acoustic foam excels in sound absorption but lacks the cushioning and durability required for shoe insoles, whereas Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption, flexibility, and lightweight comfort ideal for footwear. EVA foam's closed-cell structure provides long-lasting support and moisture resistance, making it the preferred material for ergonomic shoe insoles.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Acoustic Foam | Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sound absorption and noise reduction | Shoe insoles, cushioning, shock absorption |
| Density | Low to medium density (20-80 kg/m3) | Medium to high density (100-300 kg/m3) |
| Compression Resistance | Low, not ideal for heavy load bearing | High, excellent for repeated impact and pressure |
| Durability | Less durable under constant pressure | Durable with good resilience and longevity |
| Moisture Resistance | Absorbs moisture, prone to degradation | Water-resistant and quick-drying |
| Comfort | Soft but compresses quickly | Provides consistent cushioning and support |
| Price | Generally lower cost | Moderate to higher cost due to durability |
| Suitability for Shoe Insoles | Not recommended due to low durability and moisture issues | Highly recommended for cushioning, shock absorption, and durability |
Introduction to Shoe Insole Materials
Shoe insoles require materials that combine cushioning, durability, and moisture resistance, making ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam a popular choice due to its lightweight, flexible, and shock-absorbing properties. Acoustic foam, designed primarily for sound absorption, lacks the mechanical resilience and comfort needed for prolonged foot support. EVA foam's closed-cell structure provides superior support and odor resistance, essential qualities for effective shoe insoles.
What is Acoustic Foam?
Acoustic foam is a porous material designed to absorb sound waves and reduce noise by converting sound energy into heat through its open-cell structure. Unlike ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam used in shoe insoles for cushioning and shock absorption, acoustic foam primarily focuses on soundproofing and acoustic treatment applications. Its lightweight, open-cell polyurethane composition optimizes sound absorption rather than providing the durable comfort and flexibility needed for footwear insoles.
What is Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) Foam?
Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate (EVA) foam is a lightweight, flexible material commonly used in shoe insoles for its excellent cushioning and shock absorption properties. Unlike acoustic foam, which is designed primarily for soundproofing and noise reduction, EVA foam offers superior comfort and durability, making it ideal for footwear applications. Its closed-cell structure provides moisture resistance and resilience, enhancing the overall support and longevity of shoe insoles.
Comfort and Cushioning Comparison
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior cushioning and shock absorption in shoe insoles, providing enhanced comfort for prolonged wear due to its flexible and resilient structure. Acoustic foam, designed primarily for sound absorption, lacks the durable support and energy return properties essential for all-day foot comfort. EVA foam's closed-cell composition ensures better moisture resistance and durability, making it more suitable for insoles focused on cushioning and overall foot comfort.
Durability and Longevity
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior durability and longevity for shoe insoles compared to acoustic foam, which tends to compress and degrade more quickly under repeated foot pressure. EVA foam maintains its cushioning and structural integrity over extended use due to its excellent elasticity and resistance to wear and tear. Acoustic foam, designed primarily for sound absorption, lacks the resilience needed for prolonged insole performance and often requires more frequent replacement.
Shock Absorption Capabilities
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers superior shock absorption for shoe insoles due to its resilient and flexible cell structure, effectively reducing impact forces on the feet during walking or running. Acoustic foam, primarily designed for sound absorption, lacks the necessary density and durability to provide comparable cushioning and impact dispersion in footwear applications. EVA's combination of lightweight properties and excellent energy return makes it the preferred material for maximizing comfort and reducing foot fatigue.
Moisture and Odor Resistance
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam exhibits superior moisture resistance compared to acoustic foam, making it an ideal material for shoe insoles that require durability in wet conditions. EVA's closed-cell structure prevents water absorption and inhibits odor-causing bacterial growth, enhancing foot hygiene and comfort. Acoustic foam, typically open-cell and designed for sound absorption, tends to retain moisture and harbor odors, which reduces its suitability for shoe insole applications focused on moisture and odor management.
Weight and Flexibility
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam offers a lightweight and highly flexible solution for shoe insoles, enhancing comfort and reducing foot fatigue. Acoustic foam, while effective in sound absorption, is typically denser and less flexible, making it less suitable for dynamic movement within footwear. EVA's balanced combination of low weight and superior flexibility makes it the preferred material for insoles requiring cushioning and adaptability.
Cost and Availability
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is generally more cost-effective and widely available for shoe insoles compared to acoustic foam, which is specialized and less commonly used in footwear. EVA foam offers excellent cushioning and durability at a lower price point, making it the preferred material in mass-market insoles. Acoustic foam, designed for sound absorption, tends to be pricier and less accessible in bulk, limiting its practical use for shoe manufacturing.
Which Foam is Best for Shoe Insoles?
Ethylene-vinyl acetate (EVA) foam is widely regarded as the superior choice for shoe insoles due to its excellent cushioning, shock absorption, and lightweight properties that enhance comfort and reduce foot fatigue. Acoustic foam, designed primarily for sound absorption, lacks the durability and supportive qualities necessary for prolonged foot wear, making it less suitable for insoles. EVA foam's resilience and flexibility specifically address the demands of foot biomechanics, ensuring better impact protection and longevity in shoe insoles.
Infographic: Acoustic foam vs Ethylene-vinyl acetate foam for Shoe insole
 azmater.com
azmater.com