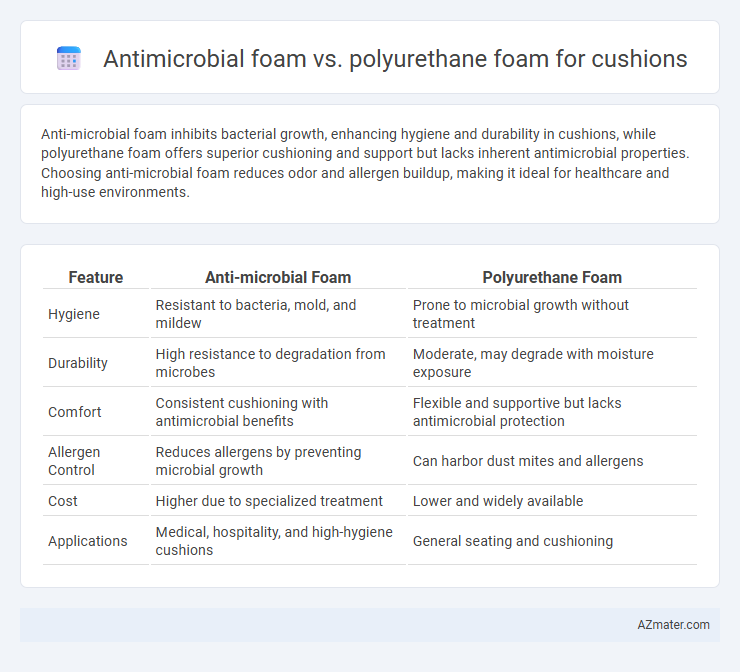
Anti-microbial foam inhibits bacterial growth, enhancing hygiene and durability in cushions, while polyurethane foam offers superior cushioning and support but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. Choosing anti-microbial foam reduces odor and allergen buildup, making it ideal for healthcare and high-use environments.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Anti-microbial Foam | Polyurethane Foam |
|---|---|---|
| Hygiene | Resistant to bacteria, mold, and mildew | Prone to microbial growth without treatment |
| Durability | High resistance to degradation from microbes | Moderate, may degrade with moisture exposure |
| Comfort | Consistent cushioning with antimicrobial benefits | Flexible and supportive but lacks antimicrobial protection |
| Allergen Control | Reduces allergens by preventing microbial growth | Can harbor dust mites and allergens |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized treatment | Lower and widely available |
| Applications | Medical, hospitality, and high-hygiene cushions | General seating and cushioning |
Introduction to Cushion Foams: Anti-Microbial vs Polyurethane
Anti-microbial foam for cushions incorporates specialized agents that inhibit bacteria, mold, and mildew growth, enhancing hygiene and durability in high-use environments. Polyurethane foam, widely used for cushioning, offers excellent support and comfort due to its open-cell structure but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties. Choosing between anti-microbial and standard polyurethane foam depends on the need for health safety, with anti-microbial foam providing a superior option for environments requiring enhanced cleanliness.
Key Material Differences: Anti-Microbial and Polyurethane Foams
Anti-microbial foam contains additives that inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and mildew, enhancing hygiene and durability in cushions. Polyurethane foam, a versatile polymer-based material, offers superior cushioning and support but lacks inherent antimicrobial properties unless treated. The primary difference lies in anti-microbial foam's specialized formulation aimed at preventing microbial contamination, whereas polyurethane foam focuses on comfort and resilience.
Anti-Microbial Properties: Benefits for Health and Hygiene
Anti-microbial foam features built-in agents that actively inhibit the growth of bacteria, mold, and dust mites, enhancing health and hygiene in cushions by reducing allergens and unpleasant odors. Polyurethane foam, while versatile and widely used, typically lacks inherent anti-microbial properties and may require additional treatments to achieve similar protection. Choosing anti-microbial foam for cushions is particularly beneficial in environments prone to moisture or high usage, promoting a cleaner and safer living space.
Polyurethane Foam: Versatility and Common Applications
Polyurethane foam is highly versatile and widely used in cushions due to its excellent comfort, durability, and cost-effectiveness. It provides superior support and resilience, making it ideal for furniture, automotive seating, and bedding applications. Unlike anti-microbial foam, polyurethane foam prioritizes structural performance and flexibility over specialized microbial protection.
Durability and Longevity: Which Foam Lasts Longer?
Anti-microbial foam incorporates biocides that resist mold, bacteria, and mildew, enhancing its durability by preventing breakdown caused by microbial growth. Polyurethane foam typically offers robust structural integrity and compressive strength, which contributes to its long-term shape retention and support under regular use. When comparing longevity, anti-microbial foam may have an edge in environments prone to moisture and contamination, while high-density polyurethane foam excels in maintaining firmness and cushioning over extended periods.
Comfort and Support: User Experience Comparison
Anti-microbial foam offers enhanced comfort by inhibiting microbial growth, reducing odors, and maintaining a fresher cushion environment compared to traditional polyurethane foam. Polyurethane foam provides firm support and durability but may lack the breathability and hygienic benefits of anti-microbial variants, potentially affecting long-term comfort. Users often report that cushions with anti-microbial foam deliver a balanced experience of softness and support, promoting better usability in high-moisture or extended-use scenarios.
Allergen and Odor Resistance: Effects on Indoor Air Quality
Anti-microbial foam cushions inhibit bacterial and fungal growth, significantly reducing allergens such as dust mites and mold spores, thereby improving indoor air quality. Polyurethane foam lacks inherent anti-microbial properties, often leading to increased allergen accumulation and potential odor retention over time. Choosing anti-microbial foam enhances odor resistance and minimizes airborne irritants, creating a healthier indoor environment.
Environmental Impact: Sustainability and Disposal
Anti-microbial foam often contains synthetic chemicals that can complicate recycling and may release harmful substances during disposal, raising environmental concerns. Polyurethane foam, while widely used, poses sustainability challenges due to its petroleum-based composition and slow biodegradability, often ending up in landfills or incinerated with potential toxin emissions. Innovations in bio-based polyurethane and recyclable foam technologies are emerging to reduce ecological footprints and improve end-of-life management for cushioning materials.
Cost Analysis: Anti-Microbial vs Polyurethane Foam Cushions
Anti-microbial foam cushions typically exhibit higher upfront costs compared to traditional polyurethane foam due to specialized treatments that inhibit bacterial growth, mold, and odor. Over time, anti-microbial foam can reduce maintenance and replacement expenses by extending the cushion's lifespan and improving hygiene, especially in healthcare or hospitality settings. Polyurethane foam, while more cost-effective initially, may incur additional costs related to cleaning, frequent replacement, and potential health risks from microbial contamination.
Choosing the Right Foam for Your Cushion Needs
Anti-microbial foam offers superior resistance to bacteria, mold, and allergens, making it ideal for cushions in healthcare, hospitality, or allergy-sensitive environments. Polyurethane foam provides versatile cushioning with excellent durability and comfort, suitable for general use in furniture and automotive applications. Selecting the right foam depends on prioritizing hygiene and microbial protection versus cost-effectiveness and resilience for everyday cushioning needs.
Infographic: Anti-microbial foam vs Polyurethane foam for Cushion
 azmater.com
azmater.com