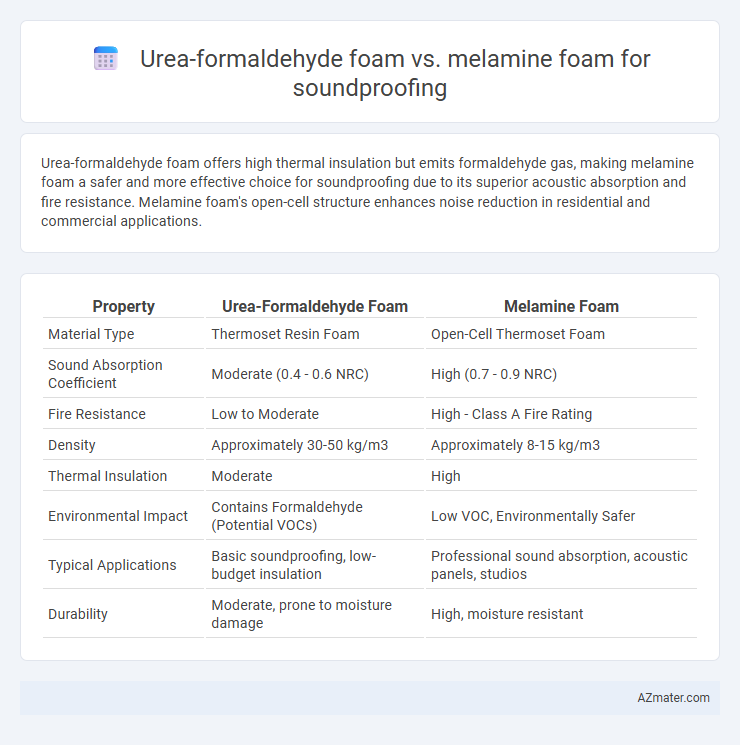
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers high thermal insulation but emits formaldehyde gas, making melamine foam a safer and more effective choice for soundproofing due to its superior acoustic absorption and fire resistance. Melamine foam's open-cell structure enhances noise reduction in residential and commercial applications.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Urea-Formaldehyde Foam | Melamine Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Thermoset Resin Foam | Open-Cell Thermoset Foam |
| Sound Absorption Coefficient | Moderate (0.4 - 0.6 NRC) | High (0.7 - 0.9 NRC) |
| Fire Resistance | Low to Moderate | High - Class A Fire Rating |
| Density | Approximately 30-50 kg/m3 | Approximately 8-15 kg/m3 |
| Thermal Insulation | Moderate | High |
| Environmental Impact | Contains Formaldehyde (Potential VOCs) | Low VOC, Environmentally Safer |
| Typical Applications | Basic soundproofing, low-budget insulation | Professional sound absorption, acoustic panels, studios |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to moisture damage | High, moisture resistant |
Introduction to Urea-formaldehyde and Melamine Foam
Urea-formaldehyde foam is a rigid, low-cost insulation material known for its high thermal resistance and moderate sound absorption properties, often used in wall cavities to reduce noise transmission. Melamine foam is a lightweight, open-cell material with superior sound absorption capabilities across a broad frequency range, making it ideal for acoustic panels and noise control applications. Both foams offer unique benefits in soundproofing, with urea-formaldehyde excelling in thermal insulation and melamine foam providing enhanced acoustic performance.
Chemical Composition and Manufacturing
Urea-formaldehyde foam consists of a polymer formed from urea and formaldehyde through a condensation reaction, resulting in a rigid, thermosetting resin with excellent sound absorption properties due to its closed-cell structure. Melamine foam is manufactured by polymerizing melamine and formaldehyde under controlled conditions, producing an open-cell foam known for its lightweight and highly porous composition ideal for acoustic insulation. The chemical composition of urea-formaldehyde involves nitrogen-rich urea molecules, while melamine foam contains melamine units with triazine rings, contributing to its thermal stability and sound absorption efficiency.
Acoustic Performance Comparison
Urea-formaldehyde foam provides effective sound absorption with a medium noise reduction coefficient (NRC) typically around 0.5 to 0.7, making it suitable for general acoustic dampening in residential settings. Melamine foam exhibits superior acoustic performance, boasting higher porosity and NRC values often exceeding 0.8, enabling more efficient absorption across a wider frequency range, especially in mid-to-high frequencies. This makes melamine foam a preferred choice for professional soundproofing and environments requiring enhanced noise control and reverberation reduction.
Sound Absorption Coefficients
Urea-formaldehyde foam exhibits sound absorption coefficients ranging from 0.60 to 0.75 at mid to high frequencies (500 Hz to 4000 Hz), making it effective for reducing airborne noise in residential and commercial applications. Melamine foam offers superior sound absorption, with coefficients typically between 0.70 and 0.90 across a broader frequency spectrum, including lower frequencies around 250 Hz, due to its open-cell structure and lightweight composition. Both materials provide efficient acoustic insulation, but melamine foam's higher absorption coefficients contribute to enhanced noise reduction and improved soundproofing performance in diverse environments.
Durability and Longevity
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers high-density soundproofing qualities but tends to degrade faster over time due to formaldehyde off-gassing and brittleness, impacting its durability. Melamine foam, known for its open-cell structure and fire-resistant properties, maintains stability and effectiveness longer under varying environmental conditions, resulting in superior longevity. Selecting melamine foam ensures prolonged soundproof insulation performance with minimal maintenance compared to urea-formaldehyde alternatives.
Health and Safety Considerations
Urea-formaldehyde foam releases formaldehyde gases that pose significant respiratory and carcinogenic risks, necessitating proper ventilation and protective measures during installation. Melamine foam is non-toxic, fire-resistant, and does not emit harmful volatile organic compounds (VOCs), making it a safer choice for indoor air quality. When prioritizing health and safety in soundproofing, melamine foam offers superior performance with minimal health hazards compared to urea-formaldehyde foam.
Installation Process and Flexibility
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers a rigid structure that requires precise cutting and fitting during installation, making it less adaptable to irregular surfaces. Melamine foam is highly flexible and easy to install, conforming effortlessly to complex shapes and uneven areas without specialized tools. This flexibility in melamine foam enhances its practicality for soundproofing applications where quick and adaptable installation is essential.
Cost-effectiveness and Value
Urea-formaldehyde foam offers a cost-effective soundproofing solution with high thermal insulation properties, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects. Melamine foam, while more expensive, delivers superior acoustic absorption and fire resistance, providing greater long-term value in environments requiring enhanced safety and noise control. Evaluating the balance between upfront cost and performance needs is crucial for selecting the most suitable foam for soundproofing applications.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Urea-formaldehyde foam releases formaldehyde gas, a known carcinogen, contributing to indoor air pollution and posing significant health risks, while its production relies on non-renewable petrochemicals. Melamine foam, made from melamine resin, offers a lower environmental impact due to its lighter weight and potential for recycling, though it is still derived from synthetic materials. From a sustainability perspective, melamine foam is generally preferred as it emits fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and can be more effectively recycled or disposed of compared to urea-formaldehyde foam.
Best Use Cases for Each Foam
Urea-formaldehyde foam excels in thermal insulation and soundproofing within walls and ceilings due to its high density and rigidity, making it ideal for residential and commercial building applications seeking energy efficiency and noise reduction. Melamine foam offers superior acoustic absorption and fire resistance, best suited for studios, theaters, and industrial environments where controlling echo and managing fire safety are critical. Selecting between urea-formaldehyde foam and melamine foam depends on balancing considerations of thermal insulation, acoustic properties, fire resistance, and specific environmental demands.
Infographic: Urea-formaldehyde foam vs Melamine foam for Soundproofing
 azmater.com
azmater.com